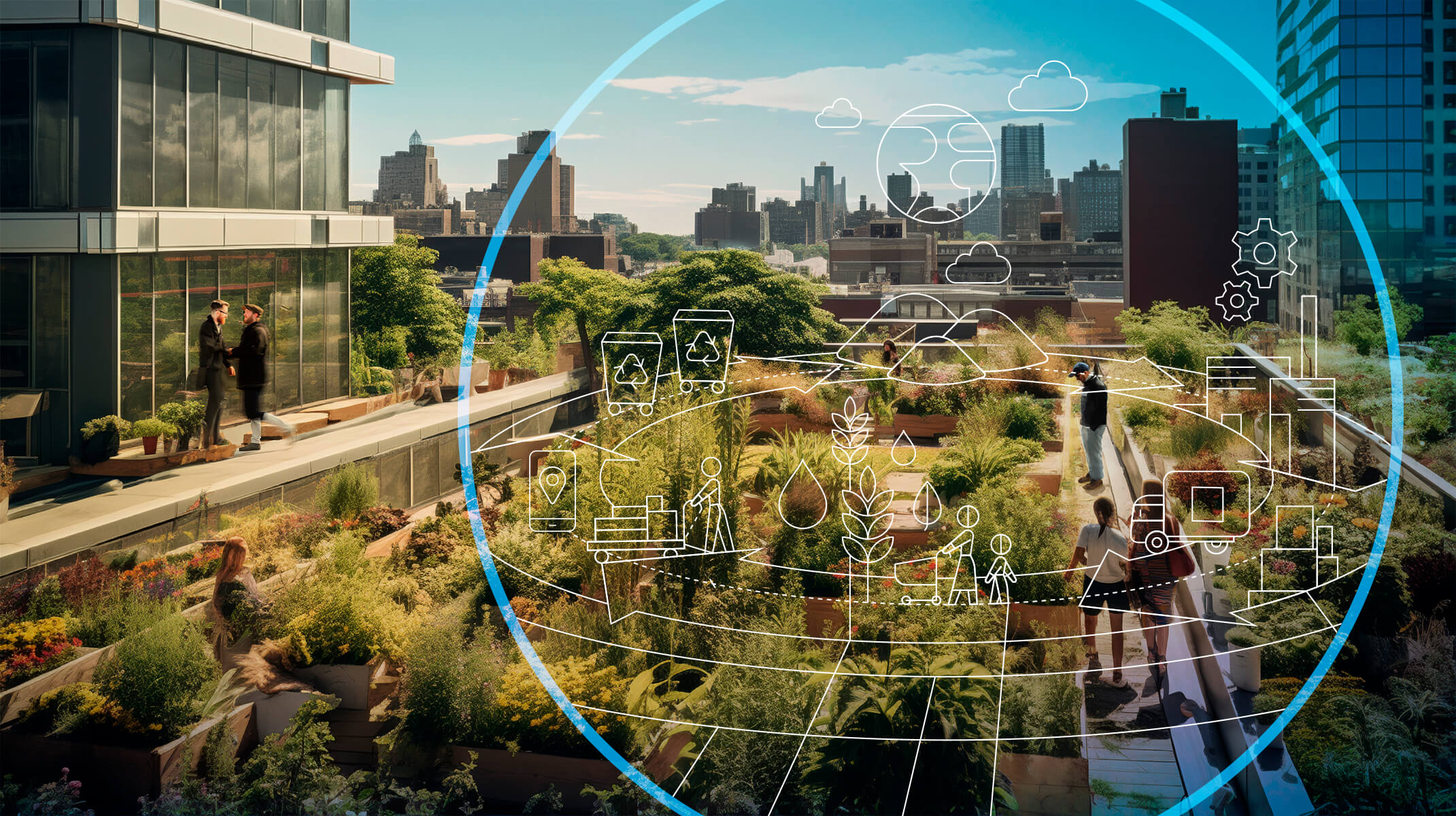
Circular Economy
The circular economy is gaining significant traction as a sustainable approach to resource management. By adopting principles such as reducing, reusing, and recycling, organizations and consumers alike can minimize waste, maximize resource utilization, and contribute to the restoration of natural ecosystems.
What is the Circular Economy?
The circular economy definition, as described by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, represents a restorative and regenerative system. It is based on three key principles: eliminate waste and pollution by redesigning production processes, keep products and materials in use through innovative reuse and recycling strategies and regenerate natural systems by transitioning to sustainable materials and methods. This new model challenges the conventional "take-make-waste" linear economy by encouraging businesses to innovate, reduce resource consumption, and close the loop on material use.
Circularity in Action
At the core of the concept of circular economy lies the idea of circularity, where resources are kept in use for as long as possible. Real-world adoption of circular economy strategies demonstrates the tangible benefits of this approach. Embracing Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE® platform allows organizations to reimagine their operations, aligning them with the principles of the circular economy. From design phase to lifecycle analysis, businesses can create products that contribute positively to the green economy while meeting consumer demand for sustainable solutions.
What Does it Mean for Your Business?
Circular economy practices mean rethinking how organizations operate within their environment and value chain ecosystem. It requires embracing bold new business models, based around eco-design and product reusability. It means striving to eliminate waste from your operations in all its forms, from minimizing power use and chemical products, to making sure products are designed to have long lives. And it means integrating disassembly considerations into a product's design stage to support its reuse.
The Challenges of Circular Economy
The circular economy offers a radical new approach to business-as-usual. But as with any radical approach, it means grappling with existing legacy structures and processes. Many current production operations are based on the “take-make-waste” model. Circular economy solutions mean rethinking operations from the ground up, and that means you need a full view of your operations and a way to simulate a new model before making the physical changes to your business.
How One Industry Leader Is Decarbonizing Processes By Improving Part Reuse
By implementing circular economy practices empowered by Dassault Systèmes’ innovative solutions, a major equipment manufacturer was able to mitigate risks, decarbonize processes and successfully reduce scrap and waste.
Real-World Results, As Told by Our Customers
Read how our customers have used Dassault Systèmes’ solutions to integrate circular economic principles into their operations.
Solutions for a Circular Economy
Creating a framework where circular economy practices can grow and thrive can be achieved in a number of ways:
Adopt Eco-Design Practices
Implementing eco-design practices involves looking beyond conventional boundaries and utilizing lifecycle assessment techniques to comprehensively track the environmental impact of products throughout their entire life cycle. This approach involves engaging the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to product disposal, to identify areas for improvement and minimize environmental impacts at every stage.
Design for Recyclability
Designing products with recyclability in mind from the outset ensures that end-of-life considerations are integrated into the design process. By understanding how a product can be disassembled and its components reused or recycled, designers can create products that are inherently ready-made for circularity. This approach not only facilitates the recycling process but also reduces the energy and resources required for remanufacturing or reprocessing materials.
Explore New Materials
Continuous research into sustainable materials and bioplastics plays a crucial role in developing a greener product lifecycle. By identifying and utilizing materials that are renewable, biodegradable, or sourced responsibly, businesses can reduce their reliance on finite resources and minimize environmental harm. The adoption of innovative materials can also lead to new opportunities for circular product designs and foster more sustainable consumption patterns.
The Benefits of Dassault Systèmes’ Technologies
Dassault Systèmes 3DEXPERIENCE® platform can provide organizations with the solutions they need to establish the holistic view of production chains necessary for transitioning to circular economy practices.
Dare to create bold new business models
Eco-design, develop and simulate new products; taking into account their manufacture, maintenance and end-of-life for a service economy.
Strive to eliminate waste
Optimize the use of materials to their pure functional needs while maintaining the manufacturability, testing and development of new materials.
Design for the 3Rs
Integrate the disassembly process directly into product development and manufacturing engineering.
Making a Positive Impact on Society
FAQ About Circular Economy Sustainability
Related Content
Circularity in Action
It’s time for concerted action. Here’s how to make the circular economy achievable, scalable and profitable.
Eco-Design
By integrating sustainability throughout the product development cycle, eco-design unlocks the potential for sustainable design without compromising time-to-market or increasing costs.
Biodiversity in Business
Biodiversity is essential to maintain clean air and water, regulate climate or make pollination possible. Our well-being - along with that of the entire ecosystem - depends on it. And our economy is no exception.
Designing Disruption to Accelerate Sustainability
By modeling entire value chains, virtual twins can improve the sustainability of products and services across the lifecycle, cradle to cradle.



