CATIA SCANeR
Revolutionizing Autonomous Vehicle Testing and Simulation
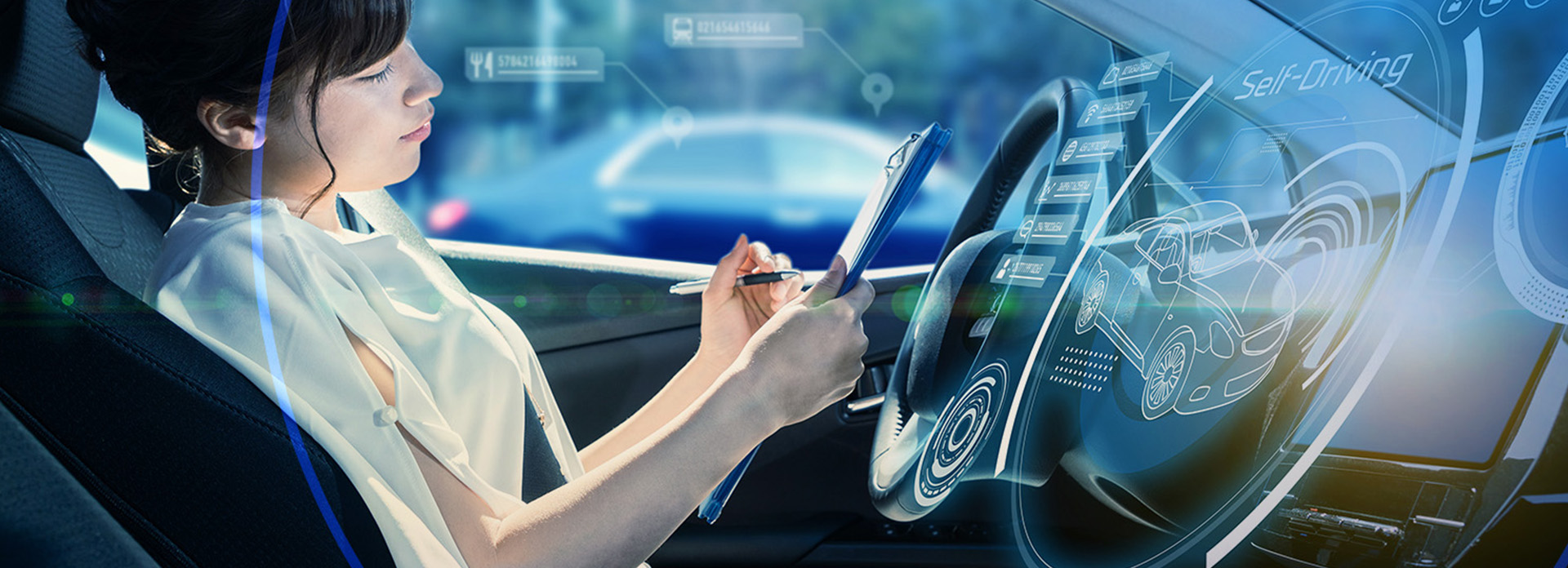
Advancing Autonomous Driving Evaluation with Realistic 3D Simulations
Thanks to the support of industry standards and the openness of the CATIA SCANeR API, test engineers and function engineers can design scenes & scenarios correlated with reality by importing high definition maps, roads define with OpenDrive standard, importing the embedded systems thanks to FMI, co-simulate with various vehicle dynamic models, co-simulate with ROS.
The uniqueness of the solution is its versatility in its operability, the user can test both, functional and performance use cases in Model In the Loop (MIL), Software In the Loop (SIL), Processor in the Loop ( PIL),Hardware In the Loop (HIL), Driver In the Loop (DIL) and Vehicle In the Loop (VIL) with massive simulation capabilities and helpers to better cover the design of space.
Autonomous and connected vehicles simulation
CATIA SCANeR allows engineers creating real-world test scenarios using road network and vehicles, defining the actors’ actions, events and validating a system with high quality 3D animations. CATIA SCANeR is designed to validate, Advanced Driving Assistant System (ADAS), taking into account: Human Factors studies, Model In the Loop (MIL), Software In the Loop (SIL), Hardware In the Loop (HIL) and Driver In the Loop (DIL).
The CATIA SCANeR portfolio includes several roles for multiple engineers: CATIA SCANeR Designer offers capabilities to model scene, scenario, vehicles, software and control features as well as sensors and simulate vehicles in a high fidelity virtual world. CATIA SCANeR Designer is a prerequisite for other specialized roles (e.g. for AD/ADAS engineers, headlights analysts, human factor analysts, vehicle dynamics engineers, driver test benches designer,...)
New generation of car development at Renault Group
CATIA SCANeR and the 3DEXPERIENCE platform are the foundation of the compliance of the Renault Group vehicle digital twin. It is used in an agile process for verification and validation with digital and immersive platforms at any phase of the project. The workflows based on SCANeR enforce a digital thread using and reusing scenarios as well as running the different type of vehicle models. In a continuous and robust integrated design process, CATIA SCANeR is used to validate the compliance of the digital vehicle synthesis with massive simulation, performing virtually millions of km at each phase of the process.
Join the conversation in the CATIA MBSE Cyber System User Community!
CATIA SCANeR FAQs
Also Discover
Learn What CATIA Can Do for You
Speak with a CATIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right CATIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering