Electric Vehicle Engineering
Simulations optimize EV design, enhance performance, and shape the future of sustainable transportation
Steering the Digital Future of Electric Vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) are propelling us into an era of efficient, affordable, and clean transportation. They are set to revolutionize travel and become a cornerstone of the mobility landscape in smart cities.
To integrate this new generation of vehicles, innovators, OEMs, and suppliers must rethink vehicle engineering. The compressed development cycles demand unprecedented collaboration among all stakeholders. As multiple systems within the vehicle are impacted, integrating new technologies presents a complex engineering challenge. Electrification requires innovative solutions that unify disciplines and offer a clearer view of vehicle performance.
Key Benefits of Simulation for Electric Vehicle Engineering
Enhanced performance
Electrification improves torque and acceleration, boosting EV acceptance.
Increased battery efficiency
R&D and simulation extend the driving range and reduce charging times.
Reduced cost
Affordable EVs lower costs and increase accessibility.
Virtual Twin Experience for Vehicle Electrical System Simulation
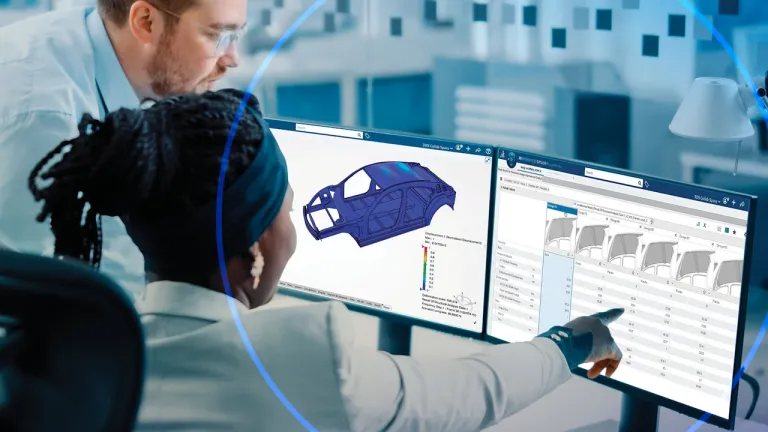
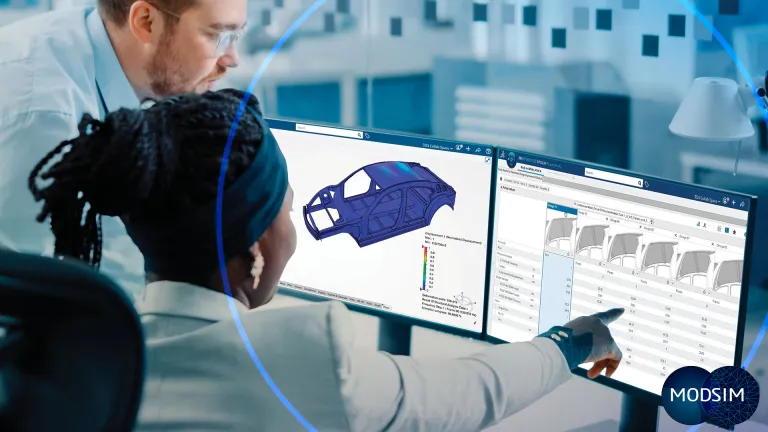
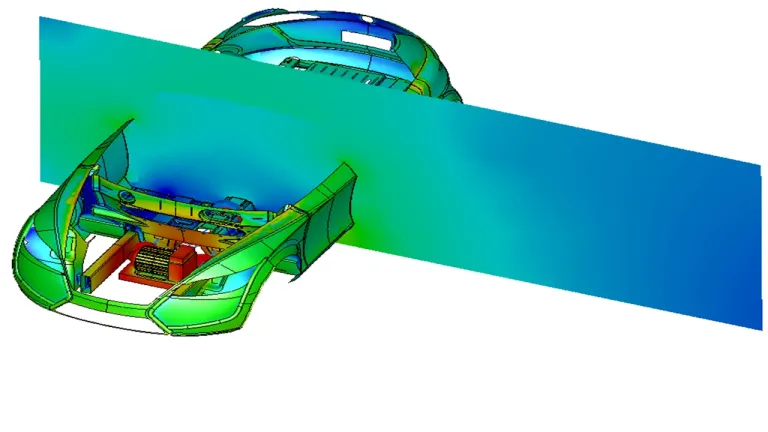
Developing an electric vehicle is a lengthy process involving multiple iterations from concept to final design, along with extensive prototyping and testing. Simulation creates a virtual twin experience that captures all relevant design data and accurately reproduces real-world behavior. This virtual testing replaces physical tests, reducing the number of prototypes and significantly cutting development time and costs.
MODSIM Facilitates Electric Vehicle Modelling
Unified modeling and simulation (MODSIM) eliminates silos between design and analysis by integrating computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) into a single environment. This integration allows engineers to receive immediate feedback on the impact of design changes, ensuring optimal performance. All stakeholders in EV design can actively participate and democratize simulation, and team members work with the same, up-to-date data, maintaining a single source of truth.
Fundamentals of Electric Vehicle Engineering Processes
- Component Level
- System Level
- Full Vehicle Level
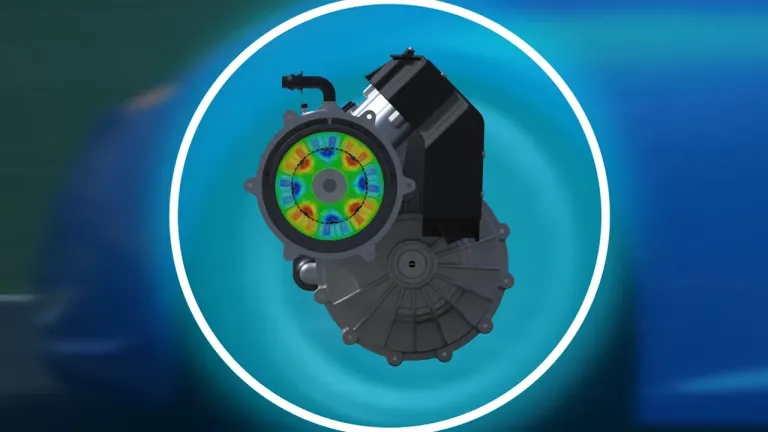
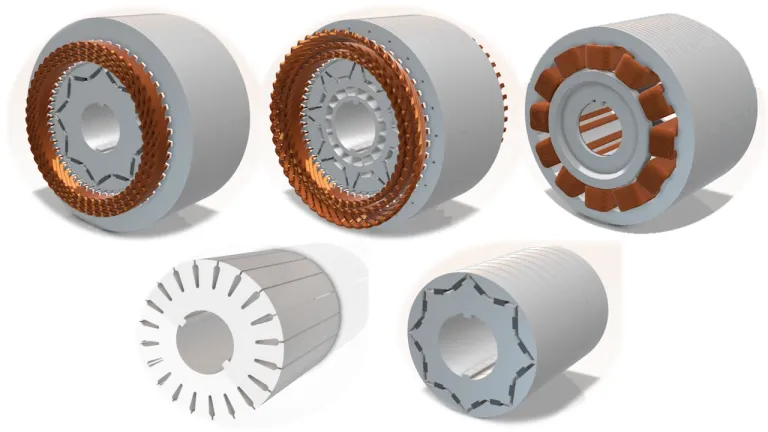
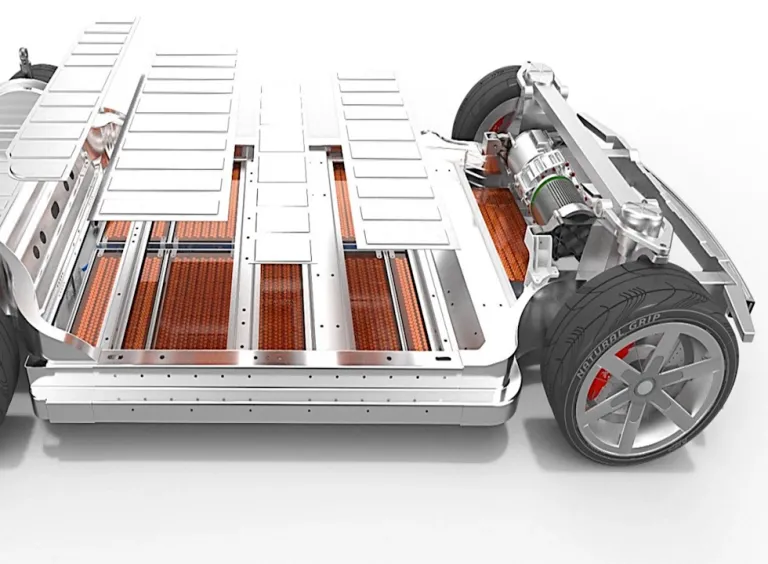
Electric Motors for Traction Applications
Electric motors are crucial components in electric and hybrid vehicles, trains, and industrial machinery. They convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, enabling motion. Traction motors are engineered for high torque and efficiency, providing powerful acceleration and smooth operation across various speeds. These motors are typically robust, lightweight, and designed to withstand harsh operating conditions. Key features include precise speed control, low maintenance, and high energy efficiency, making them ideal for sustainable transportation solutions. Ongoing advancements in motor technology continue to improve their performance, reliability, and integration with modern power electronics systems.
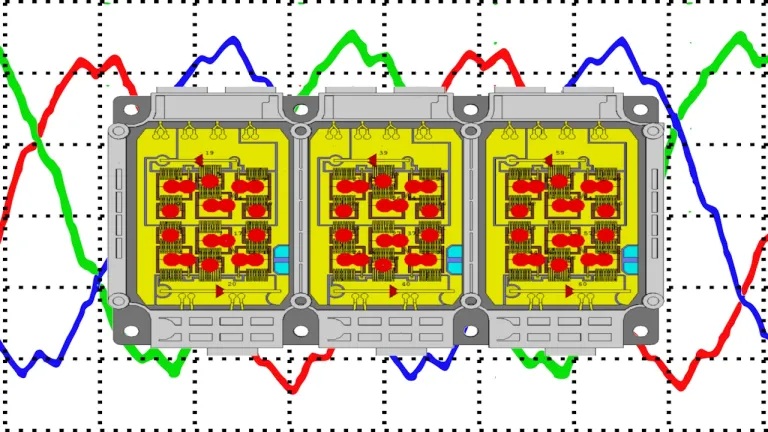
Power Electronics Engineering
Power electronics for traction applications play a crucial role in controlling and converting electrical energy to drive electric motors in vehicles and trains. These systems manage power flow between the energy source (like batteries or power grids) and the traction motor, ensuring optimal performance. Key components include inverters, converters, and controllers that regulate voltage, current, and frequency to achieve efficient and precise motor operation. Power electronics enable regenerative braking, which recovers energy during deceleration, enhancing overall efficiency. Their compact design, reliability, and efficiency are critical for advancing electric and hybrid traction systems, supporting the shift towards greener transportation.
Mechanical Gear Drive Simulation
Gear drives in electric vehicles (EVs) are vital components that transmit power from the electric motor to the wheels, optimizing performance and efficiency. Unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, EVs often use single-speed transmissions due to the broad torque range of electric motors. This simplicity reduces mechanical complexity, weight, and maintenance needs. Gear drives ensure smooth torque delivery, enhancing acceleration and energy efficiency. Some advanced EVs incorporate multi-speed gearboxes for improved performance at high speeds. The design focuses on minimizing noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), contributing to the overall quiet and smooth driving experience that electric vehicles are known for.
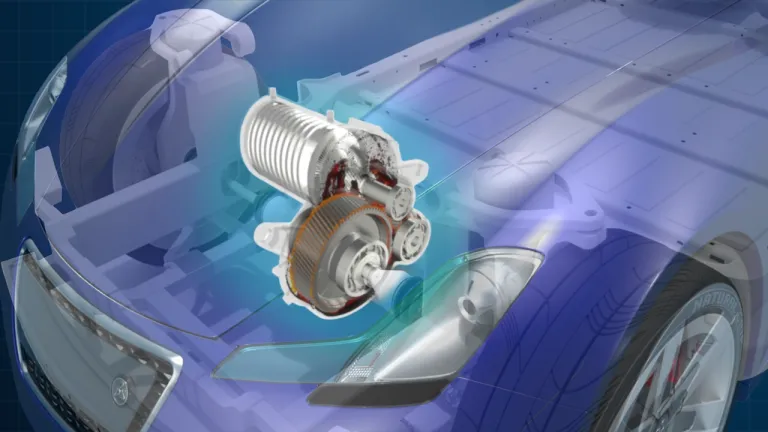
Electric Drive Engineering
Electric drive engineering is a multidisciplinary field focused on designing, developing, and applying systems that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. These systems, known as electric drives, are integral to electric vehicles. Although electric machines have been around for a while, using electric propulsion systems for traction systems widely opens up new engineering challenges.
The electric motor is at the core of electric drive systems, and it is controlled by an electronic controller that regulates speed, torque, and position. The engineering involved in these systems includes several key areas: electrical engineering, control theory, power electronics, and mechanical engineering.
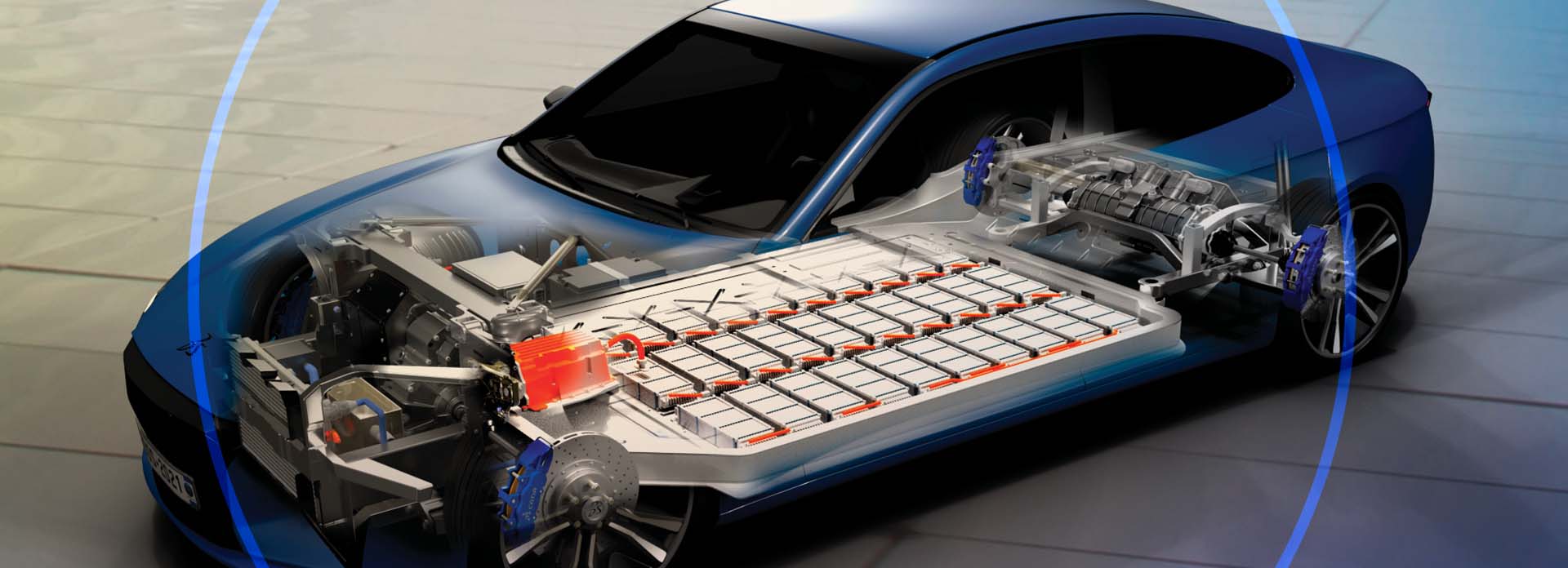
Automotive Battery Pack Design
Battery packs are the heart of electric vehicles (EVs), providing the energy needed to power the electric motor. They must store as much energy as possible to minimize range anxiety and maintain safety in unexpected events.
Battery packs consist of numerous lithium-ion cells arranged in modules, optimized for energy density, longevity, and safety. The design focuses on maximizing range, minimizing charging time, and ensuring thermal management to prevent overheating. Advanced battery management systems (BMS) monitor the health and performance of each cell, balancing the charge and discharge cycles. Innovations in battery technology, such as solid-state batteries and fast-charging capabilities, are driving the evolution of EVs, making them more efficient, reliable, and accessible for widespread adoption. Batteries are highly complex systems, requiring advanced engineering methods at all levels: from chemistry to cell engineering, to module and pack engineering, and finally integration into full vehicles.
Thermal Behavior Analysis
Electric vehicle thermodynamics focuses on managing heat within the vehicle to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Unlike internal combustion engines, EVs generate less heat, but efficient thermal management is still crucial, particularly for the battery, power electronics, and electric motor. Systems like liquid cooling, heat pumps, and phase change materials are used to maintain optimal temperatures, preventing overheating or cold-related efficiency losses. Proper thermodynamic management enhances battery life, charging speed, and overall vehicle performance. As EVs evolve, advanced thermal systems become increasingly important for maximizing range and reliability across different climates and driving conditions.
Electromagnetic Compatibility
Electric vehicle electromagnetics plays a critical role in the operation and efficiency of EVs, particularly in the design of electric motors and charging systems. In motors, electromagnetic fields convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, with precise design needed to maximize torque, efficiency, and power density. Electromagnetic principles are also applied in wireless charging systems, where energy is transferred through inductive coupling between coils. Effective electromagnetic design minimizes energy losses, reduces heat generation, and limits electromagnetic interference (EMI) that could disrupt vehicle electronics. As EV technology advances, optimizing electromagnetics is key to enhancing performance, improving range, and ensuring reliable and safe operation.
