Surface Refinement
Going from Concept to Production Quality Class A Surfaces
What is Surface Refinement?
Surface Refinement is a discipline involved in all processes involving complex surfaces design or re-work. The title “Surface Refinement” is an industry expression encompassing all the processes required to reach a very high level of quality in surface design. The corresponding tasks for CAD users are mainly:
- Geometry quality & mathematic optimization
- Continuities between surfaces
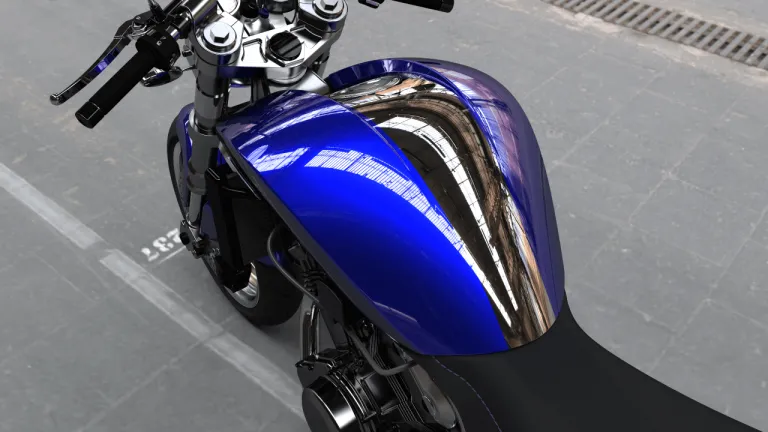
- Curvature & reflection highlight refining
- High-quality & realistic rendering review
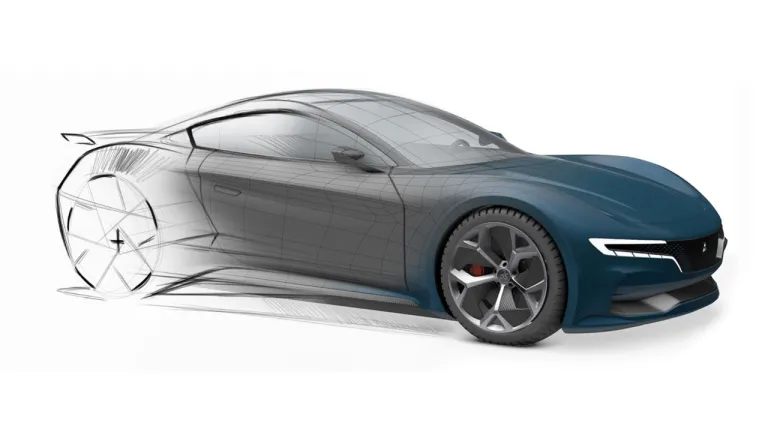
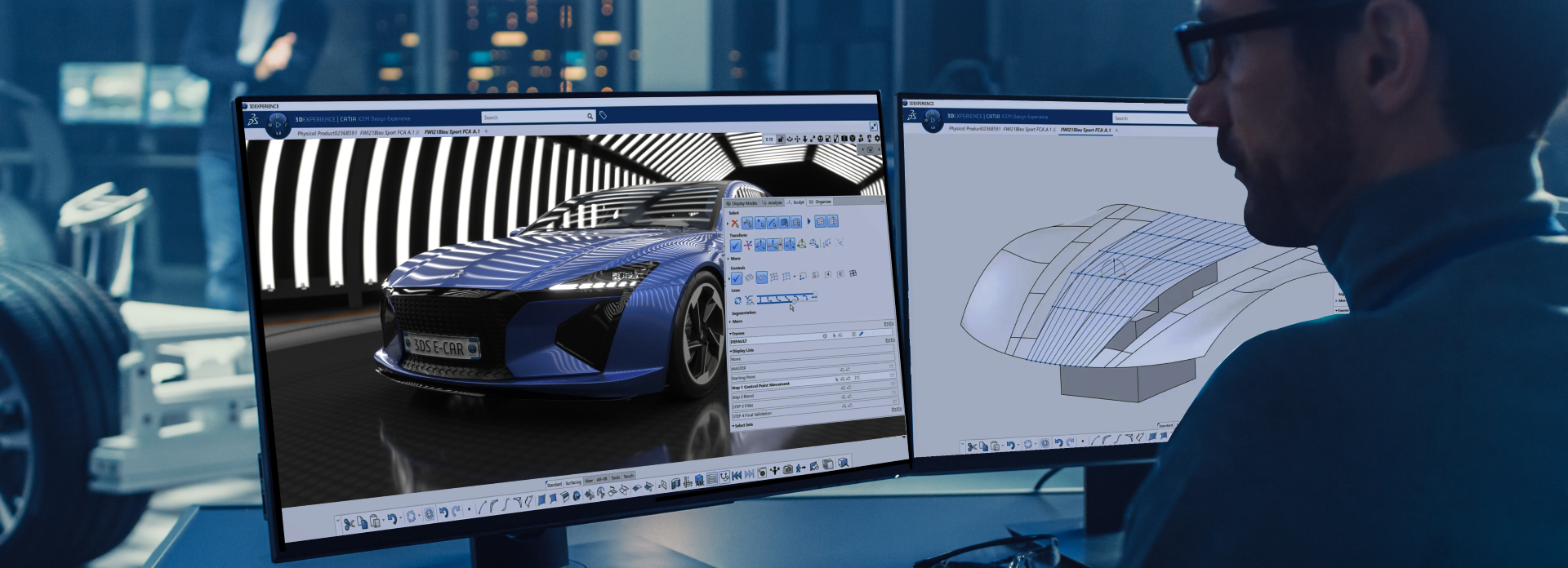
The Art of Explicit Surface Modeling
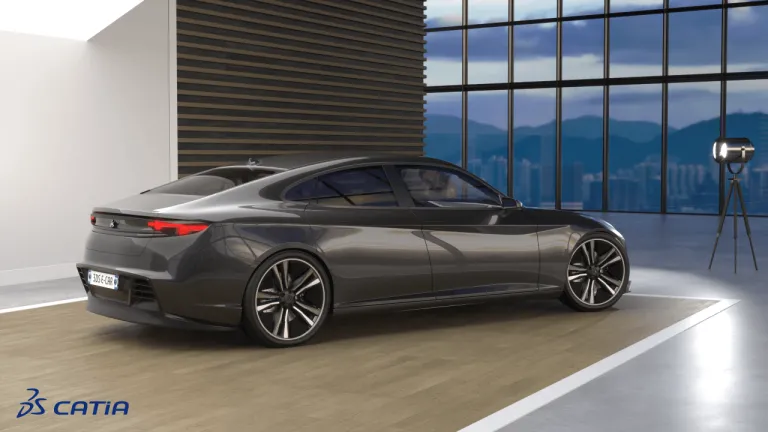
Thanks to the powerful and industry leading Curve and Surface modeling tools (ICEM Surf), designers have the full freedom to create high quality Class A surface geometry within intuitive and ergonomically optimized user interface supporting the need for rapid and efficient interactions during geometry creation and modifications.
The next generation of surface modeling for Styling & Class A ICEM Design Experience delivers an innovative, new, specialized modeling application on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform for CAS and Class A surfacing specialists. It delivers a comprehensive and completely integrated set of tools for industrial design, providing a high level of design freedom, an efficient and intuitive user interface, and precise, industry-leading surface results.
Improve Your Design Shapes and Production Surfaces
Why do we believe that our customers are facing an increasing need for high quality complex shapes? In all industries, product sophistication is a necessary trend to meet final customer expectations. To get a chance to stay competitive on the market, companies now have to take care of aspects that cannot be avoided anymore, among which:
- High technology
- Industrial design merging nature and technology
- Customization (market segmentation)
- Sustainability
Seek for Perceived Quality
CATIA Surface Refinement solutions, as the globally accepted industry standard, offers key benefits to reach aesthetical criteria within technical constraints:
- Innovative flexible sculpting tool
- Sophisticated industry-driven diagnostics
- Explicit and parametric solutions
- Highly accurate precision
- Scalable from entry-level to expert solutions
- Reach of the right level of surface quality on time
Optimizing Your Workflow with CATIA Surface Refinement on the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform
On the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, CATIA Surface Refinement software products are packaged as Roles to get you up to speed faster and work more efficiently with all needed applications available at your fingertips. Select a package that corresponds to your role in an organization.
"Make Design Changes on the Fly"
Start Your Journey
The world of product design is changing. Discover how to stay ahead with CATIA.
Join the conversation in the CATIA Creative Design & Styling User Community!
Surface Refinement FAQs
Also Discover
Learn What CATIA Can Do for You
Speak with a CATIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right CATIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering