Video 3D Printing FDM
Discover in video how the 3D Printing process FDM Material extrusion works with 3DEXPERIENCE Make, the on-demand manufacturing, by Dassault Systèmes and his partner Bombyx.
Video Introduction to 3D Printing FDM
Hello, we’re here at Bombyx prod, a 3DEXPERIENCE Marketplace partner. Today we’ll be discussing FDM.
So, what is FDM? FDM means Fused Deposition Modeling. It’s a 3D printing process where material filament layers are fused on a plate to make an object.

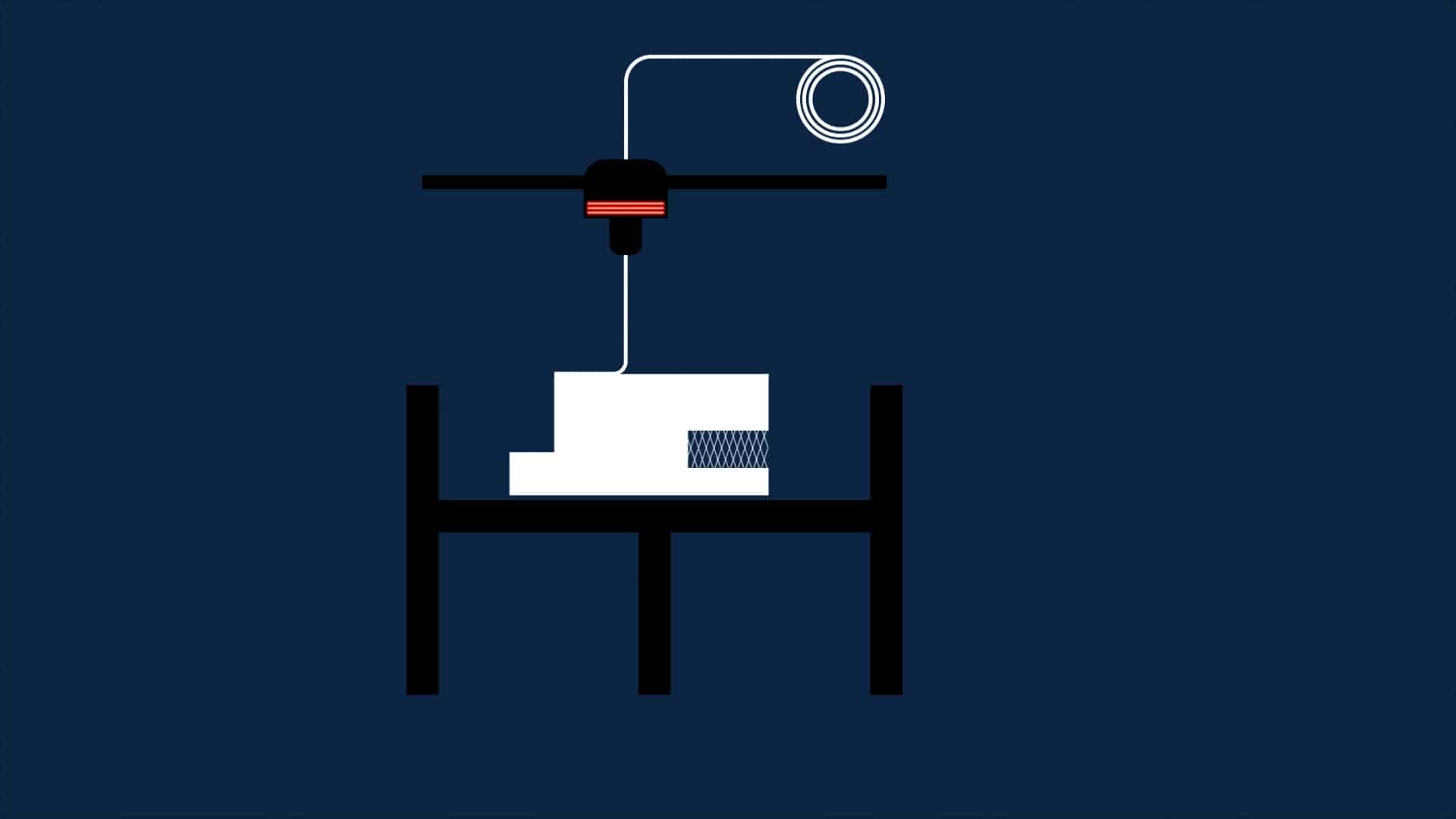
How does FDM work?
It’s simple. Most times, we have a filament, which comes in the form of a spool, which is deposited on the plate through a nozzle which heats it. The object takes shape layer after layer. At the end of each layer, the plate goes down. We print a layer and continue the process until we have the finished object.
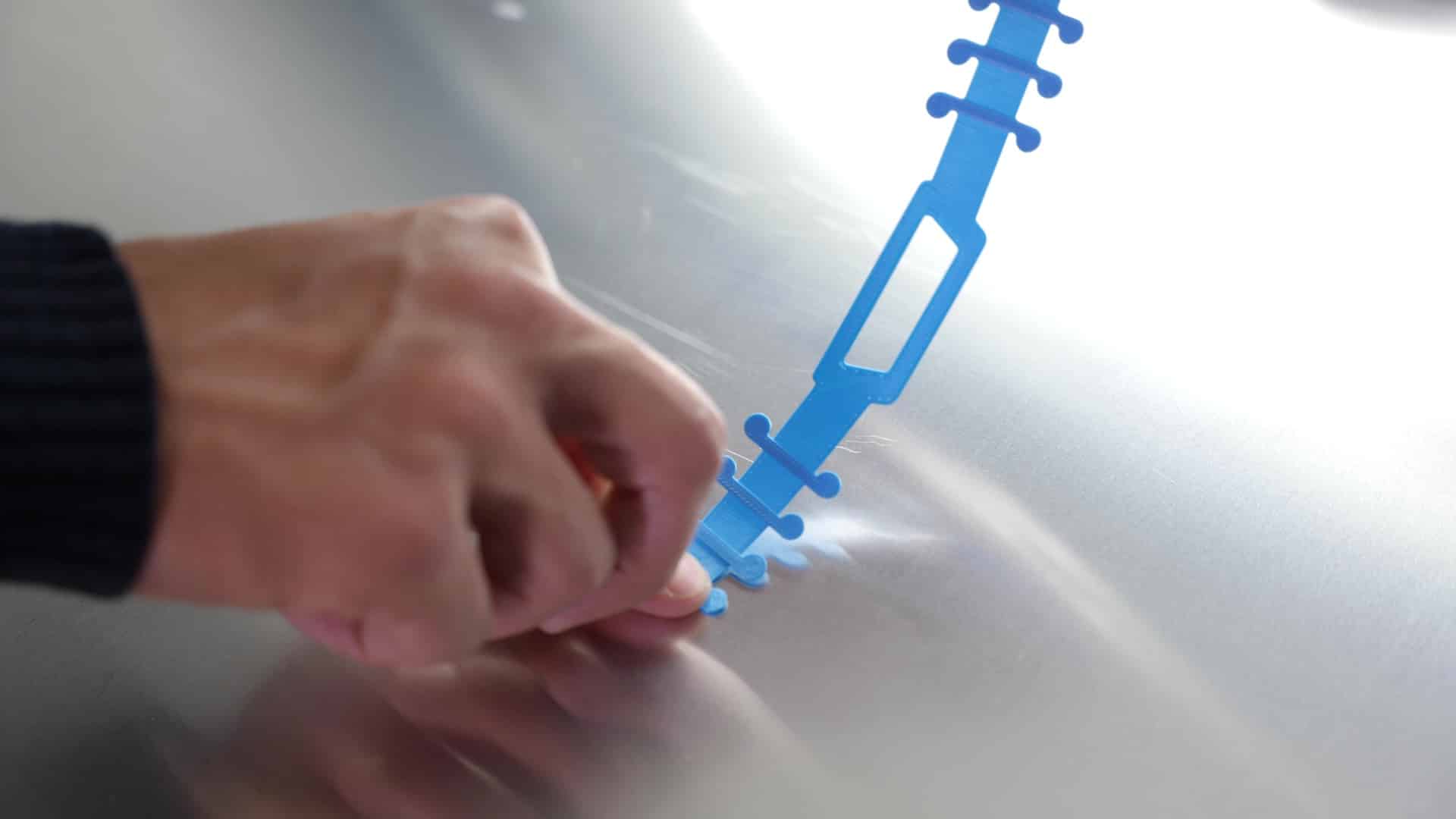
What are the advantages and limitations of FDM?
FDM has the benefit of adapting to all project types regardless of prototypes or series. This is due to the range of usable materials. FDM works with plastics, composites and even for multi-material printing. Another advantage: it’s cost-effective technology. For instance, at Bombyx prod, machines have several print heads. So, we have the power of several machines in one. Overall, the FDM has few drawbacks. This is what makes it a robust solution. But you do need to use print substrates on a regular basis. And at times, finishing is required to produce a perfect and clean final surface.
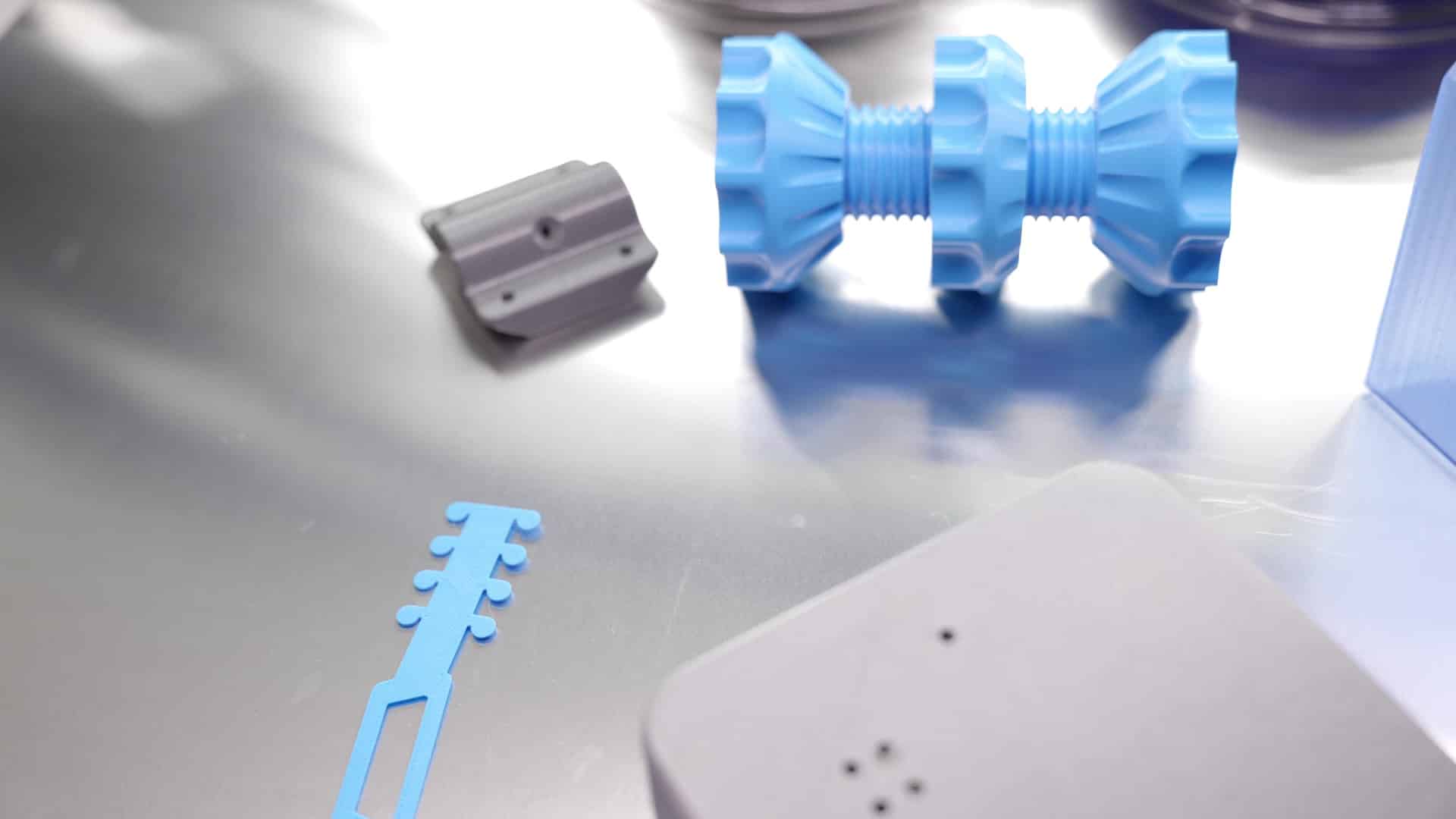
What are the usages in the industry of FDM?
Last, in terms of use, plastic and composite FDM are well suited to rapid prototyping and functional prototypes. Applications are used in the series as is the case at Bombyx prod. In terms of metal FDM, for now, interest centers on tooling and the manufacture of mechanically resistant functional prototypes. FDM is generally used in the medical and rail industries as well as in aerospace.
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds