Design & Styling
A Unified Industrial Design Workflow Solution
Imagine, Create, Experience Sustainable & Delightful Design Experiences
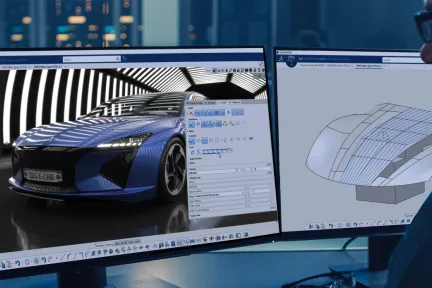
From product to transportation industries, the style & design of the product plays a major role in its success on the market. Develop shape & material creativity, reach a high level of surface sophistication & quality, and get the right decision tools with physical & virtual prototypes: these are the key elements of CATIA Design & Styling to boost design innovation.
CATIA Design & Styling provides all the solutions for design creativity, surface excellence and product experience, meaning that you can combine 3D sketching, subdivision surface, Class-A modeling to 3D printing, reverse engineering, realistic visualization and virtual and augmented product experience, to create and develop renderings in an integrated process, with a seamless workflow.
CATIA Design & Styling Key Benefits
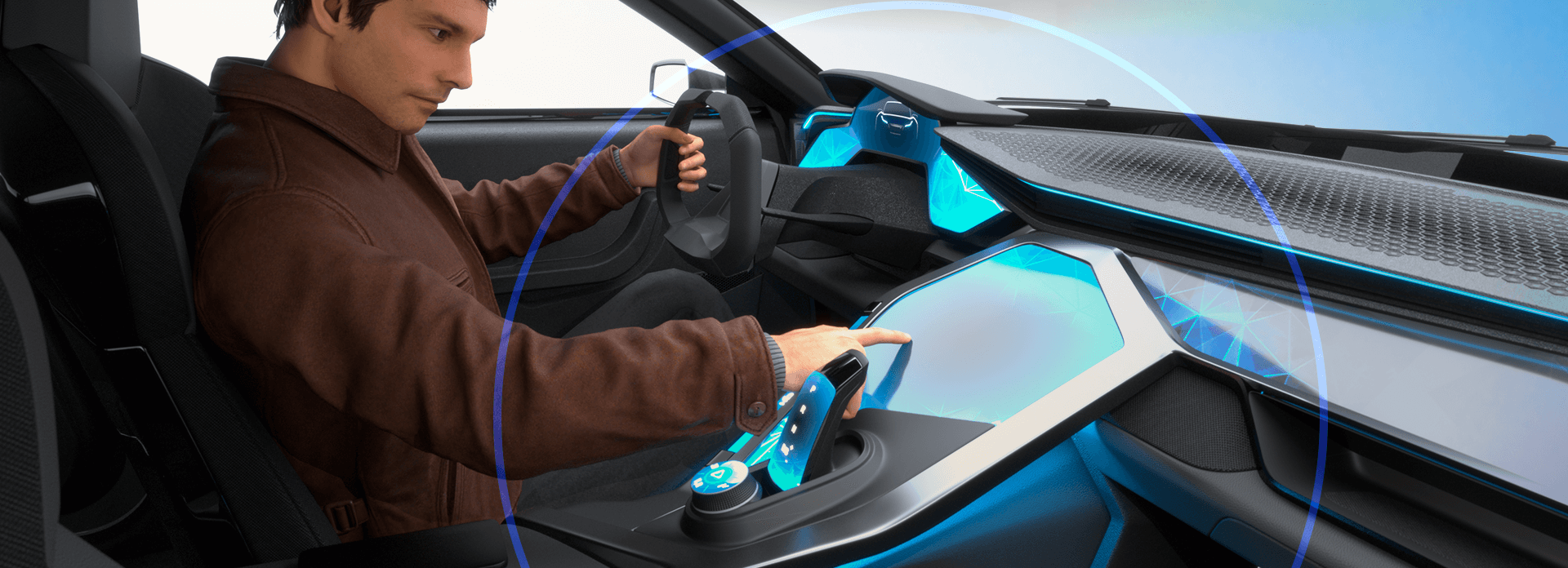
Boost Creativity & Experience Design Thinking
Create and explore innovative conceptual ideas with an integrated creative workflow, all in the context of the Human to enrich the Design experience.
Create Faster the Most Sophisticated Surfaces
Create the best surface Quality, Optimization and Performance to reach the high standards of Automotive Class-A Surfaces, Aero lofting or Naval Architect Hull form.
Make the Right Decision Quicker with the Virtual Twin
Take advantage of a high-end visualization with Immersive Virtual & Augmented Reality Experience, for an Accurate Decision Making during the product development process.
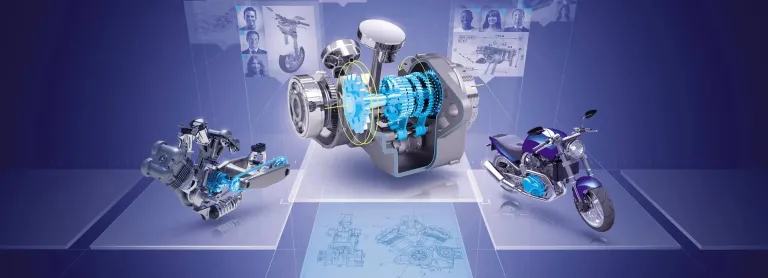
Boost Design Innovation
Imagine, Create & Experience the products of tomorrow with no limits, and take advantage of intuitive CATIA solutions, from creative design to surface modeling to product experience, to explore more ideas at every phase of the design process thanks to the 3DEXPERIENCE platform. Explore the following disciplines.
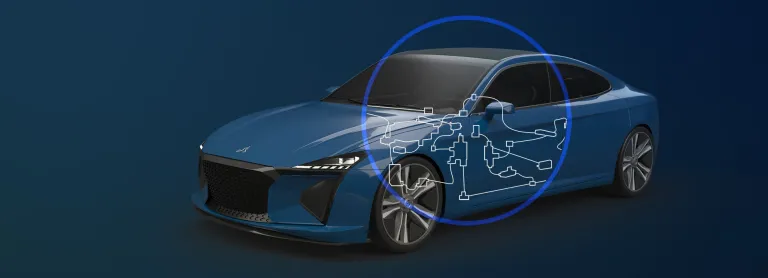
Creating Consumer-Centric Experiences
CATIA Creative Design and Styling portfolio empowers our users to perform design sketch integration, ultra-fast 3D ideation concept modeling with subdivision surfaces, high-end surfacing, high-end real-time visualization, photo-realistic rendering and rapid prototyping: all in context of the Human and with design thinking methodologies, to create consumer-centric experiences. These solutions, applicable to all industries and scenarios, allows to create and develop renderings, surfaces and prototypes seamlessly, thanks to a unified workflow, a collaborative platform and interconnected solutions.
CATIA Design & Styling Roles
CATIA Design & Styling software products are packaged as Roles on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform to get you up to speed faster and work more efficiently with all needed applications available at your fingertips. Select a package that corresponds to your role in an organization.
Join the conversation in the CATIA Creative Design & Styling User Community!
Start Your Journey
FAQ about Industrial Design Engineering & Process
Also Discover
Learn What CATIA Can Do for You
Speak with a CATIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right CATIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering