Everything you need to know about weld design
Welding is a crucial process for product design, construction, and manufacturing. The Dassault Systèmes Weld Design application allows designers to precisely model welds for assemblies.
What is weld design?
As a concept, weld joint design relates to creating a sound plan for welders to follow during manufacturing. Weld design describes the methods and materials allocated to a welder to join pieces of metal.
Accurate weld design provides a welder with a precise guide to what type of weld they need to create. The weld design will provide details on the materials to be used, how they are to be welded together, and how they relate to other parts of an assembly.
Weld joint design focuses on the geometry, dimensions, and properties of objects that are to be welded. The tolerances of the joins and the materials used are of particular importance to the weld designer.
To create reliable designs for welded assemblies, engineers and designers use advanced computer aided design (CAD) software. CAD programs can produce highly detailed 3D renderings that accurately represent where and how components are to be welded.
Discover all Dassault Système's store solutions for weld design
CATIA from Dassault Systèmes has been used by engineers and designers in specialized fields such as the automotive and aeronautical industries for decades. CATIA weld design software is flexible, reliable, and powerful enough to deal with assemblies of any size.

CATIA Mechanical Designer
Advanced mechanical design solution used for aeronautical and industrial applications. This innovative software creates highly accurate and consistent 3D geometry suitable for large assemblies.
CATIA Sheet Metal Designer
Entry-level mechanical design package suitable for industrial applications. Allows for complex sheet metal parts to be designed in 2D and 3D to ensure easy fabrication.
Why is weld design important in manufacturing and construction?
Welding is an essential process in manufacturing and construction. Virtually all metal objects require welding. Welding is done by fusing molten metal together or by applying a filler-metal (consumables) to a joint. The result is that the welded material is stronger and more resilient than before.
Without a professionally produced weld design, the joints of a structure may not be strong enough and may fail. A poor weld design will result in suboptimum welds regardless of the skill of the welder or the quality of the materials and welding equipment used.

Common welding processes
Welders use oxyacetylene welding machines for the fabrication of metal parts, structures, and machinery. Welding can be highly hazardous. Safely creating a weld that is robust requires considerable skill on the part of the welder as well as the weld designer.
Common welding processes include:
- Stick welding
- Resistance-welding
- Submerged arc welding
- MIG-welding
- Gas metal arc welding
- Gas tungsten arc-welding
The key principles of weld design
Why is CAD design software so important for quality weld design?
Advanced 2D and 3D computer aided design (CAD) software is used by mechanical designers and mechanical design engineers at all skill levels and across all industry sectors. The complex designs required for welded assemblies could not be created using manual drawings.
Using 3D rendered models, designers can produce realistic visualizations of products, machines, and structures. 3D models can be used to accurately simulate welding operations, identify potential problems, and optimize welding paths and sequences.
2D and 3D CAD software enables highly precise, complex assembly designs to be created quickly. Many of the top CAD tools are equipped with automated artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning functions that can greatly speed up the design process.

Browse all the Dassault Systèmes store applications
We feature in our store some of our best software to design, collaborate and innovate throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Content related to weld design
Where and how is weld design used?
A knowledge of welding and weld design is integral for many different professions and areas of study. Weld design professionals work in such diverse sectors as the mining industry, the construction industry, information technology, aviation, the automotive industry, and many others.

Metallurgy
Welding is a specialized subject in the discipline of metallurgy. Students study the mechanical, chemical, and physical properties of metals and the behavior of metals under different temperature gradients.
Manufacturing
Welding is crucial for the manufacturing industry. Turning raw materials like sheet metal into usable products, components, and machinery would not be possible without good weld design.


Architecture
Architecture requires welded metal for the framework of buildings and infrastructure. The architectural industry also requires welding for non-structural components such as stairs, handrails, furniture, doors, and so on.
Technology
Weld design drives the modern world forward. Computer housings, medical equipment, scientific instruments, and other types of advanced machinery all require sophisticated weld design. Circuit boards used in computers and technology are made using precise welds.
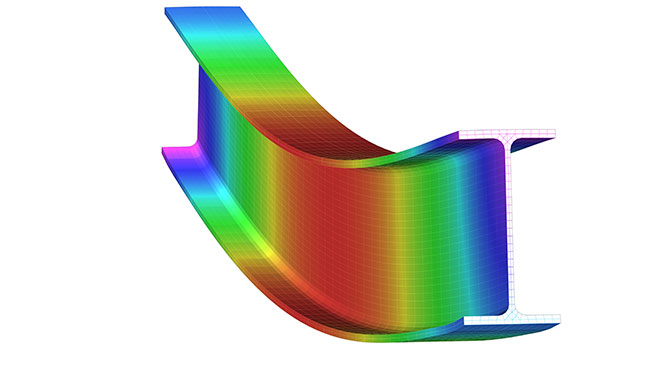
How FEA can predict the behavior of welded structure
Mechanical design engineers use 2D or 3D CAD software to conduct a finite element analysis (FEA) to determine how a weld design will react when subjected to real world environments. FEA simulates the physical effects of loads and stresses on 3D CAD rendered models using sophisticated calculations and physics.
Weld design : conclusion and perspectives
Weld design is of vital importance for a vast array of industries. Good weld design ensures the structural reliability of many of the products we use, the buildings we live and work in, and the vehicles we drive. Anyone who is considering a career in architecture, manufacturing, industrial design, or mechanical design needs to have a full understanding of the principles of weld design.
Good weld design is reliant on the skills of the mechanical design engineer or mechanical designer and on the power of the programs they use. Weld design experts turn to respected developers such as Dassault Systèmes for effective CAD solutions.
The range of CATIA mechanical design programs combined with the 3DEXPERIENCE platform gives professionals the tools they need to effectively create, collaborate, and innovate.
Why choose Dassault Systèmes for your weld design needs?

Over 40 years of delivering specialized design solutions
With more than 40 years of experience providing exemplary CAD solutions, Dassault Systèmes provides designers with the specialized tools they need to create complex assemblies. Weld design professionals in a variety of industries rely on our powerful, intuitive, and innovative software.
All the tools a designer needs to create a complicated weld design can be found in CATIA. The software gives users the choice of 15 welding bead shapes and preparations that are compliant with ISO standards. Parts and edges are automatically chamfered, and all weld features are fully integrated into the final 3D design.
Unmatched versatility with the 3DEXPERIENCE platform
The CATIA suite works in conjunction with the powerful 3DEXPERIENCE platform. This innovative cloud based solution allows mechanical designers and engineers the ability to easily collaborate and communicate and safely store their files in the cloud using any device.
Users can work with complete confidence knowing that all their files are stored securely on the cloud. Automatic updating ensures your team will always view the latest version of a project. Access to files can be restricted so only authorized persons can view entire projects. You can share designs and work together with colleagues at any time, regardless of where you or your team are located.
Frequently asked questions
The three most important basic principles in weld design are strength, resistance to fatigue, and distortion.
Advanced CAD programs such as CATIA Sheet Metal Designer and CATIA Mechanical Designer are ideal for highly complex weld designs.
The most common types of welds found in weld design are full fillet welds, staggered intermittent fillet welds, and chain intermittent fillet welds.
Designers use CAD software for finite element analysis (FEA) of weld designs. FEA simulates real world loads and stresses on 3D rendered models.
Welds must be able to withstand loads and stresses over time. The three most important principles in weld design are strength, resistance to fatigue, and distortion.
There are five basic designs or joints that are most commonly used. These designs are selected based on specific factors such as the strength required, type of connected parts, and geometric configuration of the parts to be welded.
Butt Joint, Tee Joint, Lap Joint, Corner Joint, Edge Joint, each of these joints has a specific purpose and is designed to optimize the strength and durability of the weld design.


