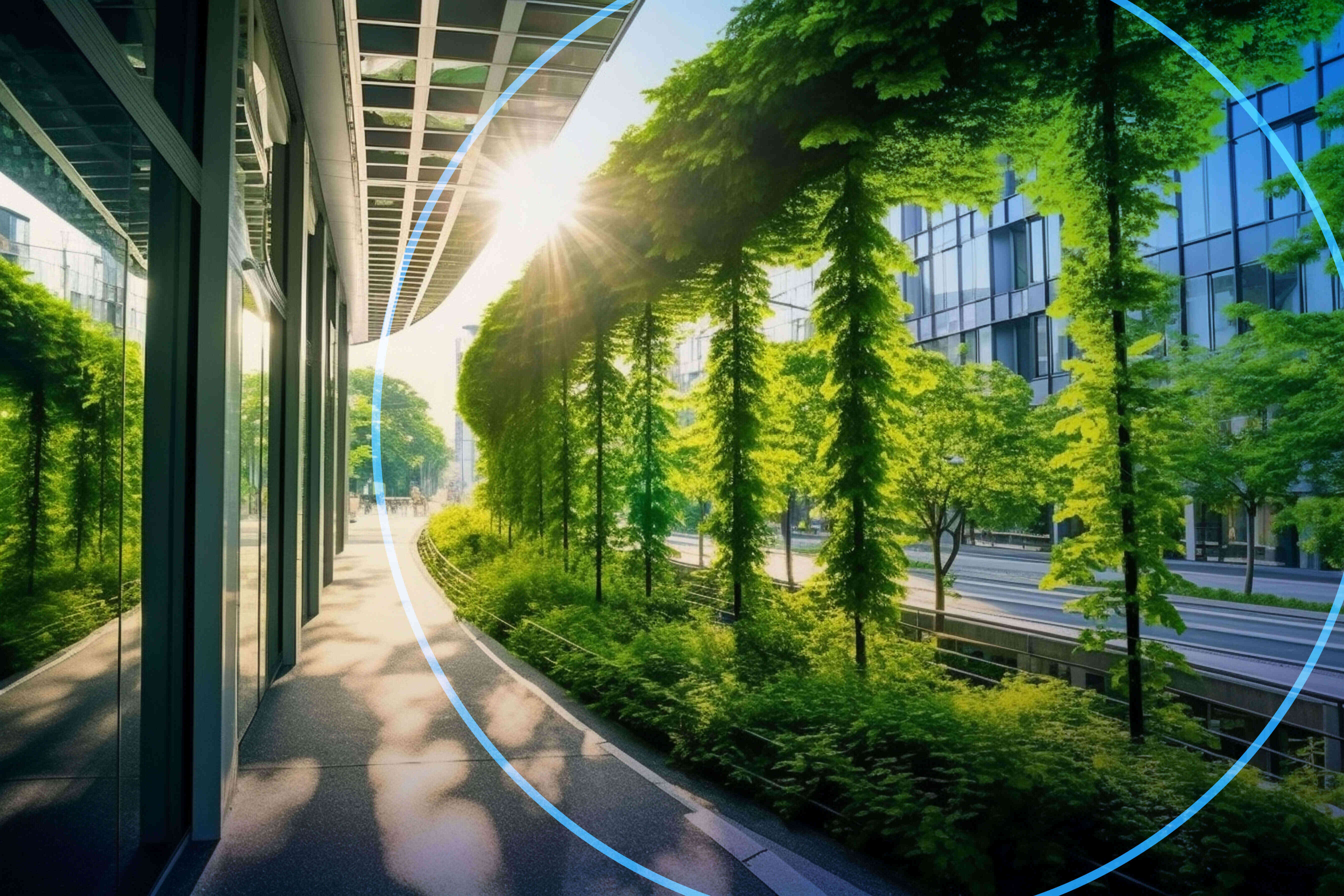
Decarbonization
Decarbonization aims at reducing emissions throughout the product and service’s life cycle and across the full value chain.
What is Decarbonization?
Decarbonization aims at creating a carbon-free global economy through the targeted and technologically enabled reduction of emissions across value chains. Decarbonization techniques encompass a range of solutions including alternatives fuels, electrification, renewable energy, carbon-offset projects, lifecycle assessment processes and sustainable working practices.
The Challenges of Decarbonization
Decarbonizing your business cannot be solved with a single stroke. It is a broad, multifaceted challenge that involves changing multiple processes and collaborating with a wide range of stakeholders. It therefore requires solutions that can provide a holistic and realistic view of company-wide operations, allowing businesses to understand the nature of the challenges, and co-ordinate, test, and implement effective responses.
What Does It Mean for Your Business?
As regulatory pressure grows, decarbonizing your operations is no longer an option, it is a necessity. Doing so, however, should not be seen as an additional cost but an opportunity. From accelerating the development of new business models to creating more sustainable products that better serve increasingly environmentally conscious consumers, reducing your whole-chain carbon emissions enables your business to benefit from making a positive difference.
Digitalization of the Transportation Sector: An enabler for the low-carbon transition
The global shift towards clean energy is reshaping industries, particularly in the aviation and automotive sectors. Reducing carbon emissions is critical to combat climate change, and the integration of low-carbon energy solutions is key to driving sustainability in product development, manufacturing and usage.
Solutions for Effective Decarbonization
There are a range of options organizations can take when looking to reduce carbon emissions:
Carbon removal: Carbon can be actively taken from the atmosphere, via a natural approach like reforestation, or a high-tech one like direct air capture.
Electrification and renewable energy: Companies can reduce GHG (Greenhouse Gas) emissions by increasingly electrifying their operations, powered by green energy sources like renewables or hydrogen.
Carbon offsetting: In the short term, businesses can invest in environmental and decarbonizing projects to balance out their own carbon footprint.
Sustainable business practices: Rethink business-wide working practices to reduce waste and improve efficiencies.
Benefits of Dassault Systèmes’ Technologies
Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE® platform provides a powerful suite of tools that can help understand and transform your organization’s energy production, use and infrastructure

Lead the Decarbonization Journey
Integrate and trace the application of GHG reduction standards into your product and service’s lifecycle development and across the full value chain.
Be right and green the first time
Integrate and trace the application of GHG reduction standards into your product and service’s lifecycle development and across the full value chain.

Reduce your own carbon footprint
Analyze then reduce your Scope 3 GHG indirect emissions that occur in your value chain: from the use of goods sold, maintenance and waste reduction to end of life
Real-World Results, As Told by Our Customers
Take a look at our case studies to see how Dassault Systèmes solutions are helping customers decarbonize their unique businesses.
Making a Positive Impact on Society
FAQ About Decarbonization of Energy & Technology
Related Content
Decarbonizing Industry Operations
Through digital transformation, industries can rethink their operations, from product design to supply chains, and move toward more sustainable, resource-efficient processes.
Realize Climate Neutrality Across Your Value Chain
To achieve climate neutrality, companies must implement climate-neutral practices across all carbon emission categories in our value chain.
Biodiversity in Business
Biodiversity is essential to maintain clean air and water, regulate climate or make pollination possible. Our well-being - along with that of the entire ecosystem - depends on it. And our economy is no exception.
Sustainable Energy
Low-carbon energy generates substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions over their entire lifecycle. With advanced digital tools and processes, organizations can make strategic decisions to reduce their energy use and carbon footprint.


