What is Computer-Aided Engineering?
Professional engineers and designers use specialized computer-aided engineering (CAE) software to help them design, develop, test, and manufacture a wide range of products. We take a look at the different types of computer-aided software engineering and how this technology is helping to shape our world.
What is computer-aided design engineering?
Also known as CAE, computer-aided engineering is a term used to describe the process of bringing a product to market. It refers to every stage taken in the engineering process of a product, from the initial design to the development phases, to the testing of a product using simulations, and finally to planning the product's manufacturing.
Computer-aided engineering is used in combination with CAD, computer-aided design software and various engineering disciplines such as finite element analysis, computational fluid dynamics, multibody dynamics and kinematics, and computer-aided manufacturing.
Virtually every major industry you can imagine uses computer-aided engineering to refine its products. CAE is used to develop automobiles, airplanes, domestic products, electronics, and medical equipment. In the CAE process, a designer will create a highly detailed computer-aided engineering drawing that engineers will then use to refine the design, test it using digitally rendered 3D models, and then develop an efficient process to manufacture it.
Discover computer-aided design solutions tailored for engineers in the Dassault Systèmes store
Dassault Systèmes provides you with powerful computer-aided software engineering
tools. Get access to an entire range of exceptional engineering CAD programs with the SOLIDWORKS Cloud Offer. CATIA Mechanical Designer delivers end-to-end mechanical design solutions.

SOLIDWORKS xDesign
Get ready for the next generation of design solution, developed by the same team that brought you SOLIDWORKS 3D CAD
How does computer-aided engineering work?
Before the advent of computer-aided engineering, product development was a long and painstaking process.
Computer-assisted engineering has dramatically changed the way we develop products. Designers can use graphic design CAD and mechanical design CAD software to create product designs that can be easily and quickly iterated. Computer-aided engineering software can be used to test realistic 3D models without the need to build expensive physical prototypes. Digital simulations allow stakeholders to make more informed decisions on materials, parts, and components earlier in the design process.
The accuracy of computer-aided design programs and computer-aided engineering software significantly reduces the likelihood of manual errors. Automated processes mean that designs can be changed in less time and shared more easily between colleagues. Computer-aided engineering results in a better quality product that can be brought to market in less time and for less money.

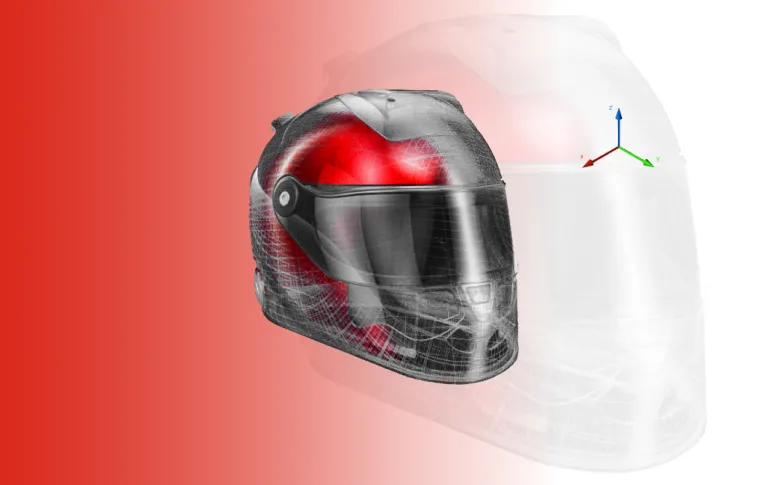
What are the phases of a computer-aided engineering task?
There are four major stages involved in the computer-aided engineering process: the pre-processing stage, the analysis stage, the post-processing stage, and the final decision-making stage.
- Pre-processing
- Analysis
- Post-processing
- Decision-making
Pre-processing
During this stage, the initial concept of the product is produced and defined. A 3D model is created using computer-aided design programs. Engineers will decide what environmental stresses and any other factors the model will be subjected to in the analysis phase.
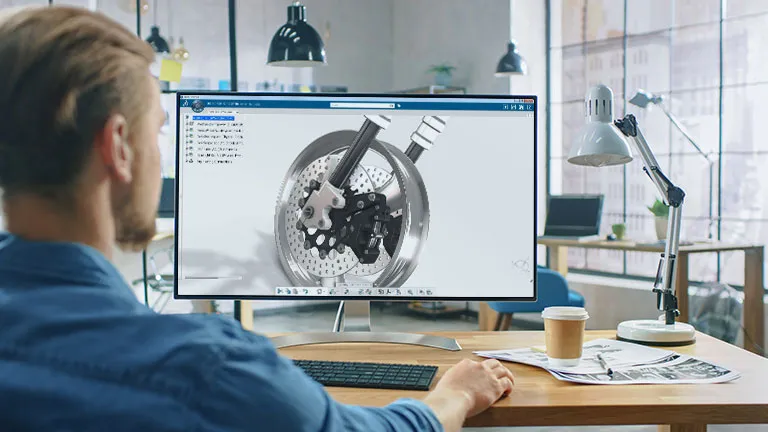
Analysis
Engineers will use powerful and highly sophisticated computer-aided design programs to test the 3D product model and analyze the results. This process is often completed using cloud-based CAE software that has high computational power.
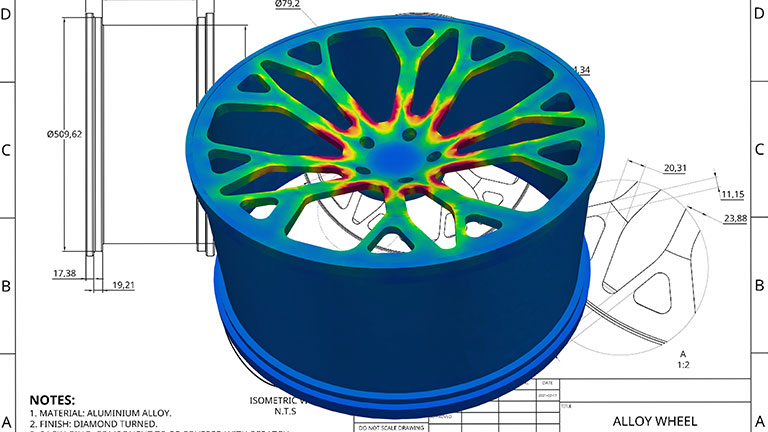
Post-processing
When the prototyping and analysis stage has been completed, engineers must then move into the post-processing phase. This involves visualizing how the product will look in its final form and analyzing the simulation testing results to determine the optimum manufacturing method.

Decision-making
At this point, stakeholders need to decide if there are any final changes to be done to the design, if a new analysis stage is required, or if they can proceed to the last step of the development process and release the product forward for manufacturing.

What are the areas covered by computer-aided engineering?
The main aim of the computer-aided engineering process is to clearly define and test the physical properties of a product. Engineers and designers seek to determine the most efficient, most robust, and most durable combination of materials, components, parts, and assemblies. To do so, they use a variety of disciplines.
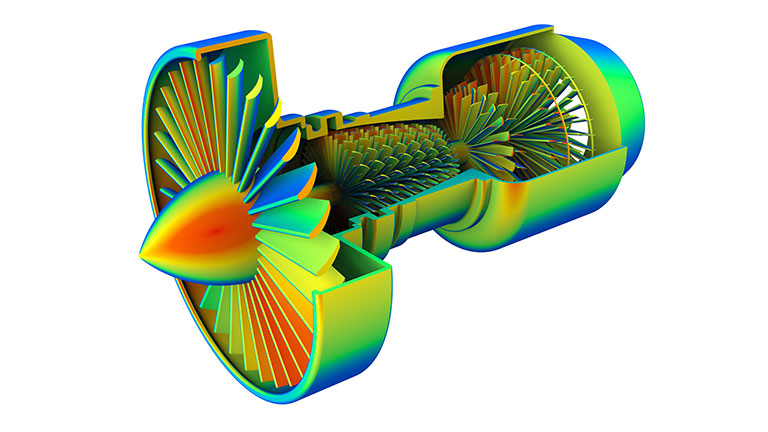
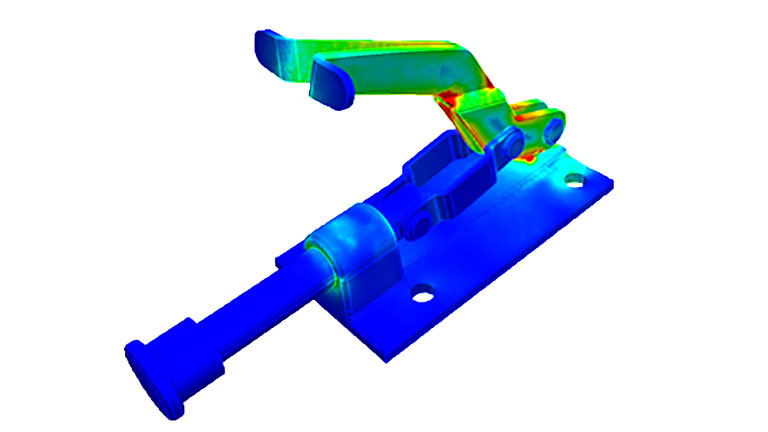
Finite element analysis - FEA
FEA is an analytical methodology used to determine how a product model will react to real-world stresses and environmental factors such as heat and vibration.
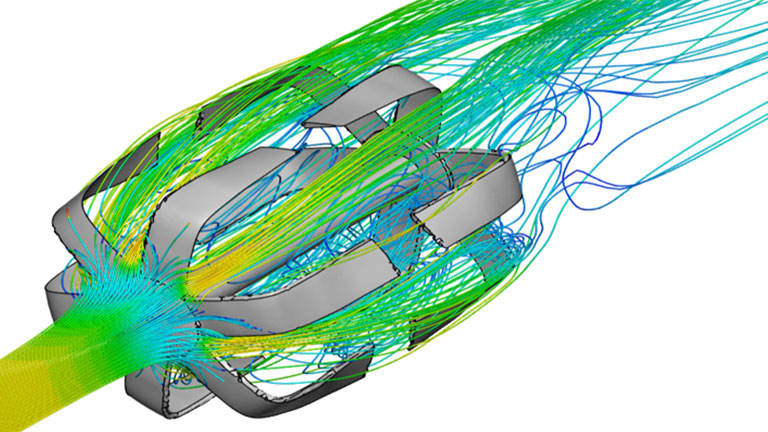
Computational fluid dynamics – CFD
Often used to determine the aerodynamics of aircraft or vehicles, computational fluid dynamics is the study of how liquid or gas flows around or through an object.
Multibody dynamics and kinematics - MBD
Multibody dynamics and kinematics is an analysis of how all the joins that connect the parts and components of a product work in conjunction with each other.
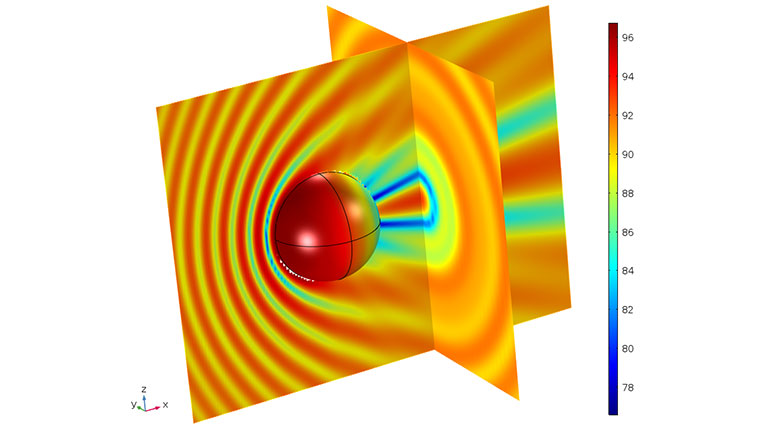
Boundary element method – BEM
The boundary element method is a numerical modeling technique used to solve engineering issues involving complex physical boundaries. It is often used to refine electrical equipment such as antennas.
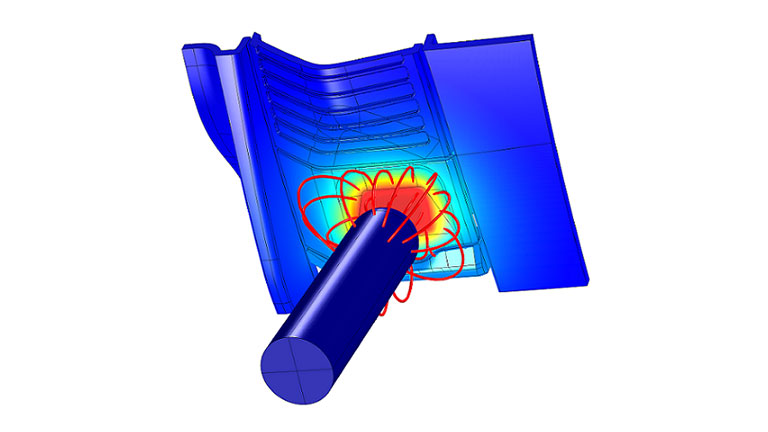
Mechatronic system simulation - 1D CAE
A mechatronic system simulation analyzes a product’s systems and their multidisciplinary performance. It is used to determine the optimum combination of hydraulic, mechanical, electrical, or pneumatic systems.
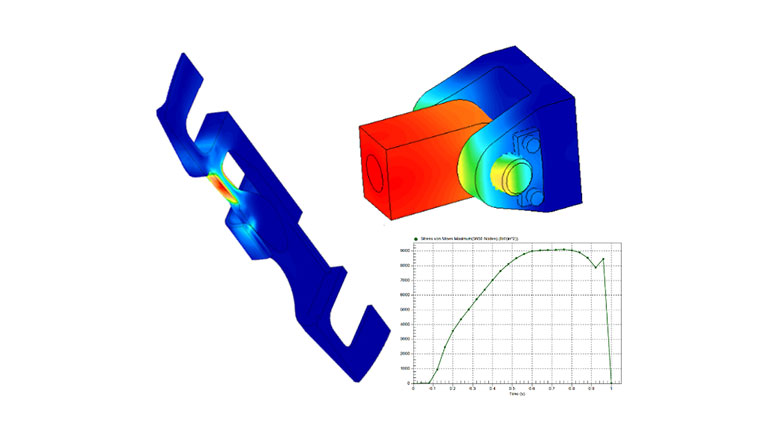
Mechanical event simulation – MES
Mechanical event simulation is a stress analysis method that combines rigid and flexible body dynamics with kinetic dynamics. It aims to determine how components react under stress.
Computer-aided manufacturing - CAM
Computer-aided manufacturing refers to tools and processes that are controlled by software to manufacture highly precise components and parts. CAD CAM engineering techniques can also be used to optimize manufacturing processes, storage requirements, and logistical elements.
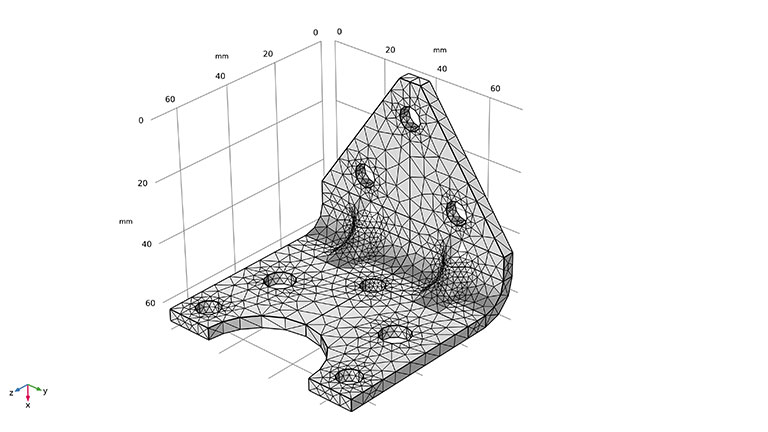
How does all this analysis help build better products?
Computer-aided engineering techniques analyze every stage of the product development lifecycle to determine the most efficient and cost-effective methods of production. The end result is a high-grade product that can be manufactured cheaply and brought to market quickly.
Browse all the Dassault Systèmes store applications
We feature in our store some of our best software to design, collaborate and innovate throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Content related to Computer-Aided Engineering
What are the benefits of CAE?
Computer-aided engineering reduces the amount of money, time, and resources that it takes to develop a product, test it, and manufacture it.
Using a 3D CAD-generated model allows engineers to perform tests and simulations of the product’s physical properties without needing to build a physical prototype. Design decisions can then be made based on the analysis results. Using computer-aided engineering drawing, the impact of changing a parameter is more visible. This helps engineers and decision-makers manage risks as they can immediately determine the implication of each decision.
Potential problems can be identified and solved early in the product development process. Engineers can quickly and cost-effectively redesign a product to meet the desired requirements.
Computer-aided engineering avoids the overuse of resources in the product development process. It provides vital information on exactly how materials, parts, and components work together and react to real-world environments.

What are the drawbacks of CAE?
While there are numerous advantages to using computer-aided engineering, there are also disadvantages. Computer-aided engineering software requires a huge amount of computing power, so on-premises systems can be expensive to install and operate.
Computer-aided engineering techniques also require engineers to know exactly what conditions the product will be exposed to (thermal, mechanical, and other such stresses) in order to reproduce them with the software. Because computer-aided engineering software can be complicated, staff may require intensive training in its use.
In which industries are used computer-aided engineering?
Computer-aided engineering is most commonly associated with the automotive industry where it is used for safety testing (crash testing), performance testing (engine and fuel efficiency), and aerodynamics. However, computer-aided engineering is also widely used in many other sectors.
The aerospace industry develops aircraft, spacecraft, and missile systems using computer-aided engineering. Civil engineers use computer-aided engineering to simulate the effects of earthquakes, wind, and temperature on buildings. Biomedical engineers develop implants and prosthetics and study viruses and biological systems using computer-aided engineering software. The manufacturing industry relies on computer-aided engineering software to reduce defects, improve processes, and lower costs.
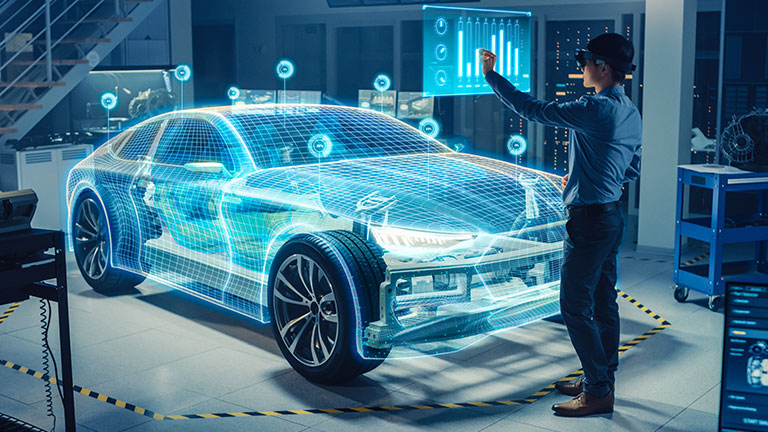

Future of computer-aided engineering

Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning CAD software will impact how computer-aided engineering will be used in the future. These technologies will result in the development of automated processes for faster manufacturing times.
Prototyping and testing will be enhanced by virtual reality and augmented reality. It is expected that there will be increased use of cloud-based solutions so smaller enterprises can access powerful engineering CAE solutions without the need for expensive infrastructure.
Computer-Aided Engineering - Conclusion & Perspectives
Computer-aided engineering uses highly accurate CAD simulations and CAD manufacturing to develop products that are cheaper to make, more durable, more efficient, and of a higher overall quality. It has replaced the costly and time-consuming previous methodology of creating and iterating designs and prototypes manually.
With technology progressing at a rapid pace, computer-aided engineering will certainly continue to be a crucial element in how engineers and designers develop the products of the future. As we move forward, computer-aided engineering will provide us with the solutions we need to overcome the challenges of the modern age.
Why choose Dassault Systèmes for your computer-aided engineering needs?
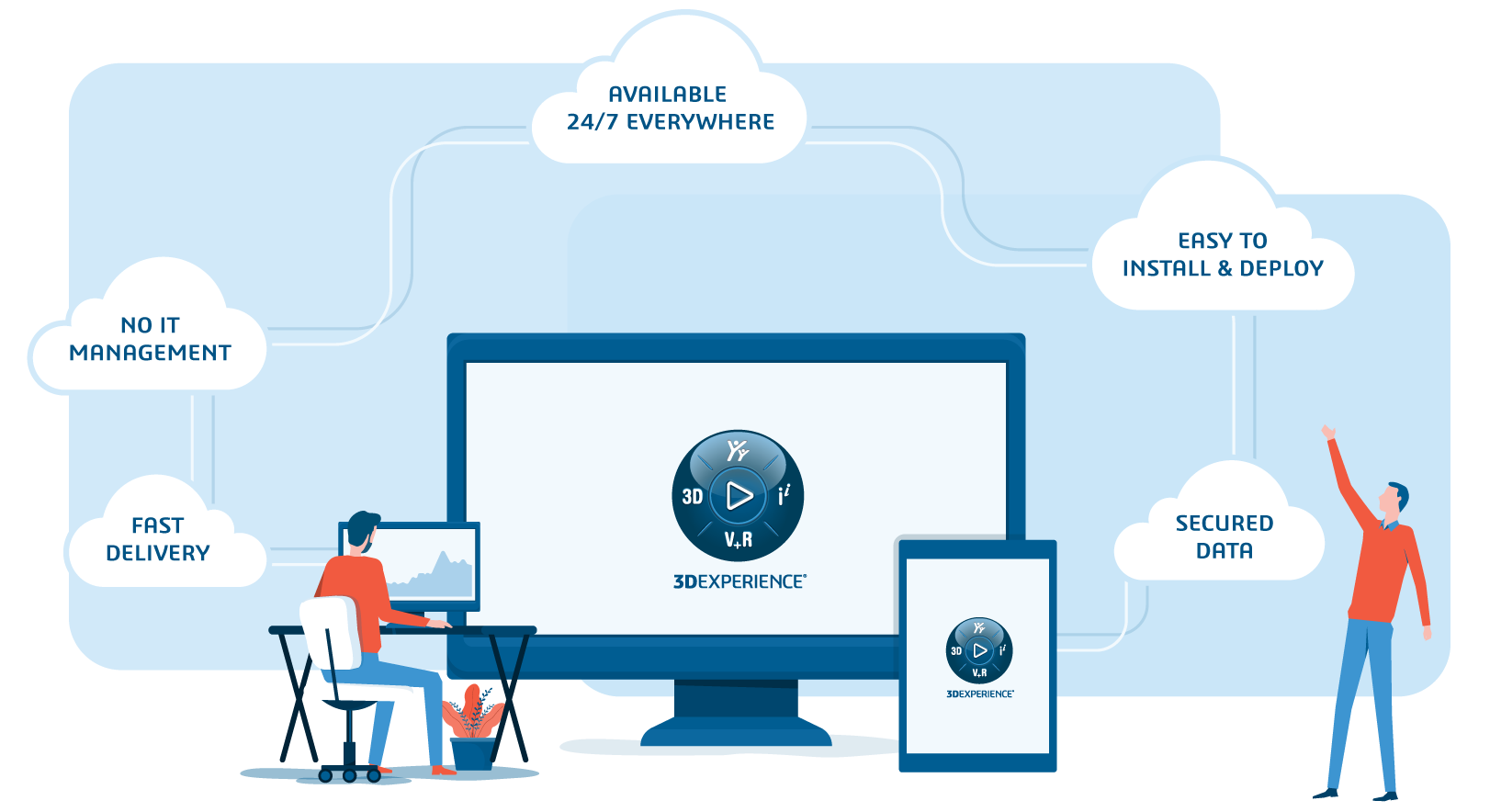
Access powerful CAE solutions with the 3DEXPERIENCE platform
Many enterprises find it difficult to access the CAD CAM design software they need because of how costly it is to set up the required IT infrastructure. Dassault Systèmes sought to provide a solution that freed companies from the restraints of traditional IT systems. To this end, we developed the innovative 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform is a cloud-based digital environment where designers and engineers can collaborate, communicate, and store their work securely. Harnessing the power of the cloud means that you can access a range of powerful computer-aided engineering software from any device.

Over 40 years of CAE and CAD experience
With a background stretching back more than four decades, we have long been known for the impact our revolutionary roles such as SOLIDWORKS and CATIA have had on the aerospace, automotive, construction, manufacturing, and engineering industries.
Our roles have been used by major companies and innovative designers and engineers across the globe to reduce development times, cut manufacturing costs, and produce more sustainable products.

