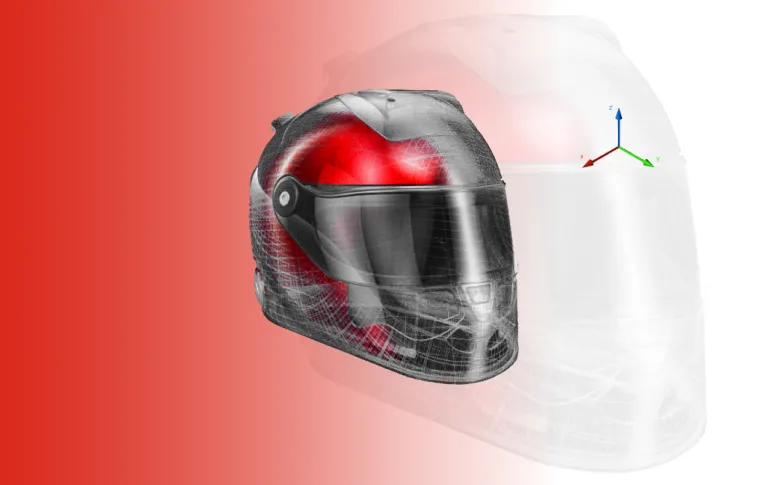
A simple guide to the basics of subdivision surfaces modeling
Subdivision modeling is a technique that designers use to create highly detailed, scalable models from simple mesh models. Using this technique, designers can produce organic-looking, realistic 3D models in less time and with more detail than other modeling methods. We take a closer look at just why subdivision surface modeling is so important.
What is sub division surfaces modeling?
Designers are often required to create shapes that mimic organic objects with flowing lines. Creating these shapes requires a different approach than using predetermined parametric models. While parametric models have their place, their rigid designs are unsuitable for depicting an object such as the hull of a boat, the fender of a car, or an ergonomic chair. To create a detailed, lifelike representation of these types of objects, many designers choose to use subdivision modeling.
Explore sub division surfaces modeling solutions at the Dassault Systèmes store
Create detailed 3D models with 3D Sculptor, innovative 3D modeling software accessible via the SOLIDWORKS Cloud Offer.
3D Sculptor allows you to design complex free-form shapes without the need for on-premises IT infrastructure.

SOLIDWORKS xDesign
Get ready for the next generation of design solution, developed by the same team that brought you SOLIDWORKS 3D CAD
How does subdivision modeling work?
While subdivision surface modeling is a complex process, it is beneficial to understand the basic principles of subdivision modeling. The basic concept behind subdividing surfaces is the act of dividing areas into smaller, more detailed regions.
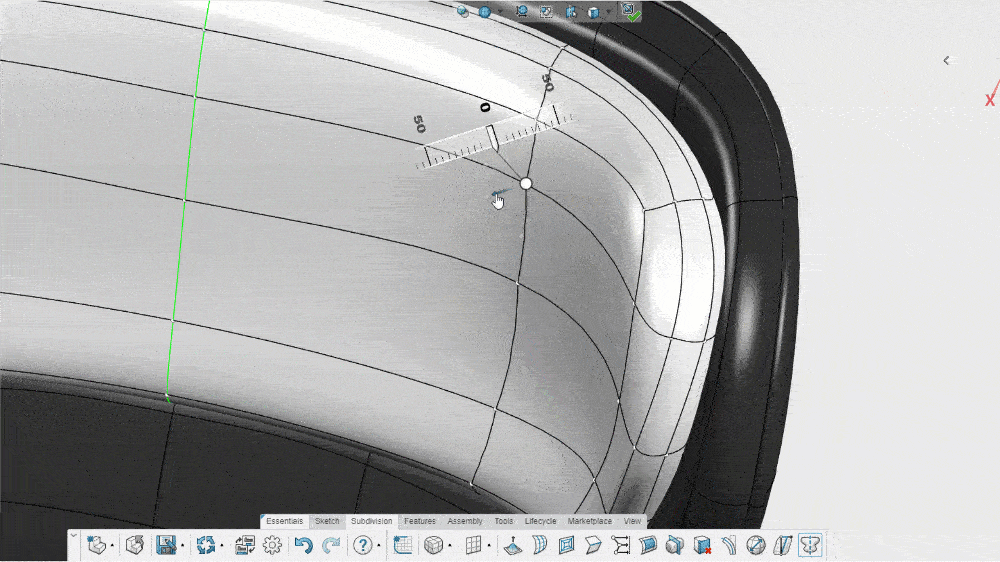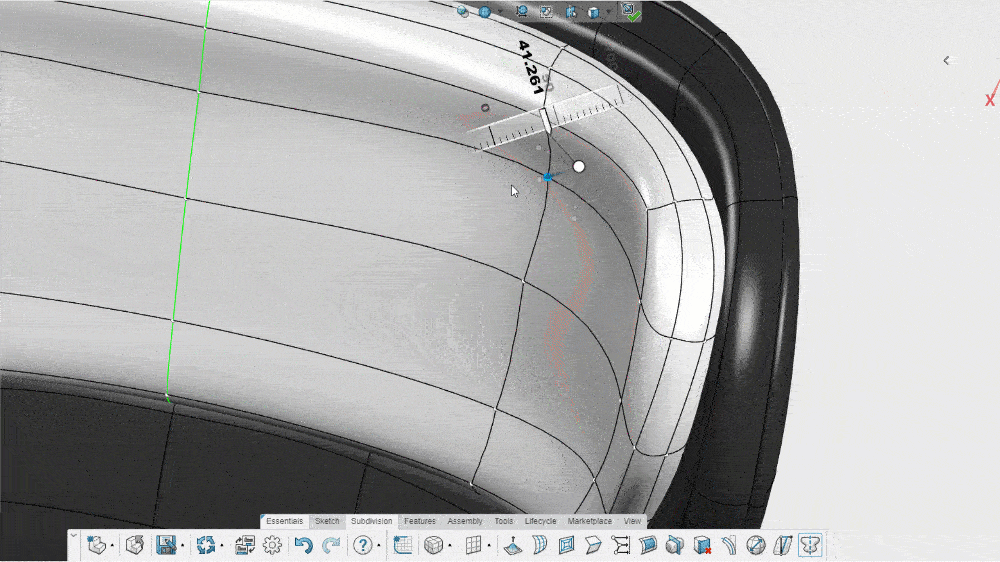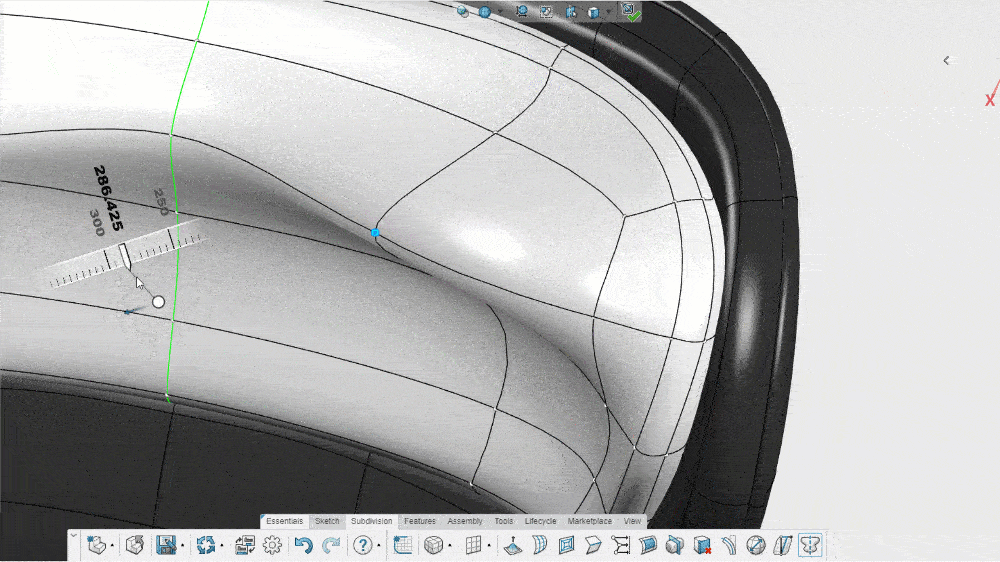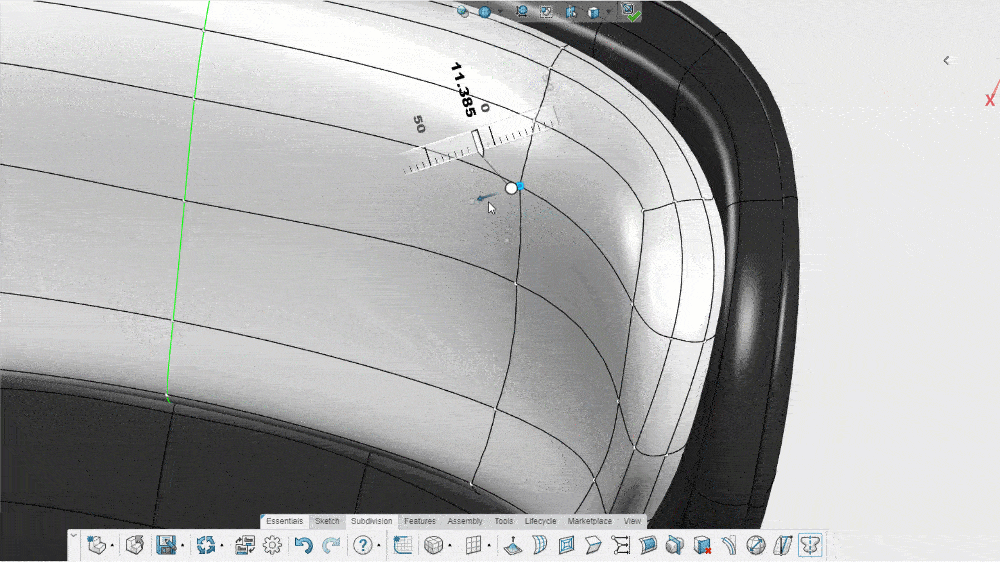
Subdivision modeling allows a designer to push and pull a simple mesh model into any shape they want. If a designer has a mesh model of a circle, for instance, they can click on a point where the mesh connects and then drag or pull that point to change the shape of the model. This allows for freeform designs that can more accurately depict natural curves.
When a designer pushes or pulls a control point, specialized 3D CAD software automatically subdivides the polygons in the existing model. This increases the number of vertices (the connecting points on the mesh) and makes the curvatures of the model smoother, more rounded, and more realistic.
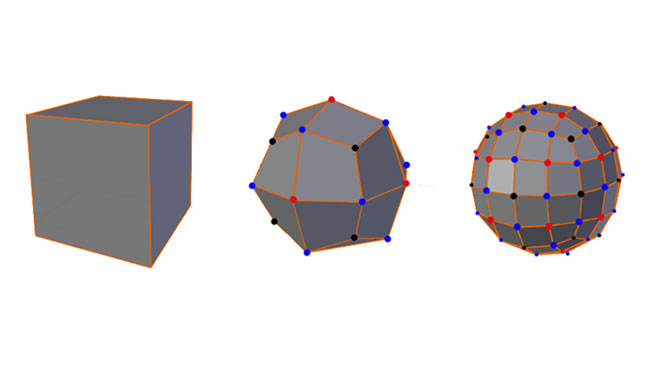
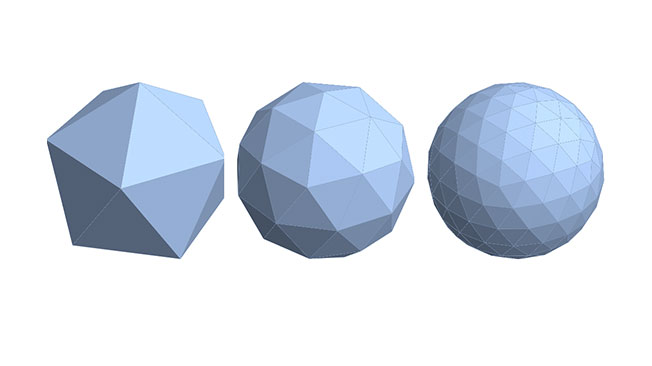
This allows for more detail to be added to the model while staying within the specified limit. As the subdivision increases, each face of the model breaks into four new faces, ensuring that the complexity remains manageable within the set limit. To accomplish this, subdivision 3D modeling software employs a mathematical process based on the Catmull-Clark algorithm.
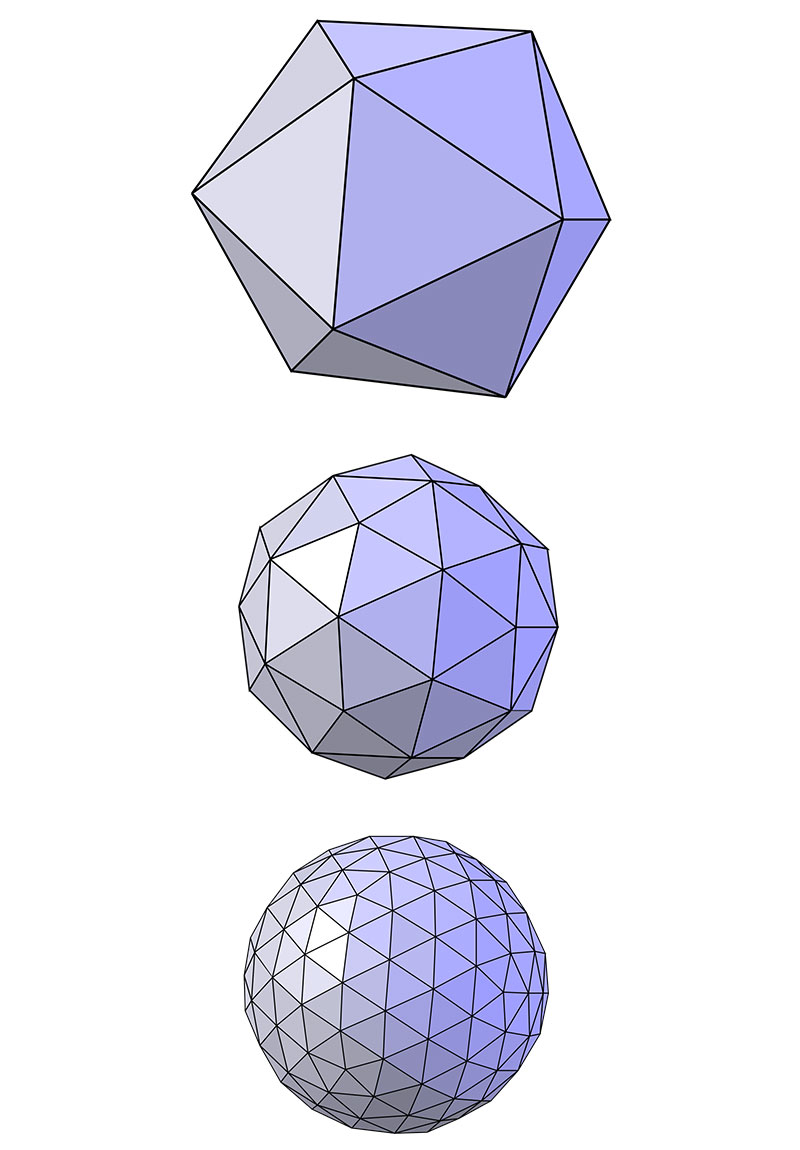
What are the advantages of sub division surfaces modeling?
Browse all the Dassault Systèmes store applications
We feature in our store some of our best software to design, collaborate and innovate throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Content related to subdivision modeling
What are the common sub division surfaces modeling techniques?
- Catmull-Clark subdivision
- Doo-Sabin subdivision
- Loop subdivision
- Butterfly subdivision
Catmull-Clark subdivision
The Catmull–Clark algorithm was invented by Edwin Catmull and Jim Clark in 1978. It defines surfaces recursively by dividing surface polygons into smaller areas. Each time a subdivision is made the algorithm bases the new area on the closest vertices. The Catmull–Clark algorithm can be used to change a cubed shape into a sphere and was used in many Pixar animated movies. Indeed, Edwin Catmull served as the head of Pixar for some years. The Catmull–Clark algorithm forms the basis of all subdivision 3D modeling tools.
Doo-Sabin subdivision
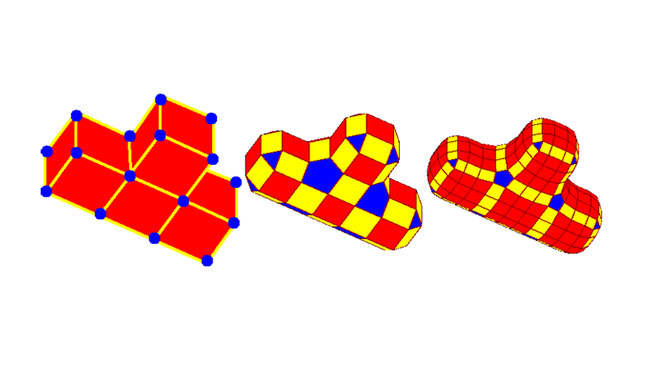
This algorithm was created by Daniel Doo and Malcolm Sabin in 1978. Where the Catmull–Clark technique is based on bi-cubic uniform B-splines, the Doo-Sabin subdivision uses bi-quadratic uniform B-splines. Many experts believe that the Doo-Sabin subdivision is simpler to use than Catmull–Clark when working with complex shapes. Alongside Catmull–Clark, it is the most widely used subdivision technique.
Loop subdivision
The Loop subdivision method was created by Charles Loop in 1987 and built on the algorithms developed by Catmull-Clark and Doo-Sabin. Unlike these algorithms, however, the Loop method uses triangular meshes instead of quad meshes. Using Loop subdivision, triangular surfaces are divided into four triangles. The Loop subdivision technique is easily scalable and is often used to depict complex, highly detailed natural features such as cliff faces.
Butterfly subdivision
The Butterfly subdivision was invented in 1990 by scholars Dyn, Levin, and Gregory and modified by Kobbelt, Zorin, Schröder, and Swelden in 1996. The Butterfly subdivision method is an interpolating technique that can be used to depict objects with highly complex fluid surfaces, such as a pool of water.
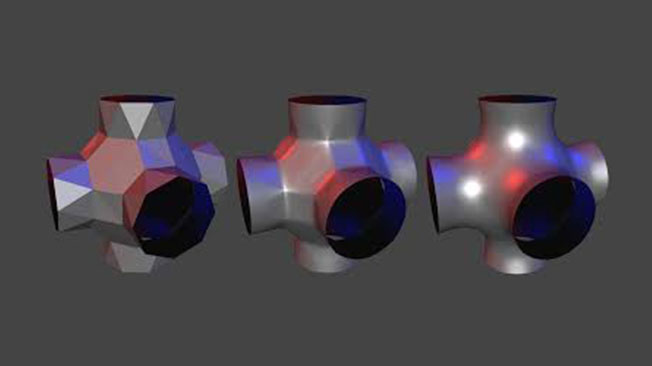
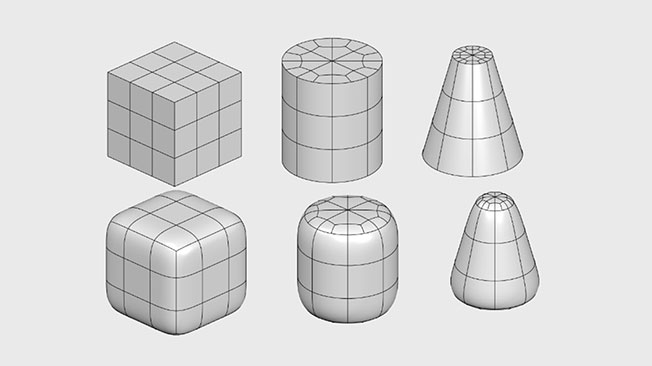
What is the process of creating subdivision models?
The process of subdivision modeling starts with the designer creating a base mesh model using polygons. This model will depict the very basic topology of the model. The designer then applies a subdivision scheme by instructing the software to convert the basic polygonal mesh into a subdivision surface. The actual subdivision modeling is done by pushing and pulling vertices to change the shape of the primitive model. In this way, a designer can refine the basic model from a rough primitive shape into a smooth, lifelike depiction of an object.
Tips for creating effective subdivision models
One of the best practices for creating clean and efficient subdivision meshes is to avoid the use of triangles and poles as they can cause smoothing artifacts. When creating a mesh, care should also be taken to space out vertices evenly and with more density in areas that require more details.
Designers also need to keep in mind that the subdivision modeling workflow needs to mimic natural forms. The focus must be kept on achieving a realistic form that mimics natural anatomies.

Explore Dassault Systèmes solutions
Discover the powerful browser-based modeling solutions from Dassault Systèmes. You can design whatever you wish, wherever you are with 3DEXPERIENCE.
Connecting data & people to foster innovation
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform on the cloud gives you access to a various set of applications that allow you to design, simulate, inform and collaborate on a project.
What is subdivision modeling used for?
Subdivision modeling is used for both low-poly modeling and high-poly modeling. The technique has its roots in character modeling for the animation industry but is now also used to depict characters in video games.
Subdivision modeling is also widely used in aeronautical and automotive design to detail the sweeping curves and flowing lines of modern vehicles. Because subdivision modeling can represent realistic textures and natural forms it is a popular method for creating architectural visualizations.
Many companies also use subdivision surface modeling during the product design process. The ability of subdivision modeling to mimic materials accurately means that companies can showcase products without having to build physical prototypes.
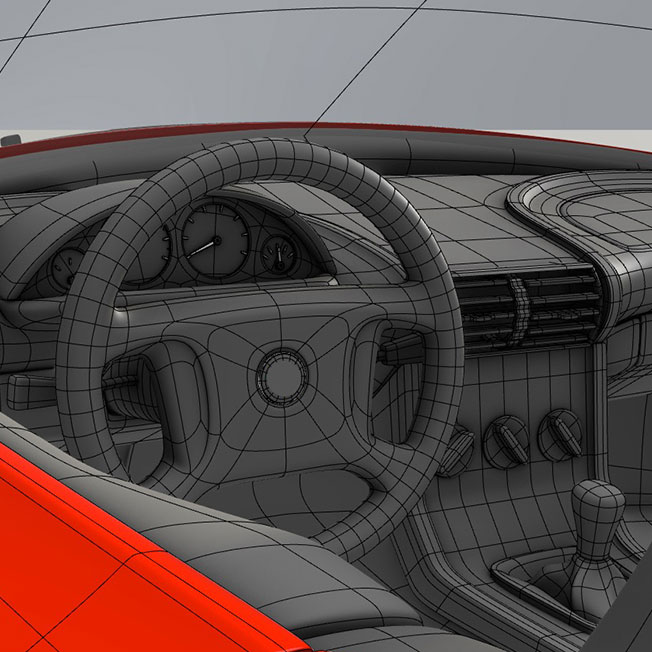
Are there any disadvantages to using subdivision modeling?
Since subdivision modeling is primarily an organic modeling technique it is not well suited for hard surface modeling or for creating geometrically accurate models. Although the process of subdivision modeling is relatively straightforward, a steep learning curve is required to truly master the technique.
There may also be performance and efficiency issues associated with subdivision modeling, especially with complex models. While subdivision modeling allows designers to experiment with shapes, it does not have the precision of other design techniques. Because there is no history tree, it can be difficult to replicate or reverse changes made to a model. The lack of continuity in the subdivision modeling workflow can hamper the design process as iterations must be done from scratch.
Subdivision modeling - Conclusion & Perspectives
Subdivision modeling is a design technique used to create high-resolution 3D models that have organic curves and realistic details. It is used to smooth out the edges of a mesh model by adding more vertices and polygons while still keeping the integrity of the form of the model intact.
Using free-form push and pull techniques to manipulate a model, subdivision modeling is fast, and intuitive, and allows designers to experiment with ideas and be creative without worrying about breaking a model or predetermined parameters. It is commonly used during the conceptual stages of product design.
The aim of subdivision modeling is to create realistic, natural-looking forms from sharp-edged polygonal models. First used in the animation industry, subdivision surface modeling is now used in the automotive and aeronautical industries, architectural firms, and the entertainment industry.
Anyone who is considering a career as a designer or engineer should have a good knowledge of the techniques of subdivision modeling and familiarize themselves with subdivision modeling software.
Why choose Dassault Systèmes for your subdivision modeling needs?
Get access to superior subdivision modeling software
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform is a cloud based digital environment where designers can store and share files, collaborate and communicate with colleagues, and get access to several powerful Dassault Systèmes CAD and PLM roles. You can access the 3DEXPERIENCE platform using any internet-enabled device, anytime you wish, from anywhere you like.
You can access our intuitive and flexible subdivision modeling tool 3D Sculptor via the 3DEXPERIENCE platform. 3D Sculptor has a range of features that will allow you to create highly detailed, lifelike 3D models. If there are any other roles that you are interested in, you can purchase them for as long or as short a time as you wish.

Gain a trusted and experienced CAD partner with Dassault Systèmes
With more than 40 years of experience developing cutting-edge CAD software, Dassault Systèmes is a true pioneer and remains a leader in the industry.
Our company is made up of 11 brands that are dedicated to providing engineers, creators, and designers with the tools they need to shape the future. From project management solutions to PLM software to the very latest 3D CAD software, Dassault Systèmes has the solutions you’ve been searching for.