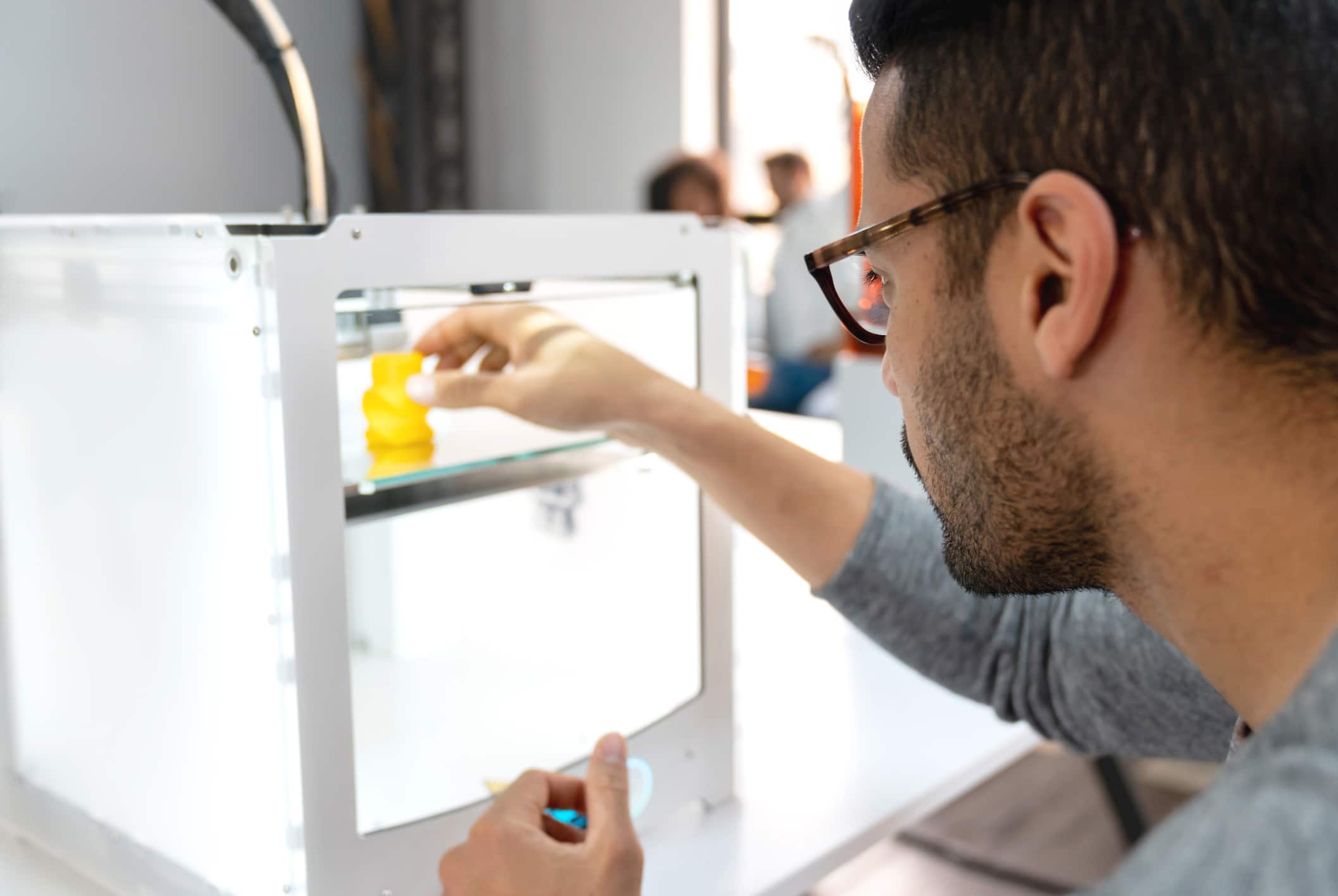
Solving the Three Most Common 3D Printing Problems
Discover how to solve the most common 3D Printing Problems.
Introduction to 3D Printing problems
3D printing has gained global popularity. Worldwide, the 3D printing market was valued at around 12.6 billion U.S. dollars in 2020. The 3D printing industry is anticipated to grow at an astonishing rate of 17 percent from 2020 to 2023. With the popularity of 3D printing also comes an increase in problems associated with 3D printing. Some of the most reported 3D printing faults include not printing at all, material not sticking to the 3D printing bed, and broken filament.
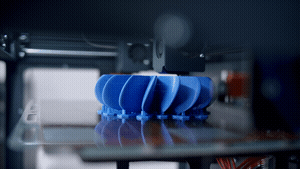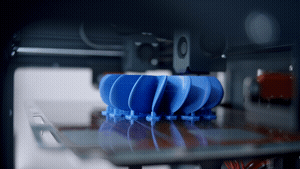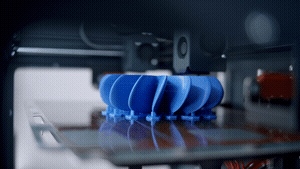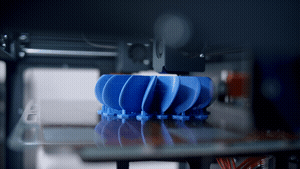
Problem One: 3D Printer Stopped Printing
One of the most frustrating and common 3D printing problems to encounter while printing a part is for the 3D printer to stop working altogether and not print the component you have loaded in the software.
Troubleshooting: 3D Printer Stopped Printing
This table gives a set of steps to find the root cause for a 3D printer stopped printing issue. Follow in order, to rule out simpler causes before diving deeper.
Problem One: 3D Printer Stopped Printing
- Check for the filament in the filament reel. Sometimes this step is overlooked because the filament reel may be hidden -> Replace the filament. Some printers require a purging of filament in the printer before loading new filament.
- Is the nozzle too close to the print bed? This causes the melted filament to remain trapped due to a lack of space to extrude. -> Raise the height of the nozzle high enough to allow extrusion but not too high to prevent the sticking of filament to the print bed.
- It may be possible that the 3D printer’s nozzle is blocked, partially or totally. Remove the nozzle to check for blockages. -> If this is the case, the filament cannot pass through the nozzle, partially or totally stopping the 3D printing. Follow your 3D printer manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide to determine how to unblock the nozzle. Some people swear by the atomic method and others prefer soaking the nozzle in a chemical bath, dependent on the filament material.
- If the nozzle isn’t blocked, somewhere else along the filament path may be harboring a blockage. The filament path will have to be disassembled to check for blockages. -> A common place for blockages is after the drive gear. A second common place for blockages is where the tubing intersects the metal bits in the printer. Blockages also commonly occur around the area of the heat break, but this is a sign of improper cooling or higher than needed retraction distance.
Dassault Systèmes provides a simple way to have your clear 3D printed parts expertly produced. Check out our website today to learn more about our innovative 3DEXPERIENCE® Make with on-demand access to industrial clear 3D printed parts service providers.
Problem Two: Material Isn’t Sticking to the 3D Printing Bed
If a print isn’t sticking to the 3D printing bed, or itself, the integrity of the 3D print is compromised. This common issue could be due to several issues which range from the insufficient contact area to a problem with bonding to the print bed surface or even a bed leveling issue.
Troubleshooting: Material Isn’t Sticking to the 3D Printing Bed
This table gives a set of steps to find the root cause for an issue with material not sticking. Follow in order, to rule out simpler causes before diving deeper.
Problem Two: Material Isn’t Sticking to the 3D Printing Bed
-
The CAD model doesn’t have enough surface area contact with the bed. This may be more obvious after a few layers of material have been printed. -> Re-orient the 3D part on the print bed. If this doesn’t seem to work, the design may need to be modified to allow for a higher printing surface area. Adding extra supports may also be a good idea.
-
The material slides off the print bed altogether.-> The print bed isn’t textured enough or correctly to allow for proper adhesion. Re-texturing or replacing the print bed are both potential solutions to explore. A simple solution is to apply a layer of glue or tape to the platform.
-
Check the flatness of the print bed. If it is not level, the material may tend to slide before it sticks.-> Adjust the legs on the printer or shim as necessary. Always refer to your printer’s guide for leveling instructions.
-
Check printer calibration. Improper or infrequent calibration can cause the first printed layer to drag on the bed, resulting in poor adhesion. -> Perform a calibration.
Problem Three: Broken Filament
Broken filament is a common 3D printing problem. Broken filament may stop your entire 3D printing process, especially if you are utilizing a Bowden feed printer rather than a direct feed printer because the breaks will be less obvious with a Bowden feed printer.
Troubleshooting: Broken Filament
This table gives a set of steps to find the root cause for a broken filament. Follow in order, to rule out simpler causes before diving deeper.
Problem Three: Broken Filament
-
The filament is too brittle. A brittle break will often have many small fractures, with residual crumbling material around the break. -> This may be related to the age of the filament, due to drying out over time. PLA and ABS filaments have a shelf life, especially becoming brittle with sun exposure.
-
The filament does not have a constant diameter. This type of break in the filament will most likely result in a cleaner break. -> The filament is probably not the highest quality. Either purchase filament of a higher quality or simply manage the breaks as they occur.
-
Check the flatness of the print bed. If it is not level, the material may tend to slide before it sticks. -> Adjust the legs on the printer or shim as necessary. Always refer to your printer’s guide for leveling instructions.
-
Idler tension is too tight. If replacing the filament with a fresh batch or other material doesn’t solve the snapping issue, then idler tension is a good root cause to explore. -> Loosen the idler tension completely. Allow the new print to start and tighten the idler tension until the filament no longer slips.
The ultimate solution in solving your 3D printing problems is to outsource your 3D printing to an expert partner. Dassault Systèmes is proud to offer a large database of expert 3D printing suppliers. 3D printing with our providers is as simple as uploading your CAD model to the 3DEXPERIENCE Make platform and getting instant quotes. Prior to uploading a CAD model for 3D printing, check out these design tips to ensure the parts are appropriately designed for 3D printing:
- Design parts with a strong base to allow for adequate adhesion and support for the first layer printed.
- Pay attention to the grain direction required to ensure the part can withstand the loading conditions.
- Pay attention to geometric features such as wall thickness, overhangs, and holes.
- Avoid sharp corners when 3D printing, if possible.
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds
