Prototyping with 3DEXPERIENCE Make
Prototyping across all processes. Upload your design, get your instant quote, choose your manufacturer and receive your prototype.
SECURE PAYMENTS
Via payment card or purchase order
PROTECTED IP
Your data is confidential and secure with us. Use your own Non Disclosure Agreement
INSTANT QUOTE
For 3D Printing and CNC Machining, get quote in few seconds.
3DEXPERIENCE Make & Prototyping
Prototyping is a vital part of the design process because it allows inventors and engineers to validate their ideas quickly and improve upon them. Speed and agility have always been important, but in today’s fast-moving world they are the keys to success.
You can’t afford to spend years perfecting a concept as the demand may have been filled by someone else or the need may have changed. At the same time, you don’t want to rush into launching a product that still needs fine-tuning.
Prototyping combines the progress that comes through iterative development with the pace required to grasp opportunities swiftly.
Prototyping isn’t a new concept, it’s been used for centuries, but like everything else around us, it has been radically transformed by technology. There’s no shortage of prototyping tools available today, from basic physical mock-ups to complex virtual simulations.
Which one is right for you will depend on your needs, your skill-level and what is being designed.
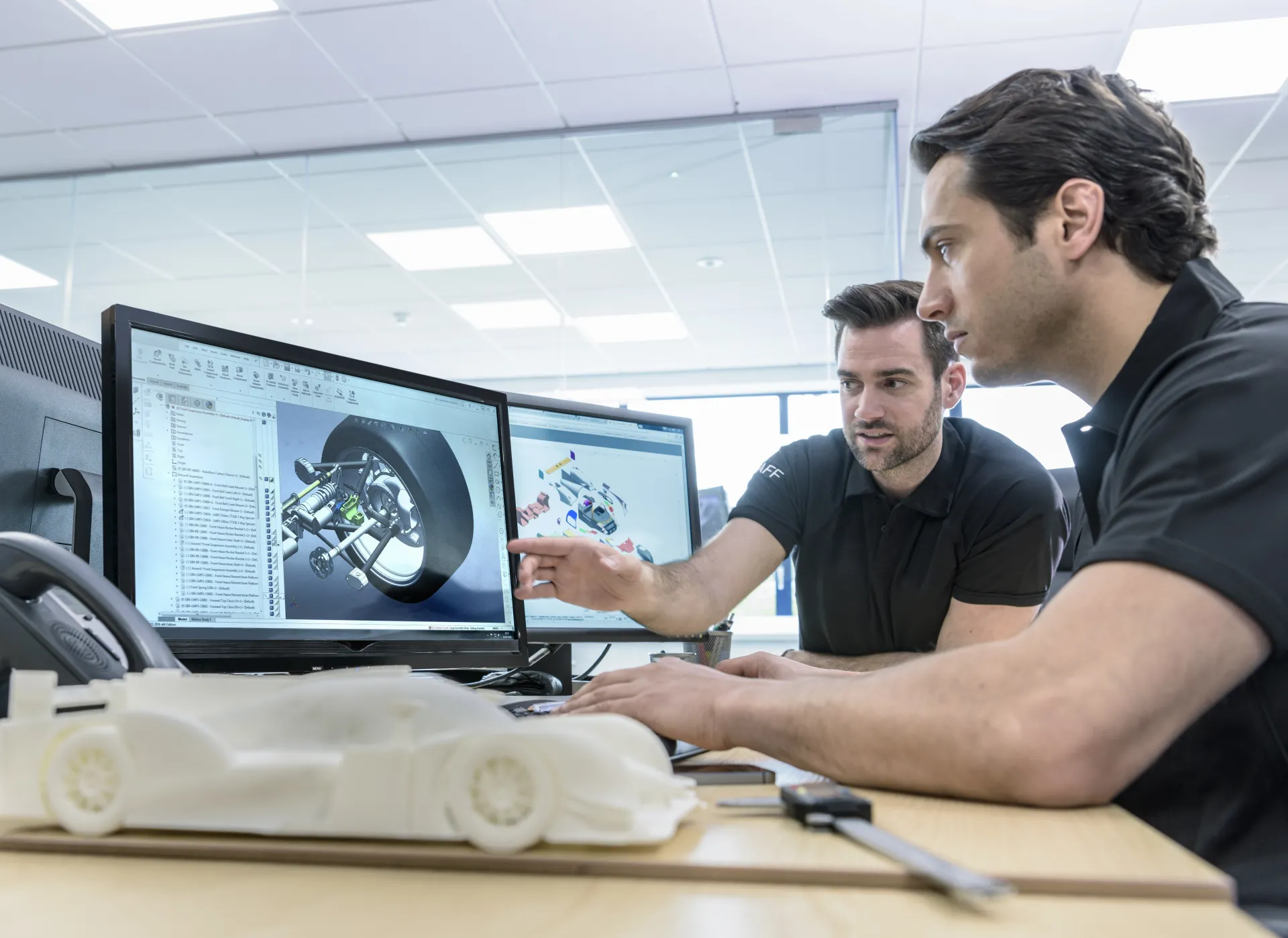
3DEXPERIENCE Make is an on-demand manufacturing platform that will allow you to create prototypes. It connects the industrial ecosystem of Designers, Engineers, Buyers and Production planners with industrial manufacturing service providers.
Discover SOLIDWORKS 3DEXPERIENCE for Makers

What is prototyping ?
Prototyping is the opportunity to take an idea and make it real. The creation of a draft or early sample allows you to see how a product might look and feel, and to test the functionality of a design.
It enables you to experiment and see how different parts relate to each other, and to assess whether the final creation serves its purpose. It also allowa for side-by-side comparisons to be made and can be shared with colleagues or customers to gain valuable feedback.
It is also far easier and cheaper to make changes at this early stage rather than after investing time and money in manufacturing.
Benefits of prototyping
Prototyping is the best way to ensure that what you intend to make actually matches the users’ need or solves a problem. It does cost time and money, however. Exactly how much will depend on what tool, material or methods is used and whether you decide to make them yourself or outsource production to a specialist manufacturer.
Solid foundation
Prototyping provides a solid foundation to experiment, iterate and make refinements, and provides invaluable feedback on the functionality, design and costs of production.
Reduce error
Prototyping enables you to catch potentially costly errors much earlier in the development process and to make changes accordingly.
Share the concept
Prototyping allows you to share the concept with multiple stakeholders (both internal and external) so they can provide their opinion as to which elements work best and which need further improvement and/or removing entirely.
Gain time
Prototyping accelerates time-to-market and reduces cost-to-market.
Our network of on-demand manufacturing providers
United States
Canada
United Kingdom
France
Germany
Netherlands
and many more...
Dassault Systèmes and virtual design
Forward-thinking businesses are already using virtual twin technologies to reconfigure their operations and products from the ground up. In doing so, they are gaining a huge degree of predictability in how that process, product, or service will work.
Today, 85% of the world’s electric vehicles and 75% of global wind power are built using Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE virtual twins. These technologies provide a myriad of capabilities and benefits across the entire product lifecycle, including:
- Research and Development – access to past product performance data; advanced scenario modeling; visibility of lifecycle impact and multidiscipline collaboration
- Design and Engineering – generative design; virtual prototyping and testing; organized access to relevant data
- Manufacturing – improved operational feedback; intelligent monitoring and maintenance of equipment; process optimization; automated controls based on real-time operating conditions
- Transport and Logistics – algorithmic planning and route optimization; fleet management; container tracking; sensor-based shipment monitoring; virtualization and visualization of infrastructure
- Product Use – advanced failure warning and risk management; software over the air performance optimization; remote asset monitoring and diagnostics; intelligent asset service and maintenance; real-time operational improvement insights
- End of Life – data-based decommissioning execution simulation and planning; detailed visibility into asset and component status; material and component recovery tracking
Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE virtual universes are being used to imagine, design, and test the radically new products, materials, and processes needed to create a sustainable future:
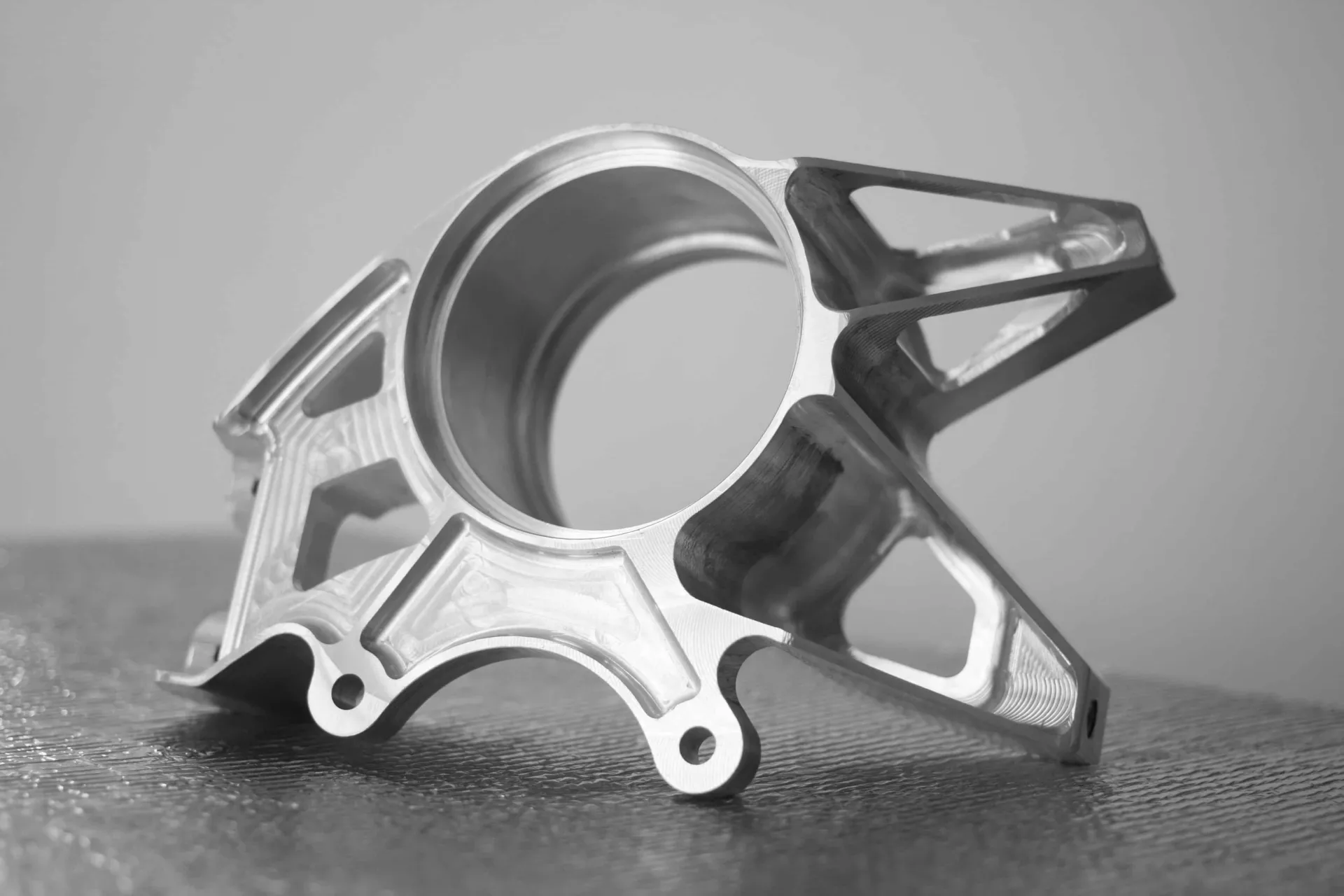
What is rapid prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is the process of quickly transforming a digital 3D model into a physical object. This is usually done by combining CAD software with automated computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) or computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools.
Common examples include lathes; routers; milling or drilling machines; water, plasma or laser cutters; electrical discharge machines (EDM), and grinders. These are all subtractive manufacturing processes. They remove material from a solid block, bar, sheet or rod.
Increasingly, designers and engineers are using additive manufacturing techniques, more commonly known as 3D printing. The term covers a variety of different processes, all of which involve a material, usually a plastic, metal or composite, being put down in lots of thin layers to build up a 3D shape.
The whole process is computer controlled, requires minimal set-up and creates almost no waste. This makes 3D printing a cost-effective and efficient method to create objects of almost any shape or complexity.
The technology is affordable and accessible, and desktop 3D printers are both compact and easy to operate. This allows the prototyping process to be brought in-house, rather than having to rely on external service providers.
Where does prototyping fit in the product development cycle?
The different forms of prototyping represent different stages of the design workflow. The first is identifying and understanding a need, a problem that has to be solved. This seed of an idea can then brought to life through the simplest and easiest forms of prototyping - a sketch or diagram.
These flat drawings are then used to create simplified 3D prototypes. These models are often not to scale and made from cheaper, more accessible materials than those intended for the final product. Common examples include cardboard, foam, clay, wood, plastic and soft metals such as brass or aluminum.
These rough versions help to identify the elements or functions in need of further improvement and lead to the creation of more detailed and functioning prototypes. Following approval, this is usually the last stage before prototyping moves into production.
What are the most common prototyping tools?
Technology advances have transformed prototyping tools, materials and methods. In the past, drawings and samples were hand-made by skilled craftspeople. They were sketched on paper, carved from clay, cut from wood or shaped in metal.
Prototyping today is faster, cheaper and more accurate thanks to digital software and machines such as 3D printers and robotic cutters. This makes the process easier and more efficient, and helps non-artists to create detailed models.
Despite access to ever-more powerful and affordable technologies, it is still common for hand tools and modern digital systems to be used in conjunction with each other.
Prototyping tools and methods can be split into four groups:
- Drawings and basic mock-ups
- Functional models
- Digital prototypes
- Rapid prototyping
- DRAWINGS AND BASIC MOCK-UPS
The most effective way to quickly conceptualize an idea. However, this method of prototyping lacks detail and misses some or all the functions. It also doesn’t represent the look and feel of the final product.
What you’ll need: General art supplies; cutting tools; adhesives; paper; cardboard; foam; clay; wood; plastics; soft metals.
Pros: Fast, cheap and efficient to produce; provides a quick overall view of the product; easy to make changes and test multiple new versions; affordable and widely accessible equipment and materials; doesn’t require a high-level of skill.
Cons: Lacks detail; may not be to scale; doesn’t show how the end product will function and perform; time-consuming or impossible to fabricate intricate parts and complex assemblies.
- WORKING MODELS
Working or demo models help to test how a concept functions in the real world. Being made fully, or in part, from the final material allows engineers and users to better assess the look and feel of the product.
Prototyping methods which produce fully functional or finely detailed models may involve large sums of time and money, however, and likely can only be done by someone highly skilled.
What you’ll need: power and/or machine tools for cutting, welding, forming and finishing; mechanical fasteners; higher-grade wood, plastics, metals, composites.
Pros: Relatively fast, cheap and efficient to make; provides a more in-depth view of the product and how it functions; still quite easy to make changes and test different iterations; power tools and materials are largely affordable and accessible.
Cons: A greater number and variety of tools and safety equipment is needed; machine tools are large and expensive; accuracy takes time and precision; limitations of machining make certain shapes expensive or impossible to make; medium to high-level of skill required.
- DIGITAL PROTOTYPES
Advances in digital software mean that prototyping can now be carried out within a computer. The result is a much more agile and efficient design workflow.
Computer-aided design (CAD) software is widely used to create everything from static 2D skeleton or wire frame models to highly detailed 3D animations.
The more recent arrival of immersive technologies such as virtual and augmented reality enable digital content to be integrated into the user’s real-world environment.
Virtual reality (VR) uses a headset to replace a user’s field of vision and audio to fully immerse themselves in a virtual simulation. Augmented reality (AR) uses apps on a smartphone or tablet to project images onto the physical world.
The most powerful digital prototype is a virtual twin. This is a scientifically accurate virtual model used to simulate, visualize, predict and optimize how an object behaves under different conditions.
Pros: Move directly from concept to creation without the time and costs involved with making physical objects; no design limitations; can produce very accurate, intricate or complex models; easy to make changes and produce different versions; incorporates past designs and performance data; can be easily shared with multiple stakeholders.
Cons: Creations are intangible; requires a large amount of computing processing power; software and equipment can be expensive and time-consuming to master at the highest level; open to potential cyber-attack.
Discover our other manufacturing services
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds