Translational medicine, targeted therapies, omics sciences and devices
Through a collaborative network approach, translational medicine and targeted therapies can both be used to accelerate research and develop treatments.
Dr. David Fajgenbaum has changed the way Castleman disease is understood and treated. He had been diagnosed with a form of the orphan disease itself (idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease), and is now in remission because of a precision treatment he identified. He set up and runs a foundation called the Castleman Disease Collaborative Network, which aims to accelerate research and development of treatments for this illness through a collaborative network approach, using both translational medicine and targeted therapies. This has become a model for other rare diseases.
The approach integrates patient perspectives to guide high-impact research and identify treatments that can be repurposed for Castleman disease. Omics sciences – such as genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics and metabolomics – have made it possible to develop new technologies, such as biosensors, diagnostic tools and treatments. As Dr Fajgenbaum says, “integrating clinical data using the MEDIDATA Omics platform has genuinely transformed our analysis and interpretation of proteomics data.” The approach has saved his life, and the lives of thousands of other patients.

In October 2020, MEDIDATA completed the acquisition of MC10, a company that specializes in developing biomarkers that show a patient’s condition or response to a treatment. MC10’s solutions are already being used in numerous clinical trials, and add new analysis capabilities to MEDIDATA’s Patient Cloud solutions, for example in order to enrich data provided by patients (ePRO) and to assess clinical trial results (eCOA).
This will provide the healthcare industry with even more ways of managing clinical trials virtually. When data taken from the real world can then interact with the real world, for example through medical devices, they become much more powerful.
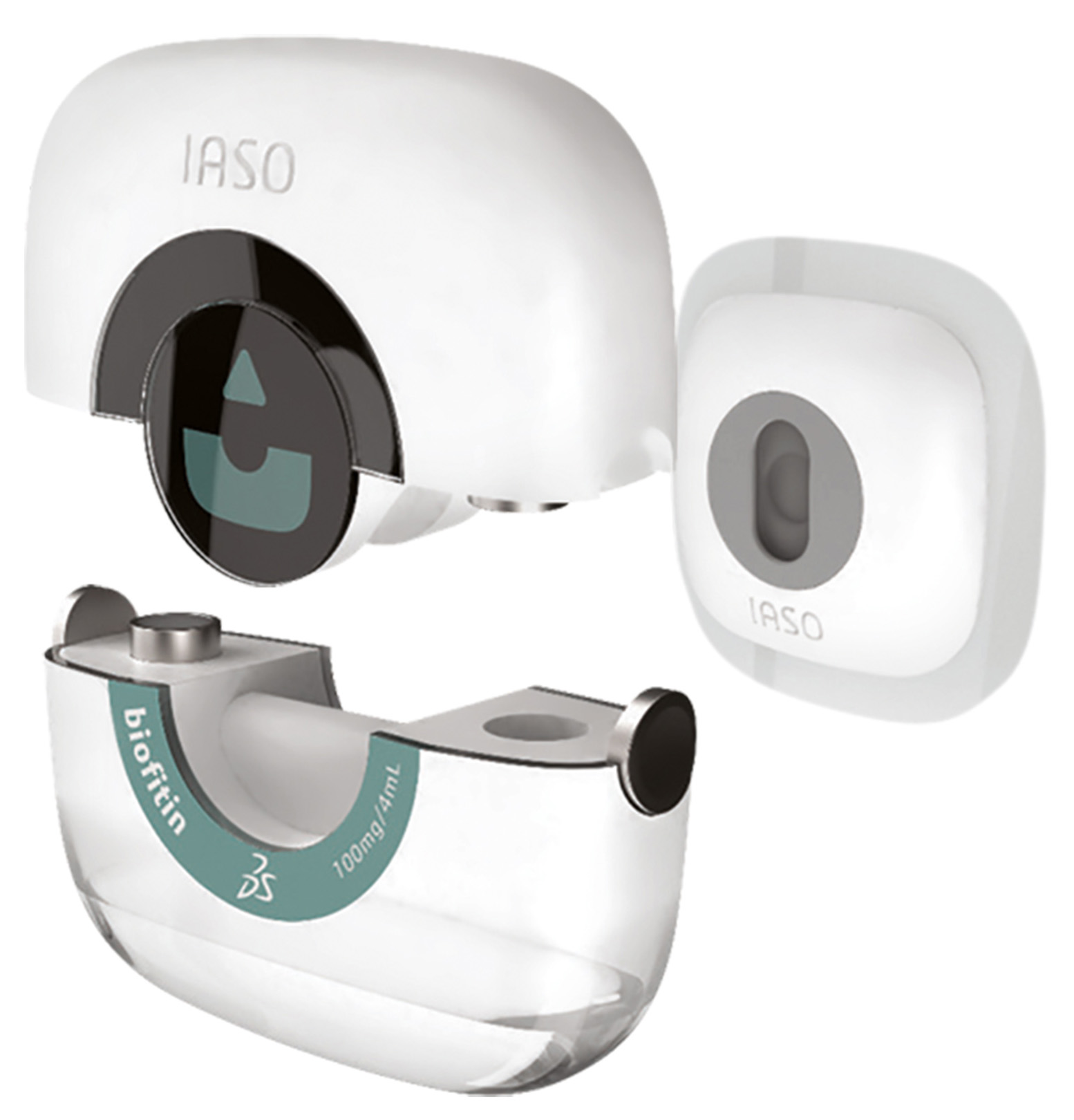
As part of the research on devices, IASO, which takes its name from the Greek goddess of recuperation from illness, is a showcase that illustrates the lifecycle of a biological product combined with an auto-injector platform, intended for the oncology market. It shows the value that the 3DEXPERIENCE platform can add for those seeking to innovate in the field of medicine or life sciences combined with medical devices.
Accelerating innovation with in silico experimentation
IASO illustrates how 3D design, collaborative engineering and digital simulation advance the development of drug candidates and medical devices. At the manufacturing stage, IASO shows how companies can develop the plant of the future by coming up with new planning and execution solutions.
Finally, IASO shows how the 3DEXPERIENCE platform promotes operational excellence, by optimizing regulatory activities and the quality management system and by providing a holistic and unified view of the patient experience.
Using physical experiments alone is not economically viable, particularly in a rapidly evolving situation like COVID-19. Scientists need a better understanding of how antiviral therapies and vaccines work. To help scientists identify molecules with new properties, BIOVIA has developed BIOVIA Discovery Studio, a modeling and simulation environment that provides a full set of tools, including biological product design and analysis methods, traditional simulations, structure- and fragment-based drug design and virtual screening.
The solution also allows users to simulate a drug’s pharmacokinetic properties (absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion or ADME) and predict its toxicity.
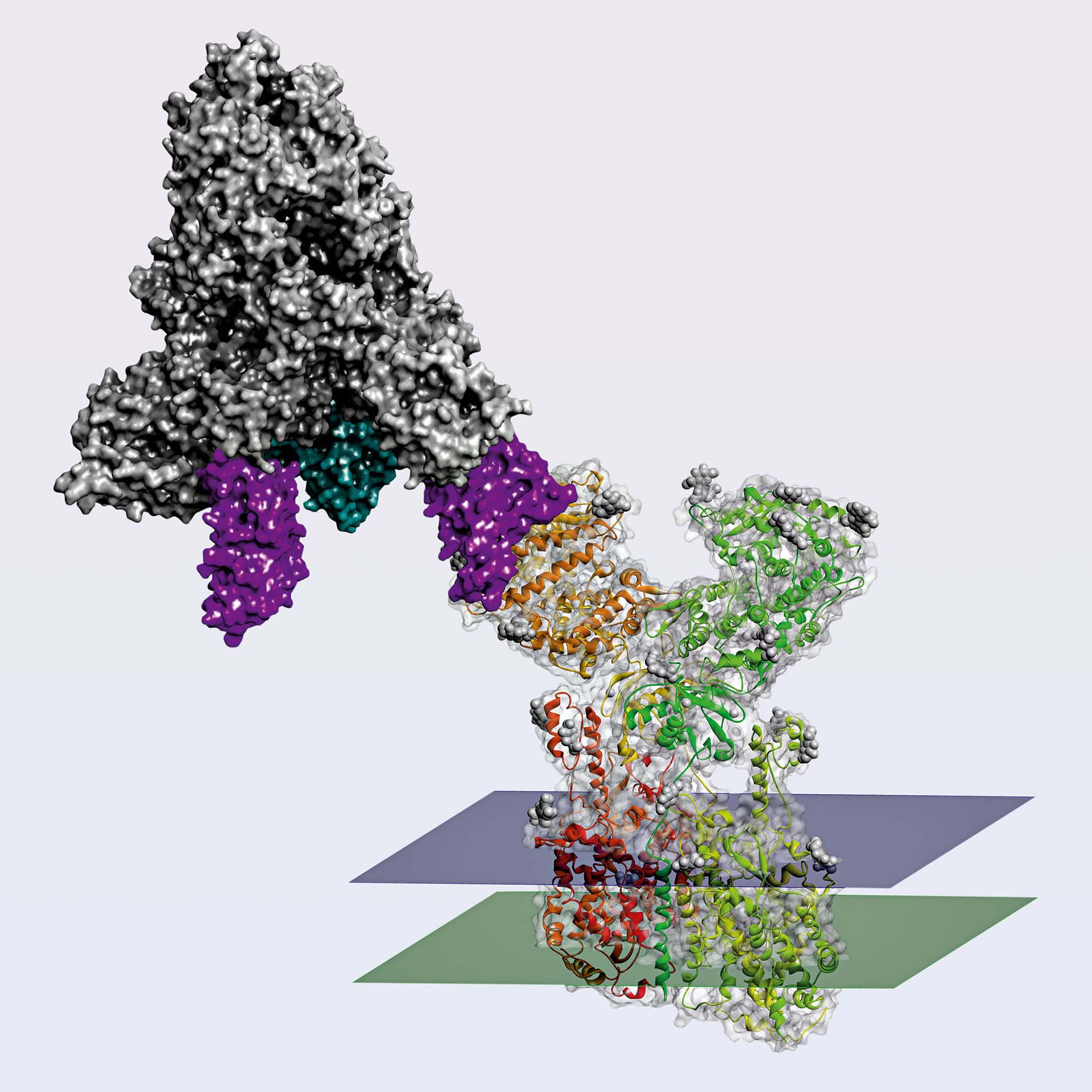
This model was built with BIOVIA Discovery Studio using PDB structure 6M17 (Human ACE2 receptor in complex with RDB domain from Sars-CoV-2 Spike protein) and 7DK4 (Sars-CoV-2 Spike protein in prefusion stabilized conformation with two RBD domain up) and superimposing both structures on the common RDB domain.