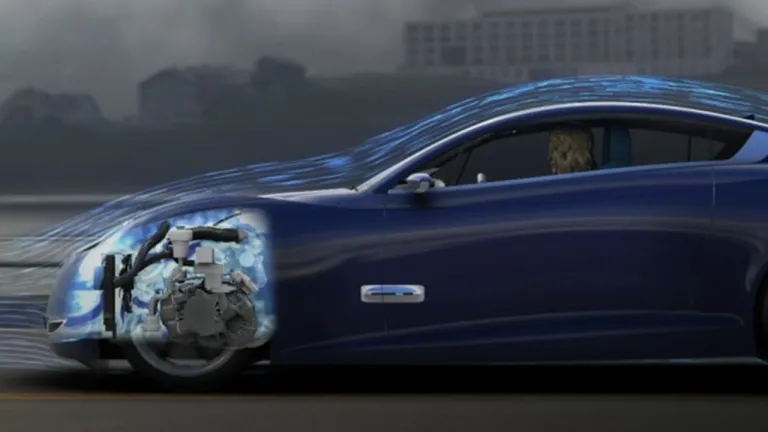
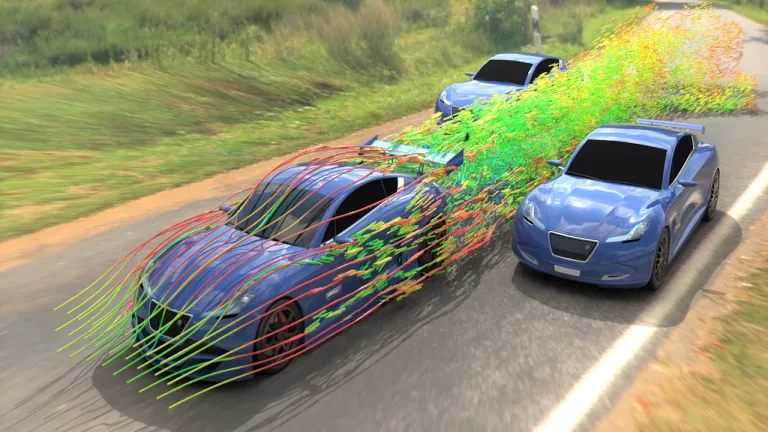
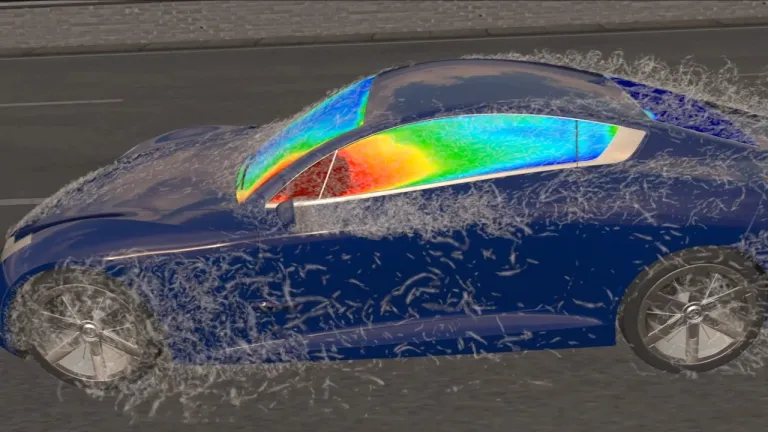
Electric Vehicle Aerodynamics
Electric vehicle aerodynamics is crucial for enhancing efficiency and extending driving range. By minimizing air resistance, or drag, EVs can reduce the energy required to maintain speed, thereby conserving battery power. Key design elements include a streamlined body shape, smooth underbody, and features like active grille shutters that close at high speeds to improve airflow. Optimizing aerodynamics also reduces noise and improves handling stability. With lower drag coefficients, typically around 0.24 for modern EVs, manufacturers can significantly increase range, making aerodynamics a vital aspect of electric vehicle design.
Acoustics, Noise and Vibration
Customer experience is a crucial factor in car-buying decisions. To ensure electric vehicles (EVs) compete effectively with traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, it's essential to offer an exceptional experience for both drivers and passengers. Unlike ICE vehicles, EVs often generate more tonal noise, which can be perceived as bothersome hums and whines. Utilizing simulations can help identify the sources of noise and vibration in the vehicle, allowing engineers to implement targeted solutions that enhance the overall experience while keeping insulation weight to a minimum.
Customer Stories about SIMULIA Electric Vehicle Simulation Tools
Start Your Journey
The world of Electrical Vehicle Engineering is changing. Discover how to stay a step ahead with SIMULIA
FAQs About Electric Vehicle Simulation
Also Discover
Learn What SIMULIA Can Do for You
Speak with a SIMULIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right SIMULIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering