Optimization for Better e-NVH Performance
Manatee provides dedicated reduction techniques for magnetic noise and vibrations
Manatee Optimization Environment and Design Exploration Tools
Manatee software offers advanced optimization tools for reducing electromagnetic noise and vibration in electric machines. The Skew Pattern Optimization feature helps engineers find the optimal skew pattern to maximize torque and minimize noise, while Harmonic Current Injection optimizes current harmonics to reduce NVH levels. The software supports parameter sweeps and multi-objective optimization, allowing engineers to explore design variables and identify the most influential parameters on acoustic performance. The Design Explorer interface enables efficient navigation and analysis of simulation results, helping engineers find the best trade-offs and optimize electric machine designs for various applications.
Predefined Noise Control Techniques
- Skew Pattern Optimization
- Harmonic Current Injection
Skew Pattern Optimization
Manatee software allows you to calculate the effect of skewing on electromagnetic noise and vibration levels. You can choose a predefined rotor skew pattern (e.g., V-shape step skew for IPMSM, linear skew) or a user-defined geometry. Manatee automatically expands electromagnetic and force calculations along the machine axis. Skewing calculations can be quickly performed when using a pre-calculated Magnetic Look-up Table. Skewing is also supported when importing the airgap flux from third-party software.
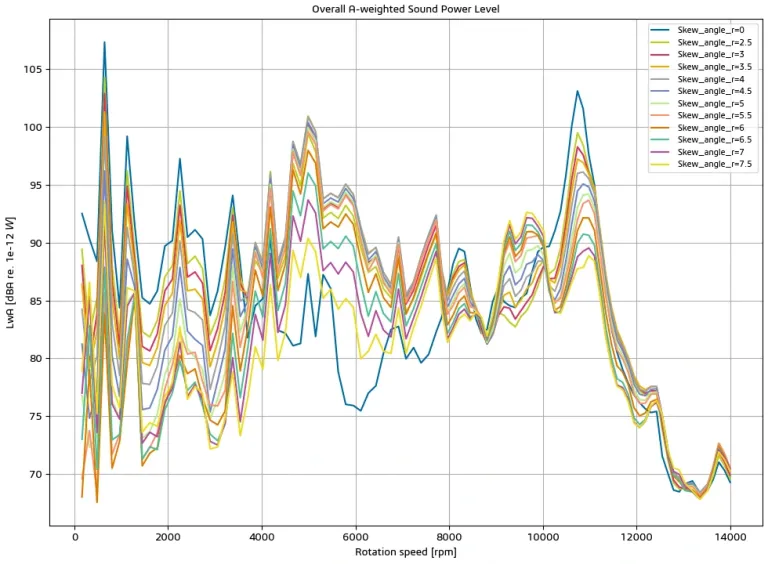
This feature allows electrical and mechanical engineers to find the optimal skew pattern, maximizing average torque and minimizing noise along the torque-speed curve while keeping torque ripple and cogging torque to an acceptable level (note: cogging torque and peak-to-peak torque ripple are generally not correlated to e-NVH).
The only required input is the skewing type to be investigated starting from a reference design. Manatee automatically defines a parameter sweep on the skew angle and tracks useful information for each design, such as average torque, peak-to-peak torque ripple, maximum sound power level over speed and the amplitude of the main noise and forces harmonics.
Skewing can excite longitudinal modes of the electrical machine structure (for example, mode (2,1) of the stator). It is, therefore, advised that it be used with a realistic 3D FEA mechanical model using the modal basis import feature.
Harmonic Current Injection
Manatee e-NVH solutions include a Harmonic Current Injection (HCI) environment designed to quickly mitigate magnetic noise and vibration produced by electric machines through optimal harmonic current injection. This environment automatically creates an optimization problem for current harmonic parameters (amplitude and phase, in DQ frame for synchronous machines) on the noisiest operating point of reference simulation to reduce noise and vibrations while maintaining an acceptable efficiency level.
Specific design and response variables are automatically defined depending on the machine and reference results and can be modified if necessary.
The Harmonic Current Injection environment is designed to help electrical engineers optimize the control of electrical machines for efficiency and e-NVH. For example, it helps find the optimal amplitude and phase of current and voltage harmonics along DQ-axes at six times the electrical frequency to dampen NVH levels at 6fe induced by torque or radial ripple.
Efficient e-NVH Design Exploration
- Parameter Sweep Definition
- Multi-Objective Optimization
- Design Explorer
Parameter Sweep Definition
Manatee software allows parameter sweeps on electrical machine multiphysics simulation inputs. Design variables that can be varied include all geometrical parameters from magnetic circuit templates (e.g., slot shapes, magnet pocket shapes, notch shape, skew rate), winding design parameters (coil pitch), control parameters (e.g., current angle for fixed speed PMSM), fault parameters (e.g., eccentricity level) or magnet temperature. Standard response variables are included in parameter sweeps (for example, torque, maximum noise level along torque/speed curve). Still, advanced output variables can also be user-defined (for example, the level of a specific harmonic in flux/vibration/noise quantities, xyz vibration on a given node, etc.).
Manatee automatically identifies the calculations affected by design variable changes so that Magnetic Look Up Tables and modal basis calculations are only updated when relevant.
Before running a detailed optimization study, electrical engineers can identify the most influential design parameters on acoustic noise and vibration levels due to magnetic forces. Mechanical engineers can also run a sensitivity study on static and dynamic eccentricity levels to specify the manufacturing tolerances better.
User-defined outputs allow NVH engineers to set up customized NVH requirements (for example Maxwell pressure levels in N/m^2, force levels in N, vibration levels at some particular points in dB etc).
Multi-Objective Optimization
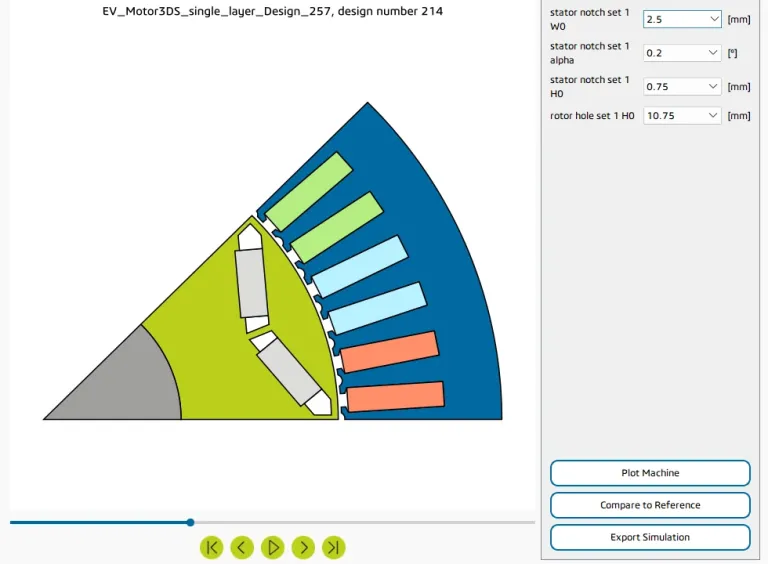
Manatee e-NVH software has a multi-objective optimization environment for electric machine magnetic circuit design variables. The default solver is the NSGA-II genetic algorithm. Design variables include geometric parameters from magnetic circuit templates (such as slot shape, notch shape, magnet pocket shape, and skew rate), winding design (e.g., coil pitch), rotor skew (e.g., skew angle), or current harmonics.
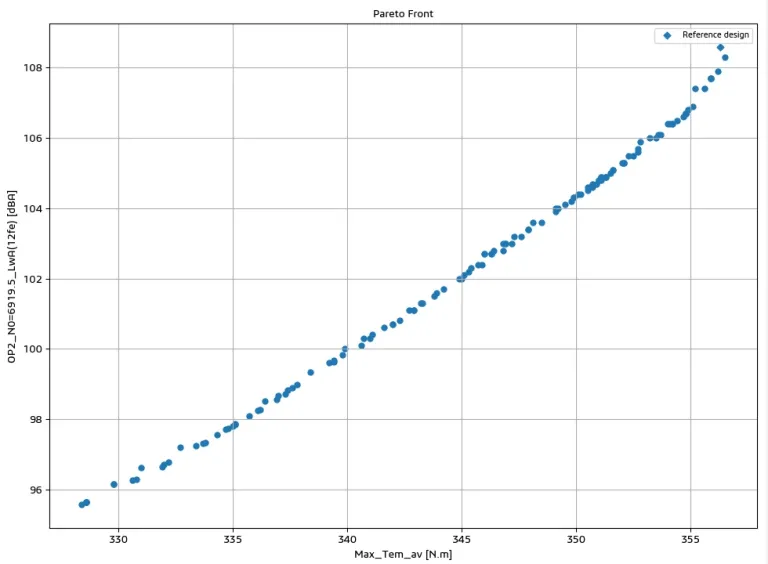
Overall noise, vibration, force or torque levels, and specific harmonics can be used as objectives to minimize or maximize. These variables can also be used to define constraints or be simply tracked during the simulation. Dedicated post-processings are automatically generated at the end of the optimization to extract the Pareto front, study the algorithm's convergence rate, or explore the final design space. It is also possible to extract a given design and run more detailed simulations on it.
The optimization environment is designed to help Electrical and NVH Engineers improve the multi-physic performances of a given design, especially in terms of noise, vibrations and electromagnetic performances. User-defined outputs allow NVH engineers to define customized requirements. This is particularly helpful in automotive applications, where different OEMs and tier-one suppliers may have different ways of specifying NVH requirements.
Design Explorer
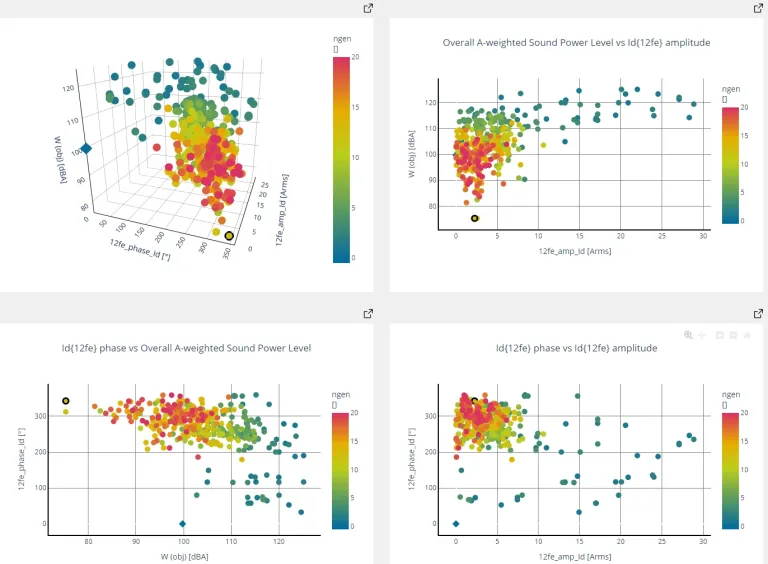
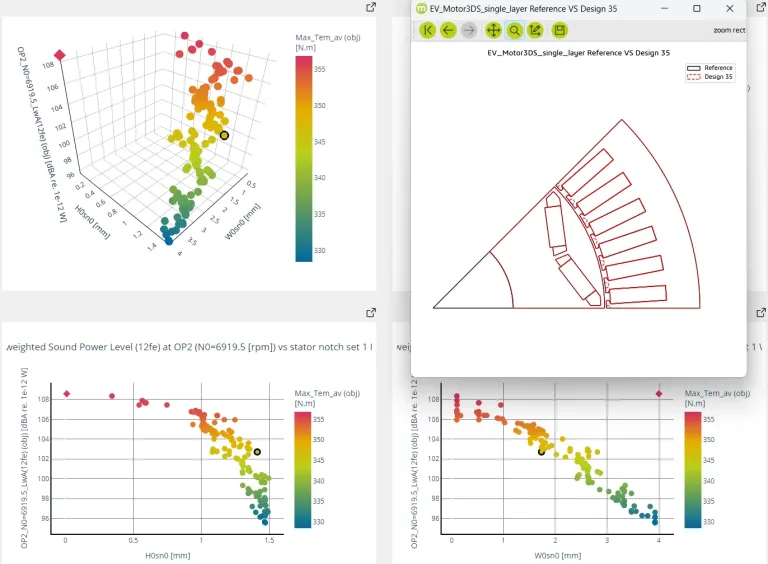
Manatee e-NVH software allows to smoothly perform electrical machine design explorations among optimization or parameter sweep results. Manatee Design Explorer provides a dedicated interface to explore all the simulated designs with 5D visualization (XYZ axes, color and size). The design cloud can be filtered on the response/design variables (for example with additional constraints).
A given electric machine design can be visualized and exported within a new simulation multiphysics workflow for further analysis with a button click. A group of designs can also be selected to compare their characteristics more easily and exported as a .csv file.
Running parameter sweeps can create massive data sets with several designs and response variables for each design. This interface enables to conveniently display and filter all the designs to find the best trade-off. This analysis can be carried out by all engineers involved in developing electric drives.
FAQs about Optimization for Better e-NVH Performance
Also Discover
Learn What SIMULIA Can Do for You
Speak with a SIMULIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right SIMULIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering