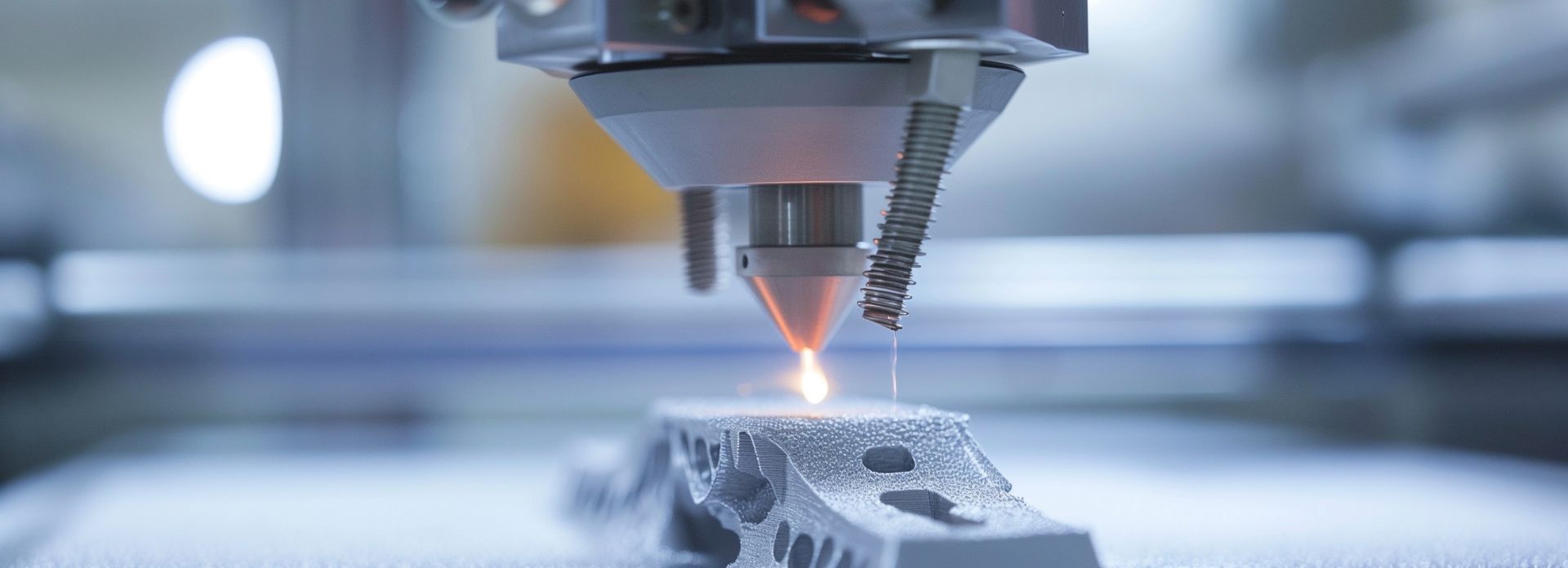
Additive Manufacturing
Enhance precision, efficiency, and scalability in 3D printing with DELMIA’s advanced additive manufacturing solutions for polymer and metal production.
Optimize Manufacturing Build Preparation
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing automates and optimizes additive processes for your manufacturing business. It is an advanced solution designed to automate and optimize additive manufacturing processes across industries. It enables manufacturers to efficiently prepare, simulate, and manage 3D printing workflows with precision.
Supporting both polymer and metal printing techniques, it helps businesses achieve greater control over additive manufacturing operations. With a user-friendly interface and powerful features, you can quickly define an accurate and detailed manufacturing build preparation with tools for 3D nesting, supports definition, part labeling and cost estimation. Scan paths based on the 3D geometry can be generated to apply appropriate strategies to control quality variables for both parts and supports for printers using one or several lasers. The build plate with parts and supports to be printed can be output in 3MF, AMF and STL standard formats. The laser path can also be output under specific printer format for Renishaw, Add-up printers as an example. This helps improve quality of the part, mitigate waste, and shorten the time required to print a quality part. DELMIA equips you with the necessary programming for most polymer and metal printing techniques.
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing & Sustainable Production
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing reduces material waste, optimizes energy use, and enables on-demand production for a more sustainable workflow. By integrating eco-friendly materials and digital simulation, it helps industries lower their carbon footprint while improving efficiency.
Key Features of DELMIA Additive Manufacturing Software
High-Precision Printing
Works directly with exact geometry, eliminating errors caused by tessellated formats for perfect accuracy and consistent part quality across every production cycle.
Assisted Build Preparation
Streamline 3D nesting, support structure definition, and part labeling with intelligent automation to reduces manual setup time and improve efficiency in the additive manufacturing workflow.
Advanced Laser Path Optimization
Generate optimized scan paths based on 3D geometry to ensure precise material deposition. Multi-laser printing strategies reduce manufacturing time.
Seamless File Compatibility
Export build plates and print-ready designs in 3MF, AMF, and STL formats, ensuring compatibility with various 3D printers.
Integrated Cost Estimation
Analyze material usage and production costs before printing to optimize budget and resource allocation leading to waste reduction while maintaining high-quality output.
Scalability for Polymer & Metal Printing
Supports multiple additive manufacturing techniques, from polymer to metal printing. This versatility allows manufacturers to scale production efficiently across various materials and industries.
Key Benefits of DELMIA Additive Manufacturing
Eliminate Errors
By working with exact geometry, DELMIA Additive Manufacturing prevents tessellation-related errors, ensuring flawless designs and superior final part quality.
Ensure Process Consistency
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing saves printing parameters with each part, guaranteeing repeatability, certification compliance, and consistent results across production batches.
Ensure Scalability
Standardized workflows and optimized laser path strategies reduce print time, minimize costs, and open the door to high-volume additive manufacturing.
Enhance Knowledge Sharing
Store and manage manufacturing rules on virtual machines, making process knowledge easily accessible across teams and suppliers for efficient collaboration.
Reduce Material Waste
With built-in cost estimation, manufacturers can optimize material usage, prevent unnecessary waste, and lower overall production costs without compromising quality.
Seamless Integration
This solution ensures a smooth transition from design to production by integrating seamlessly with CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) systems and 3D printing equipment, enhancing operational efficiency.
Supported Techniques in Industries
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
- Multi-jet Fusion (MJF)
- Binder Jetting (BJ)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
- Direct Melting Laser Sintering (DMLS)
- Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF)
- Stereo lithography (SLA)
- Digital Light Processing (DLP)
- Multi-jet Modeling (MJM)
- Fusion Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Laser Cladding (LC)
- Direct Energy Deposition (DED)
- Laser Metal Deposition (LMD)
- Laser Engineered Net Shape (LENS)
- Laser or Electron beam wire deposition (DED)
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing Software Solutions
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing software products are packaged as Roles to get you up to speed faster and work more efficiently with all needed applications available at your fingertips. Select a package that corresponds to your role in an organization.
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform allows us to put our requirements in early and to track those requirements to obtain up-to-date statistics based on live data. Managers know exactly where projects are at any point in time and can detect and correct issues before they become showstoppers.
Our Customers' Experience with Additive Design and Manufacturing
Discover how companies leverage the 3DEXPERIENCE platform to optimize workflows and drive success in additive manufacturing:
Start Your Journey
The world of manufacturing & operations is changing. Discover how to stay a step ahead with DELMIA.
DELMIA Additive Manufacturing in Action
FAQ about Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing machines—known as 3D printers—are made up of many small and intricate parts. For this reason, it’s imperative that regular, specialized maintenance and performance testing are undertaken to ensure accurate prints. Raw materials used in additive manufacturing often require delicate handling and are known to have a shorter shelf life compared to other manufacturing materials. While it is true that some 3D printing processes include the option to recycle excess build material, it’s important to keep in mind that repeated use of recycled material can compromise the properties of the material if it’s not replenished frequently enough with brand new material. One of the biggest advantages of 3D printing is that most additive manufacturing machines do not require monitoring once the print process has started. The reason for this is that the 3D printer is controlled by a pre-programmed, automated process. In fact, one of the only ways that the additive manufacturing process can be interrupted is if the 3D printer has an insufficient amount of material. For many additive methods, you can simply remove the printed component from the build platform. For other additive methods that are more industrial in nature, removing the print can involve a high degree of skill and precision as the print may still be attached to the build plate or encased in build material. For these additive methods, more complex removal procedures run by manual human operators are required, as well as a closely controlled environment and special safety precaution. After the printed part is removed from the build unit, a variety of post-processing methods can be employed. For example, SLA additive manufacturing cures printed parts under UV light and SLS metal parts may need to be heat-treated in an oven. Moreover, some additive manufacturing methods use supports, which will need to be carefully removed during post-processing. Additionally, many additive materials can be sanded, tumbled, or polished during post-processing.
Additive manufacturing is a process that builds parts and products by adding material rather than by taking away from it as in CNC machining. One of the most common forms of additive manufacturing is 3D printing. The additive manufacturing process utilizes computer-controlled machinery and CAD model. This machinery follows the programming of the CAD software to produce the intended part or product design by adding material.
Additive manufacturing is widely used in:
- Aerospace & Defense – Lightweight, high-strength components.
- Medical & Healthcare – Custom implants, prosthetics, and dental solutions.
- Automotive – Rapid prototyping and lightweight parts.
- Consumer Goods – Custom and on-demand production.
| Feature | Additive Manufacturing | Traditional Manufacturing | Feature |
| Material Usage | Minimal waste, precise material application | Higher material waste from cutting/shaping | Material Usage |
| Complexity | Allows intricate, lightweight designs | Limited by tooling constraints | Complexity |
| Production Speed | Faster for prototyping and small batches | More efficient for large-scale production | Production Speed |
| Cost | Lower for small-scale, custom parts | More cost-effective for mass production | Cost |
3D printing is a subset of additive manufacturing that builds parts layer by layer. Additive manufacturing, however, encompasses a wider range of techniques, including selective laser melting (SLM), electron beam melting (EBM), and direct energy deposition (DED), some of which don't rely on layering.
There are seven main types of additive manufacturing:
- Vat Photopolymerization – Uses UV light to cure liquid resin (e.g., SLA, DLP).
- Material Jetting – Deposits material like an inkjet printer, offering high accuracy.
- Binder Jetting – Binds powder materials with a liquid agent.
- Material Extrusion – Uses melted plastic filaments (e.g., FDM, FFF).
- Powder Bed Fusion – Uses a laser or electron beam to fuse powder (e.g., SLS, SLM, EBM).
- Sheet Lamination – Bonds layers of material together.
- Directed Energy Deposition (DED) – Melts metal powder or wire as it's deposited.
Also Discover
Learn What DELMIA Can Do for You
Speak with a DELMIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right DELMIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering