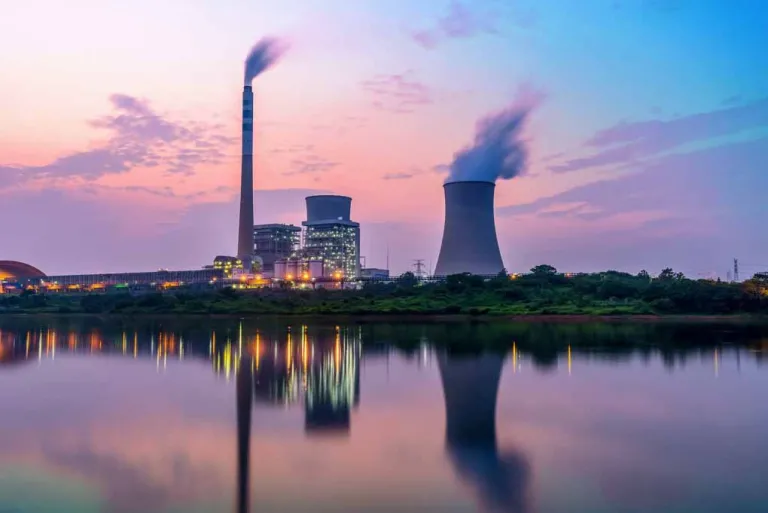
Clean Energy Technologies: Powering Up Innovation
As the need to tackle climate change gains global recognition, shifting from fossil-based energy systems to sustainable and low-carbon alternatives has become, now more than ever, crucial. Clean energy technologies that will enable this energy transition do exist. What they need now is to be scaled up, in order to reach net-zero targets.
Reaching net zero targets with low carbon energy innovations
To address this urgency, net zero commitments raised globally and global investment in low-carbon energy technologies has increased substantially, reaching $1.8 trillion in 2023 (1). Promising? Yes. But not enough. According to the World Economic Forum, clean energy production must triple by 2030 to meet sustainability targets, requiring a doubling of investment to achieve this goal.
In their turn, investments can fuel the development and deployment of breakthrough technologies that make the energy transition a reality, addressing the most challenging sectors and reducing emissions. However, as electrification intensifies, expanding and upgrading the grid will also be essential to fully harness and integrate the newer sustainable energy sources.
What is a clean energy technology?
Compared to more traditional energy production, low-carbon energy generates substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions over their entire lifecycle. It includes renewable energies, like wind and solar, “derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed" (2), and nuclear as well. The latter has indeed a minimal carbon footprint over its entire lifecycle (nuclear produces about the same amount of carbon emissions as wind (3).
Revolutionizing Low-Carbon Technologies with an Innovative Platform
However, developing the technologies that will enable a clean energy future is no easy feat. Advanced digital tools can help. Energy companies (startups and traditional players) already rely on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform’s collaboration and simulation capabilities to tackle their challenges, transform the way they operate and enable more sustainable and efficient electricity generation. Navigating the complexities of product and infrastructure development is key to ensuring a smoother transition to a low-carbon future.
Let us dive deep into each of these clean energy technologies.
Advancing the Next-Generation of Wind Technology
- Sustainable Wind Turbines:The Path Forward
- Offshore Wind Farms: A Sea of Opportunities
Sustainable Wind Turbines: the Path Forward
Sustainable wind turbines play a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and driving the global transition to renewable energy. Developed by leveraging the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, energy companies can optimize the entire lifecycle of wind turbines, ensuring their efficiency, durability, and minimizing environmental impact. This approach ensures that materials used are sustainable and that energy production is maximized while minimizing waste. Sustainable wind turbines are not just a source of clean energy; they represent a commitment to a more sustainable world.
Offshore Wind Farms: a Sea of Opportunities
Offshore wind farms, with stronger and more consistent wind conditions, offer significant potential for renewable energy production. However, these infrastructures come with their own set of challenges such as harsher environmental conditions and higher construction and maintenance costs. To overcome these challenges, the virtual twin enables energy companies to optimize the design, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the operational lifespan of wind turbines, thereby ensuring that wind farms are both economically viable and environmentally sustainable.
Accelerating the Shift to Green Hydrogen
Green Hydrogen: A Transformative Role in the Energy Transition
Green hydrogen, produced via water electrolysis powered by renewable energy, plays a crucial role in the global push for clean energy. As a carbon-free fuel, it is essential for decarbonizing industries like heavy manufacturing, transportation and for building heating and power. The transition to hydrogen technology is driven by decreasing costs, strong government support, and increasing demand for sustainable products. However, challenges remain, including the complexity of hydrogen projects, the need for new infrastructure, and managing the supply chain efficiently. With the right strategies and technologies, green hydrogen has the potential to significantly contribute to global energy transition efforts and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.
Embracing Nuclear Energy for a Net Zero World
- Reaching Sustainability Goals with Nuclear Power
- Small Modular Reactors: Scale up Nuclear Innovation
Reaching Sustainability Goals with Nuclear Power
According to a recent Nuclear Energy Agency report, nuclear capacity will need to triple by 2050 to meet net zero targets. But nuclear power plants are complex to build and challenging to maintain, due to complexities surrounding their safety-critical nature, regulatory compliance, workforce and skill shortages, and costs. The 3DEXPERIENCE platform helps companies that engineer and construct nuclear facilities collaborate, mitigate risks and deliver safe and reliable nuclear power plants.
Small Modular Reactors: Scale up Nuclear Innovation
As countries seek to decarbonize their energy systems, Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) present a viable option to meet growing energy demands sustainably and efficiently. Indeed, SMRs offer flexibility, reduced construction times, lower costs and thus overcome the common challenges of delays and budget overruns associated with large nuclear plants. And the 3DEXPERIENCE platform can play a crucial role in accelerating the deployment of SMRs by enhancing design, simulation, and collaboration processes. This helps ensure safety, reduce waste, and streamline the licensing process.
Discover our Customer Stories
Source:
1 BloombergNEF in Energy Transition Investment Trends 2024
2 United Nations Website
3 International Atomic Energy Agency, International Day of Clean Energy: Why Nuclear Power?, January 2024
4 NEA, Meeting Climate Change Targets: The Role of Nuclear Energy
FAQ about Clean Energy Technologies
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the deployment of solar PV and wind are the low-carbon energy sources with the most rapid growth. However, the deployment of clean energy systems is occurring at different speeds across the world, with China, the United States and Europe leading.
The clean energy value chain includes four key stages.
First, power generation, created from a low-carbon energy source; its storage, necessary to manage the intermittent nature of renewable energy; its transportation, involving the optimization of grids and networks; and finally its usage where energy is applied efficiently across industries to enable their decarbonization.
Coal takes hundreds of million of years to form. It is not renewable energy. Nor is it sustainable, as it is heavily carbon-intensive.
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished. When it comes to solar energy, we can expect a steady limitless supply of sunlight. So, yes, solar energy is renewable.
Renewable energy comes from natural sources or processes that are constantly replenished like:
- wind,
- sun,
- geothermal,
- bioenergy,
- hydrogen,
- water.