What is part design and what is it used for?
Any type of assembly is made up of different parts that must all work together in the most efficient way possible. Professionals whose focus is to produce components use the part design process to arrive at the most effective and economical designs.
What is part design?
On a conceptual level, part design is concerned with creating virtual prototypes of parts and components that are to be manufactured separately and then assembled to create a final product. Common applications include injection molding part design, composite part design, and part and mold design.
A good example of the part design process is to consider how all the different parts that make up a car engine are created. Every individual part of the engine must be carefully designed to ensure the entire assembly operates effectively and efficiently. By focusing on the generative design of parts, the most efficient end result can be achieved.
When designing a part, engineers must take into consideration a range of factors. They must establish what the functional requirements of the part are and how it can be designed to best perform its task. The manufacturability and overall cost of the part need to be taken into account.
To determine the cost and ease of manufacture, designers and engineers need to understand the properties of different materials and choose the right material for the part based on its requirements.
Explore effective solutions for part design in the Dassault Systèmes store
Engineering and design experts from various industry sectors use Dassault Systèmes software for its exceptional part design capabilities. Our CAD design solutions are renowned for their intuitive interfaces and powerful 2D and 3D modeling tools.

Empower smart product design and boost engineering precision

SOLIDWORKS xDesign
Get ready for the next generation of design solution, developed by the same team that brought you SOLIDWORKS 3D CAD
The part design process
Ideation and Conceptualization
The part design process begins with determining the purpose and requirements of the part. Engineers work either in teams or alone to generate different ideas that lead to a rough plastic part drawing or a concept sketch for a metal part.
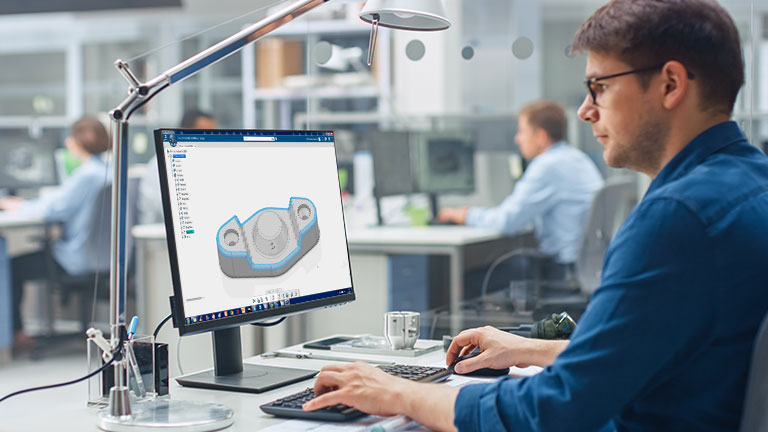

CAD modeling
Once an engineer has produced a rough sketch, a mechanical designer will create 3D models of the part. These models are used for testing the viability of the design and making any necessary modifications.
Prototype testing and validation
A final 3D model will then be used to create a physical prototype that will undergo further testing to verify it meets the design requirements. In some cases, a company may decide to forgo the creation of a physical prototype and instead use the 3D model in complex simulations generated by CAD software. In this way, manufacturing costs can be kept to a minimum and waste can be reduced.

Mass production
After the prototype has passed the testing stage, the design needs to be prepared for production. An analysis of the materials and the assembly line is done to ensure the part can be efficiently manufactured at scale.
Often, this analysis is done via specialized software that creates a 3D virtual twin model of the factory floor and the manufacturing equipment. The virtual model can then be used in simulations to test the efficiency of the manufacturing process.
Browse all the Dassault Systèmes store applications
We feature in our store some of our best software to design, collaborate and innovate throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Content related to part design
What types of professionals use part design?
The part design process is used by professional engineers and designers for a wide range of purposes. Mechanical engineers and mechanical designers use part design to develop components for assemblies. This is the most common use of the part design concept, however, there are others.
Architectural designers use part design when developing construction components. Finite element analysis used in product manufacturing often includes aspects of the part design process. 3D printed products and components are developed using the part design process.
Key considerations in part design
In order to produce reliable and operational parts, manufacturers require detailed, comprehensive designs. When designing a part, engineers must take into account a range of factors. They must carefully assess the functional requirements of the part and ensure that their design will be able to operate as it should as part of the whole.
The manufacturability and overall cost of the part must also be considered. Following best practices, both plastic and metal parts should be designed with ease of manufacture in mind. Care must be taken in the choice of material. Tolerances must be thoroughly tested. Uniformity of the material thickness across the part must be ensured to avoid deformities.
The design must be focused on achieving ease of assembly of the final product. Initial manufacturing processes and secondary processes should be kept in mind during the design stages.
In short, the overriding consideration in the part design process is how to balance design goals with cost considerations.
Explore Dassault Systèmes solutions
Discover the powerful browser-based modeling solutions from Dassault Systèmes. You can design whatever you wish, wherever you are with 3DEXPERIENCE.
Connecting data & people to foster innovation
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform on the cloud gives you access to a various set of applications that allow you to design, simulate, inform and collaborate on a project.
Best practices for part design
- Effective Communication and Collaboration
- Reduce or Eliminate the Need for Machining
- Choose Materials Carefully
Ensure effective communication and collaboration
Communication and collaboration are key to an effective machine part design process. Mechanical engineers must liaise with designers and manufacturing teams to ensure the optimum design has been achieved for every stage of the part.
All aspects of the design and the manufacturing process must be constantly and thoroughly analyzed. The part must be assessed for functionality, aesthetics, and durability.
To facilitate collaboration and enhance communication, many professionals use cloud-based software where they can share, store, and work on CAD files simultaneously. Using software that operates in the cloud allows teams to work together at any time no matter where they are located.

Reduce or eliminate the need for machining
When designing parts, the best practice is to avoid the need for machining, if possible. Machining increases the overall cost of manufacturing. Also, casting or forging is usually a faster way of producing a uniform part. Secondary machining operations such as grinding should also be avoided.
Engineers should focus on using the most generous geometric and dimensional parameters possible for stamping part design and casting part design. Stock dimensions should be used to cut down on the need for additional machining. If possible, avoid sharp corners, shoulders, and undercuts.

Choose materials carefully
A crucial aspect of part design is the choice of materials. As we have stated, the choice of materials can greatly impact the durability of the part and the cost of manufacturing.
However, the choice of material used for the part also affects the speed of manufacturing. Harder materials are more difficult to machine and slow down the manufacturing process. For this reason, the part design process is commonly used for plastic part design and plastic part design for injection molding.

Part design : conclusion and perspectives
In conclusion, part design plays a crucial role in manufacturing and engineering industries, and it's an essential factor that determines the success of any product. The proper design of a part ensures that it functions efficiently, meets all necessary requirements, and can be produced effectively and economically. Through the use of modern design tools and techniques, designers can create parts that are optimized for performance, durability, and cost.
Furthermore, the design of a part is not just about creating a functional object but also about considering factors such as materials, manufacturing processes, and environmental impact. Designers must also take into account user experience, aesthetics, and ergonomics when creating a part.
Why choose Dassault Systèmes for your part design needs ?
Industry-specific solutions and strong customer support
Dassault Systèmes' software is used by many leading manufacturers in various industries, and the company offers industry-specific solutions tailored to the needs of different sectors, such as aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods.
Dassault Systèmes has a large and experienced customer support team that can provide training, technical assistance, and other resources to help designers get the most out of their software.

The power of the 3DEXPERIENCE
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform boosts the speed of product innovation by allowing teams with diverse skills to work together in real-time on a single digital platform. With Dassault Systèmes CAD tools, people of all proficiency levels can create intricate shapes and experiment with designs using generative design.
You can instantly access our apps through the 3DEXPERIENCE store without having to install or set up any software. The Dassault Systèmes CAD apps are accessible from any web browser and device.


