Systems Validation
Continuously Integrate, Test & Validate Embedded Software & Systems to Manage End-to-End Traceability
Accelerate Verification, Validation and Certification Compliance
Integration, Test, Validation and Verification processes are facing key challenges arising from the complexity, scale, real-time, safety and security constrains of products and systems.
Thanks to Virtual Twin Experience, complex systems can be modeled and simulated taking into account their requirements and hardware and software disciplines - even starting at the very beginning of the product development cycle. Simulation Analysts and Test Engineers can continuously test and validate system's design, behavior, and performance are aligned with the customer's expectations and market regulations. End-to-End traceability enable to trace heterogeneous data in extended enterprise, from initial requirements to hardware/software deliveries and test results. It reduces iteration loops and eases compliance audit and systems certification.
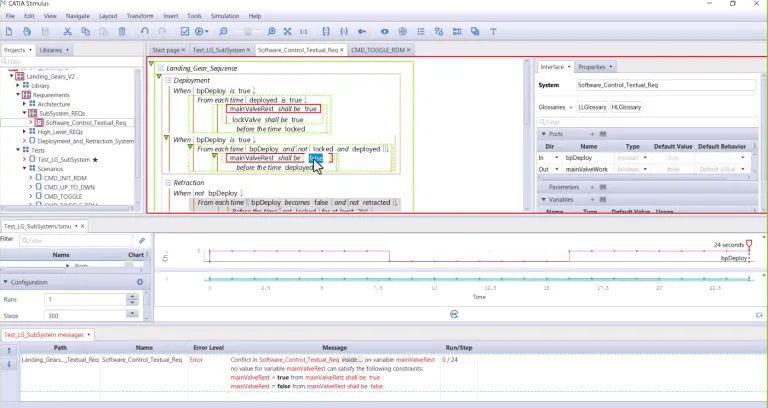
Adopt End-to-End Requirement in the Loop Validation
Defect and errors are sometimes introduced at specification phases and very difficult to detect for safety-critical embedded systems. CATIA STIMULUS deliver a paradigm shift in System Validation, where Requirement in the loop simulation can be performed at specification stage and re-use during integration test and validation. At specification phase, system architects can detect ambiguous, incorrect, missing, or conflicting requirements before the design begins. At validation phase, Test Engineers can automate test generation and check embedded software code complies with its specifications.
Perform Massive Simulation for Highly Automated Systems
Highly automated systems, such as Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) or Automated Driving (AD), face a unique challenge: testing in unpredictable environments. Massive Virtual Simulation with CATIA SCANeR empowers the execution of model, software, and human-in-the-loop simulations within realistic environmental conditions. This approach allows the identification and virtual simulation of edge cases and critical scenarios, ensuring to reach a confident level of quality and safety before these groundbreaking innovations are introduced to the market.
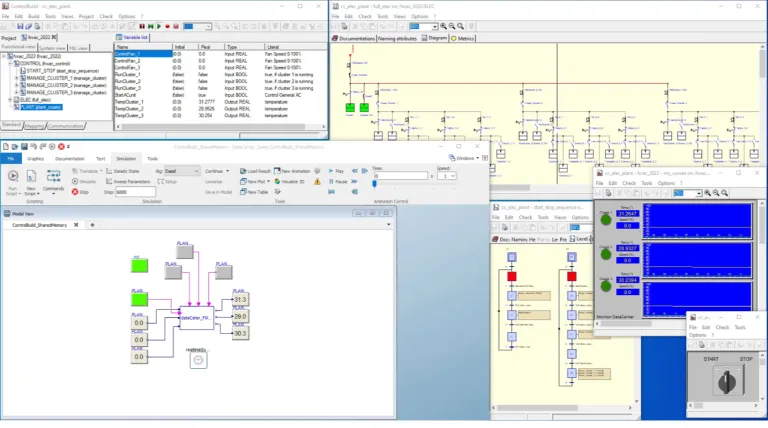
Validate Control & Monitoring Automation Systems
The Control & Monitoring system represents more than 30% of the total cost of the delivered system in Trains and Railways, Automotive, Energy and many other industries (Life Sciences, Water Treatment, Industrial Equipment, Food & Beverage, etc.). These new systems will offer a number of functionalities and high-quality services while meeting increasingly stringent certification constraints. ControlBuild is used to model, simulate, test, validate, and deploy control applications, in compliance with industry IEC-61508 and EN-50128 safety development standards.
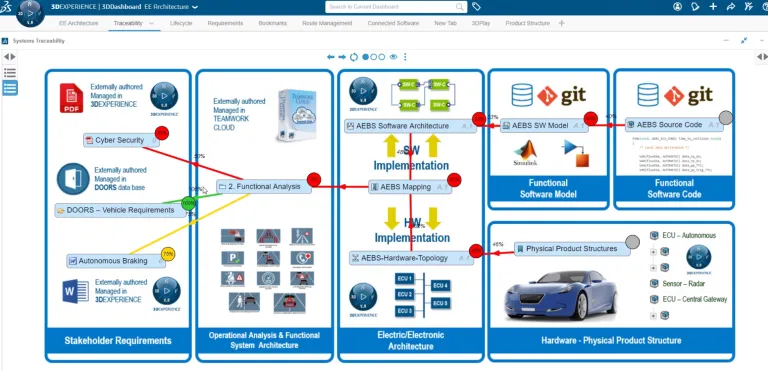
Manage Requirements Coverage and Modification Impact to Ease Certification
Traceability and Report Generation solutions facilitate collaboration among interdisciplinary teams from requirement to hardware/software to test deliveries review. Impacts of changes from systems architecture, model-based design, implementation or validation can be identified, resulting in risk mitigation. Traceability from heterogeneous tools, models and data source support Project leader, Quality & Certification Engineer to demonstrate effective integration of regulatory and safety requirements throughout the entire development process and to automatically generate reports for certification basis.
Execute and Monitor Validation & Verification Activities
To avoid costly recall, secure every aspect of the product is rigorously tested by defining test specifications and by reusing proven test methods templates. Assess how test strategies match the requirements, functional, logical, or physical aspects of the system under test. Schedule and manage test executions a monitor the overall execution progress and maturity. Link and trace tests results evidence to easily support compliance to regulations and standards.
CATIA Systems Validation Roles
CATIA Systems Validation software products are packaged as Roles on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform to get you up to speed faster and work more efficiently with all needed applications available at your fingertips. Select a package that corresponds to your role in an organization.
Discover CATIA Systems Validation Products
The End-to-End MBSE and Test Automation Solution
End-to-End Traceability
Multi-Engineering Modeling and Simulation based on Modelica and FMI
Revolutionizing Autonomous Vehicle Testing and Simulation
Join the conversation in the CATIA MBSE Cyber System User Community!
FAQ about Computer System Validation [CSV] Software
Also Discover
Learn What CATIA Can Do for You
Speak with a CATIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right CATIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering