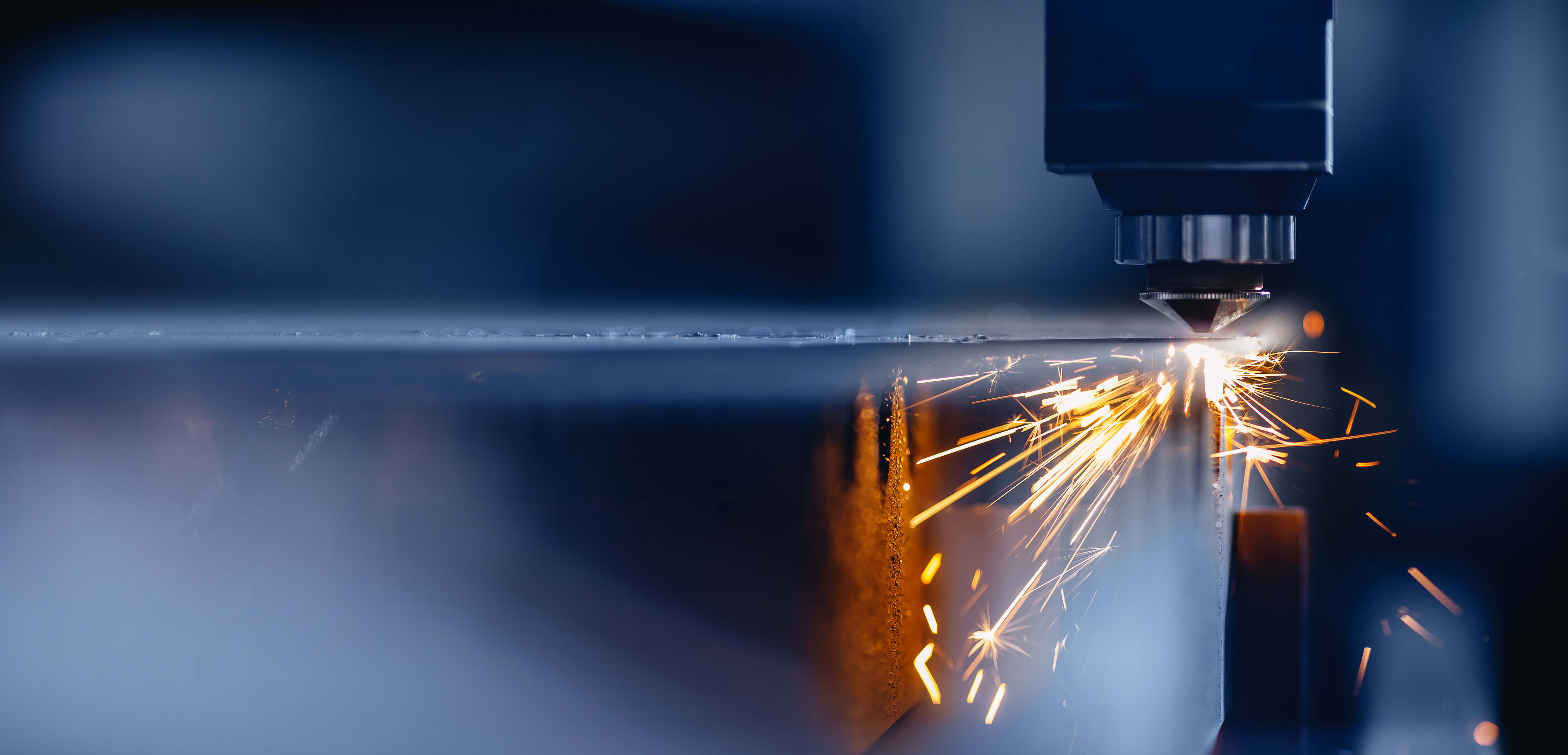
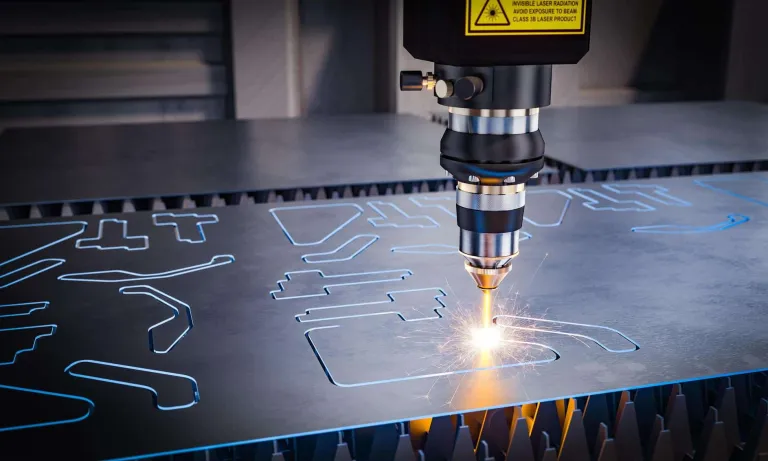
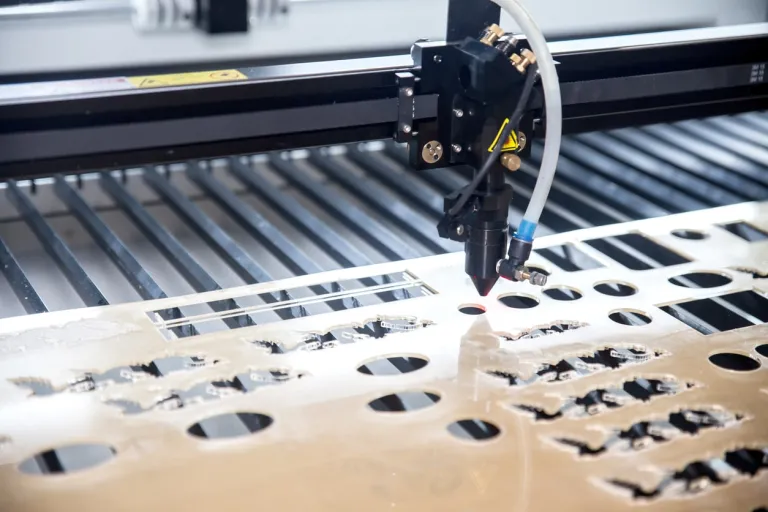
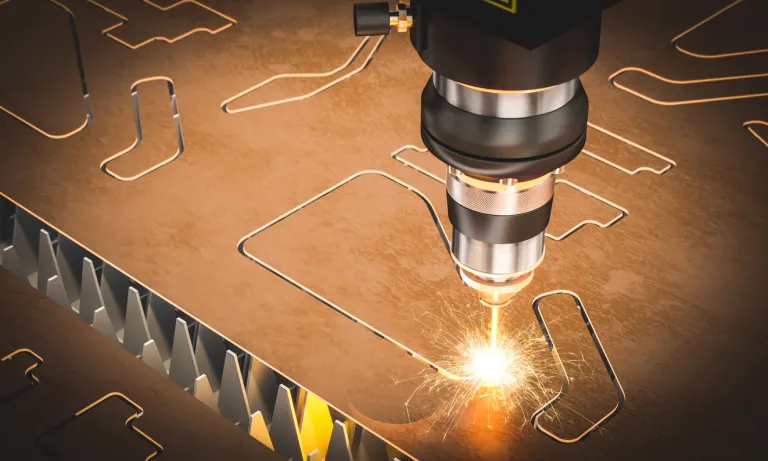
Laser cutting service
3DEXPERIENCE Make Online Laser cutting Service | Compare quotes from different expert manufacturers.
SECURE PAYMENTS
Via payment card or purchase order
PROTECTED IP
Your data is confidential and secure with us. Use your own Non Disclosure Agreement
INSTANT QUOTE
For 3D Printing and CNC Machining, get quote in few seconds.
Discover 3DEXPERIENCE SOLIDWORKS for Makers
Cutting service with 3DEXPERIENCE Make
3DEXPERIENCE Make is an On-Demand Manufacturing platform, which connects designers or engineers with industrial Laser cutting service providers. We develop a strong network of Laser Cutting services in North America and Europe. Today, laser cutting service is mainly used for small or large runs, but if you have a need for Mockups or Prototyping (technical or presentation), do not hesitate to contact us, we have also this capacity.
Our network of Laser cutting service providers offers hundreds of materials for your project, Plastic (PA, ABS, POM, PMMA, etc.), Metal (Stainless steel, 316, Aluminum, etc.) or Composite (PA Glass, etc.), and processes laser cutting, water cutting, and blade cutting.
Which Cutting subprocesses, 3DEXPERIENCE Make offers?
Laser Cutting
Water cutting
Blade cutting
Discover How 3DEXPERIENCE Marketplaces Boost Your Design to Manufacturing Process
You’re in good company. Thousands of leading companies from all industries use our solutions.
Online Laser cutting service: how does it work?
Materials of our Laser cutting Service Providers
Plastic
PA, ABS, PMMA, PMA...
Metal
Stainless, Steel...
Composite
PA Glass...
Features to help you
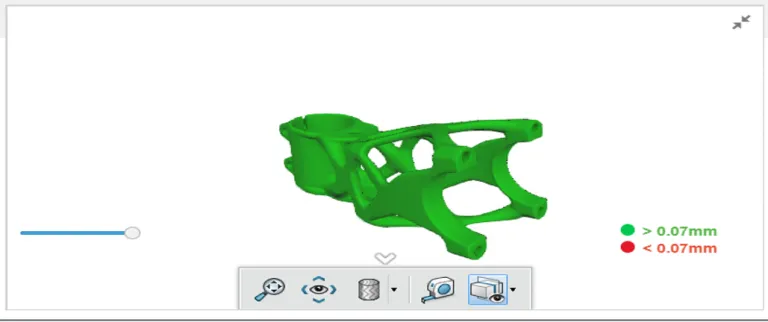
Check & repair or Geometry check is a feature that helps you to understand Geometry issue of your part and could repair it live and online.
Check & Repair
Check & repair or Geometry check is a feature that helps you to detect geometry issue on your part and repair it online and live.
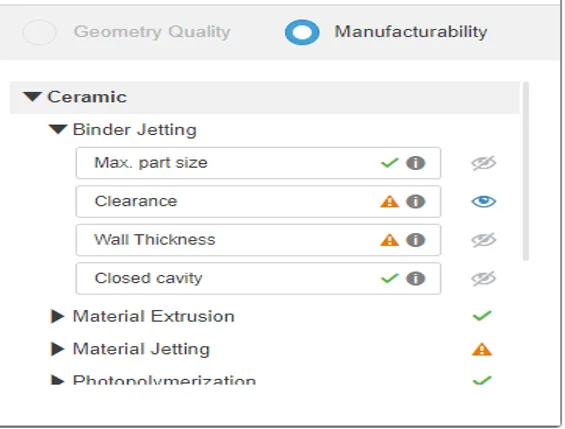
Manufacturability Check
This feature is available only for 3D Printing service. It helps you check the manufacturability of your part, depending on the materials and the process.
Instant quote engine
Receive in seconds several quotes thanks to our instant quote engine.
What is cutting?
Cutting is a common technique to which we generally don’t give much thought. Simply put, it is the separation of a physical object into two or more segments due to an acutely directed force. In the industrial domain, there are several types of cutting processes. They include laser cutting, blade cutting, and water jet cutting.
Metal cutting is a fundamental process in manufacturing and has been at the epicenter of the process throughout history. The various physical phenomenon includes chip forming, shearing, abrading, heat, and electrochemical. Each physical phenomenon consists of subcategories such as laser cutting, blade cutting, and water jet cutting.
Questions people ask about Laser Cutting Service
The increasing ease of access to laser cutting services and machines has allowed entities from garage hobbyists and up to long-established manufacturing firms to realize its benefits. The market is only expected to grow further, as the global laser cutting machine market was valued at $3.37 billion back in 2020 and could nearly double by 2027 to a value of $6.69 billion.
What is the benefit of Laser Cutting Services?
Laser is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. By focusing an intensely concentrated and powerful beam of light through a lens, a laser is produced that can cut through materials. The cutting action originates from melting and/or erosion at the location of the laser and metal interface.
From engravings to cutting through metal entirely, laser cutting opens a variety of designs from prototyping and testing to full-scale manufacturing production lines.
What are the advantages of Laser Cutting Services?
With laser cutting machines, there are several advantages to consider versus similar subtractive manufacturing processes such as CNC machines:
- Precision: The amount of kerf, or material that is burned away, is substantially smaller when laser cutting parts, typically less than 1mm. This translates to more precise cuts versus CNC router bits that are large and produce rounded corners rather than more straightened angles. Because laser cutting machines operate from vector files, they also produce parts that are highly detailed and the closest or exact to the original intended design.
- Speed: Lasers cutting machines do not require the more tedious set-ups of CNC machines; if the material is secure, no clamps are necessary. Clean-up, repeatability, and cycling to another laser cut product are also faster since there is not a large mess of wasted materials. Depending on the diode or laser emitter, the same apparatus can be used again and again without changing heads or bits. There is also little to no post-processing with completed, cut material, as cuts are not rough.
- Operability: The adaptability to cut many designs on a wide array of materials is also a positive. These include dense materials like metals and wood, softer and more delicate materials like cardboard, and thin sheets that can be cut to exacting specifications. Laser cutting machines do not require as much space as CNC machines. The learning curve and trial-and-error phase of operation are also not as steep as CNC machining.
What are the File Formats for Laser Cutting?
As previously mentioned, only vector files such as those used in graphic designs can be implemented for laser-cut designs. Files that can be loaded on a machine include .DXF, .DWG, .SVG, .PDF, as well as .AI, with the preferred type depending on the specific machine. Through software such as Dassault Systèmes’s own SOLIDWORKS or CATIA or Draftsight, designs can be created, converted, and exported to a vector file that can be read by laser cutting machines.
Because of this, 3D designs need to be broken down into multiple parts and rasterized in a 2D space, where they can afterward be assembled. The material choice will also determine what sort of laser cutting emitter designs will be run on. Red and black lasers emit lower wattage and produce less heat, CO2 laser emitters work on a wider variety of materials and are better on organic and softer materials such as plastics, foams, fabrics, and wood. Blue laser and fiber diodes are becoming more sought after because of their efficiency and absorption rate through most metals, but a word of caution is advised when working with acrylics, plastics, glass, and wood due to these materials being more conducive to warping or catching fire under more focused lazing.
What is the right Material Thickness for Laser Cutting and Distance Between Cutting Lines?
Materials choice also determines the optimal choice for wattage output of laser cutters. The rule of thumb is the denser a material is, the more power/time needed to cut through and the smaller the node’s width must be. Steels, copper, and other dense metals take longer to cut, with a maximum thickness of anywhere between 1mm to 10mm on 500W lasers, to 8mm, and up to 20mm on a 3,000W laser. Softer materials can allow for several inches, although multiple passes may be needed because of the focal distance of the laser. Again, how the material will react to lasers needs to be accounted for, as well as what type of kerf will be etched and if it will crack or burn materials.
There must also be sufficient space or distance between two cut lines in the material which is being lasered. Due to the tendency of a metal to melt and/or erode when cut with a laser, this is even more important. A good rule of thumb is to space cut lines the same distance as the thickness of the metal apart, so for a 0.25-inch-thick metal plate, the cut lines should be at least 0.25 inches apart. For some design features such as notches, the distance between the features should be greater than the material thickness, always consult with your manufacturing partner or laser machining equipment manufacturer for more specific design guidelines.
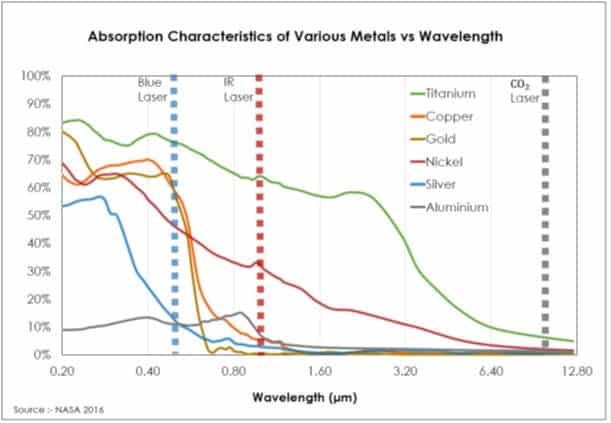
Other Design Considerations for Laser Cutting Parts
Once all considerations of what is being designed and what material is being used it can then all be brought together. 2D designs can be more easily drafted and viewed through software such as DraftSight. A lot of waste and costs can be reduced in this process before the design is ever uploaded onto the machine; cuts that are too close and narrow to each other can compromise the whole material and kerf width, however small, still needs to be accounted for in corners and jointing. Make sure that in the design that pieces will still be able to fit together using nodes, slots, and tabs like assembling a puzzle piece. Depending on the material, the size between kerfs in slots and nodes will vary.
The most optimal cutting path is that which requires the least amount of movement and cutting, follow through the rendered path lines in the final vector image to evaluate if any further optimizing can be done. Lines that intersect can completely ruin designs and materials. This can also include double lines, as some lasers are usually powerful enough to make a sufficient cut in one pass, going over twice is not only time but potential material wasted during the production process. Depending on the machine itself, thin details, joints, and sharp 90-degree turns can become an issue where the node decelerates at the pivot point and burns off more material than needed. All these common mistakes can be avoided by making the file right the first time with the right software.
It’s a balancing act to fit as many cut pieces within one piece of material, one design, and one run of cutting with the least amount of waste and cuts needed as possible. The advantage of 2D design is the ease of use and decrease of complications. As the market grows for laser cutting machines, CNC, 3D printing, and other small-scale manufacturing processes, the need for seamless design tools and methods will simultaneously grow as well.
Discover our other manufacturing services
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds