Innovative solutions for Life Science & Healthcare
Breakthrough approaches to improve patient experiences. Rapidly accelerated drug development through decentralized and more diverse clinical trials. Extensive research for deeper understanding of how medical devices work within the human body. These are among the ways our trusted, scalable 3DEXPERIENCE platform is helping to connect players across research, discovery, manufacturing and commercialization to usher in an era of safer, precision medicine.
UNTiL NOW
Medical advances resulted from trial and error
FROM NOW ON
Virtual twins are moving patient experience and safety to the forefront
Increasing the safety, efficacy and relevance of clinical studies in the United States
Advancing safe and efficient scientific solutions is the foundation of MEDIDATA. Clinical trials in the US are increasingly adding diversity across the drug development process to benefit all patients.
Historically, clinical trials have recruited disproportionately large percentages of white participants, raising concerns about the generalizability of trial results to underrepresented communities. This particularly impacts the Black population.
According to a study by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, more than half the COVID-19 cases are affecting people of color - but they comprise only about 20% of clinical trial volunteers. Unbalanced studies - those that don't reflect the actual demographics - carry a number of medical and safety risks.
MEDIDATA's research on clinical trial site diversity, based on a sample from more than 30,000 clinical trials across indications and more than 9 million patients, is available in "The State of Black Participation in Clinical Trials."
The paper's findings indicate that Black Americans continue to be underrepresented in oncology clinical trials, accounting for only 8.5% of participants enrolled in interventional trials from 2010 - 2021, even though 14.6% of Americans are Black.
In an even starker example, in the past decade 70% of sites did not enroll a single Black participant in Alzheimer's and lung cancer trials, two diseases that disproportionately affect Black Americans.
Bringing more diversity to clinical trials
Addressing the critical needs of better science, more representative outcomes and increased health equity, MEDIDATA launched the Intelligent Trials Diversity Module.
This initiative provides site-level participant demographic data including race, sex, age and ethnicity.
This will help sponsors and clinical research organizations (CROs) benchmark the diversity of their trials and identify sites that are more successful at enrolling diverse patients. It brings diversity into the beginning of the feasibility process, all while accelerating trials.
MEDIDATA's new offering supports the US FDA draft guidance to industry, a strong call to action to enroll more participants from underrepresented racial and ethnic populations into clinical trials.
Legislation like the Diverse and Equitable Participation in Clinical Trials (DEPICT) Act, which would mandate the inclusion of diverse populations, also reflects the importance for the industry to address this critical issue.
Powering greater diversity is critical for our industry and a priority for MEDIDATA. It is now possible to identify high-performing sites known to recruit diverse patients. This supports more representative outcomes, and promotes much needed equity within clinical research.
Making patient centricity the key to recovery
As treatment options become more sophisticated, medical professionals are looking at approaches to reduce stress for the patients undergoing these procedures. Our virtual twin experiences can help, by guiding a person through their treatment in advance.
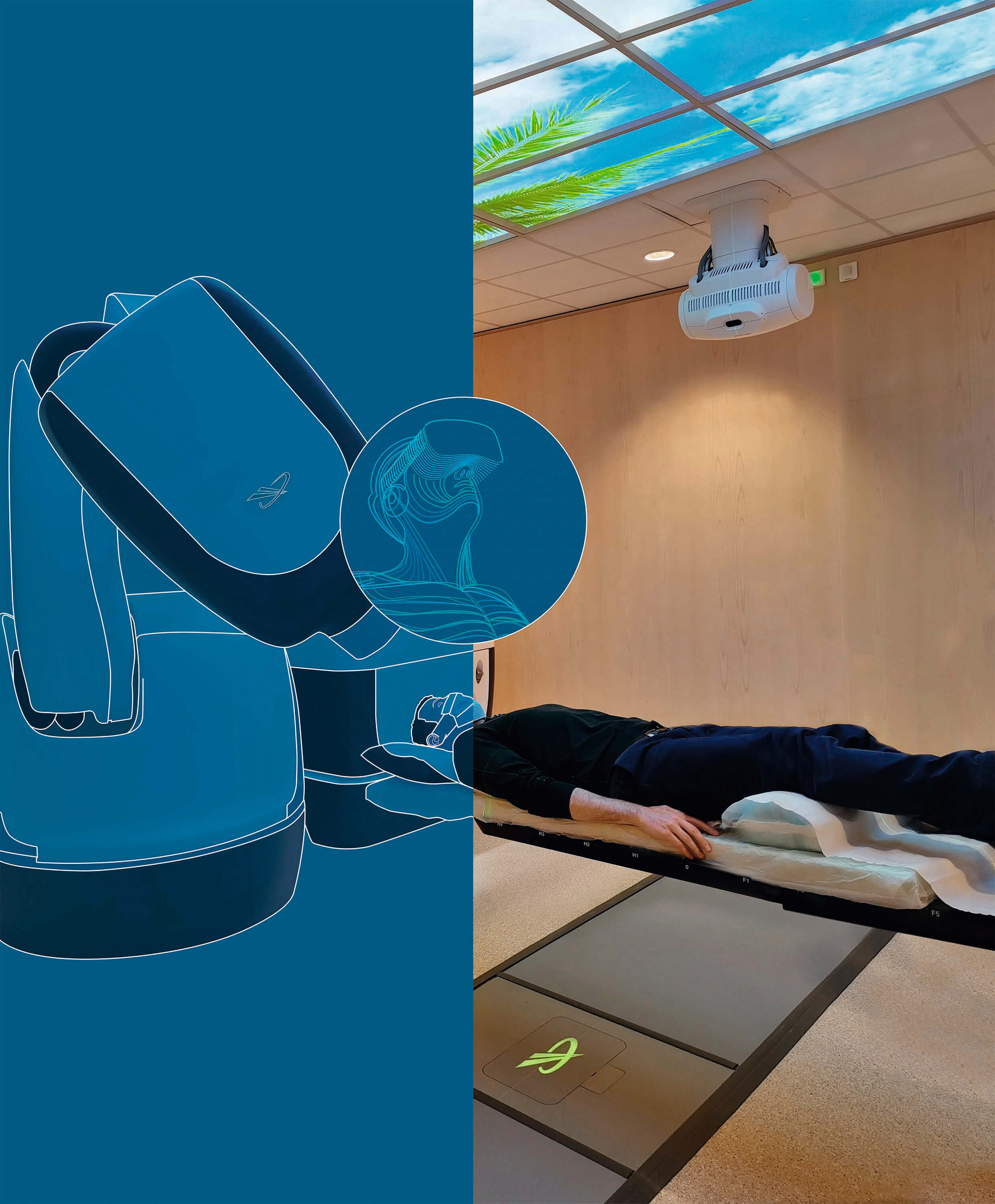
A cancer patient lies quietly on the clinical bed at the H. Hartmann Institute as the Accuray Cyberknife® robot moves and rotates, its arm beaming high doses of radiation at their tumor. For some, this can be a time of high anxiety. But thanks to virtual twin technology, a patient can now better prepare for this session, by experiencing a virtual mockup of the treatment space and the procedure in advance.
Envisioning the procedure
Along with H. Hartmann Institute and the Rafaël Institute, Dassault Systèmes developed this empowering procedure through our 3DEXPERIENCE Lab. The world's first radiotherapy room simulated entirely in 30, VORTHEx - Virtual Oncology Radio Therapy Hartmann Experience - is a completely new approach to radiotherapy. Digital continuity created by the 3DEXPERIENCE platform ensures an accurate virtual twin of both the robot and the treatment area, allowing patients to view all the technical and protocol components of their individual treatment in 3D.
They're able to project themselves into the actual procedure, going through each step from entering the radiotherapy room, getting into position on the table and receiving treatment through the Cyberknife, a high-energy X-ray machine that precisely delivers radiation beams to destroy tumor cells and stop tumor growth while avoiding damage to healthy tissue.
After the virtual experience and before the treatment, the patient ask their care team specific questions to gain further understanding and reassurance.
VORTHEx will change how radiotherapy works, helping patients to comprehend their treatment better and, by reducing anxiety, greatly increase the chances of a successful recovery. Next up: clinical tests measuring the effects and performance of this simulation in the patient journey that will be carried out on our MEDIDATA clinical trial platform.

Million new cases of cancer worldwide every year
Of cancer patients will receive radiation therapy (*source: www.cancer.org)
Enhancing our understanding of lung function
Lung disease is one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide – and was even before the COVID-19 pandemic. A new research project funded by La Fondation Dassault Systèmes in the US offers hope for inaugurating novel avenues for pulmonary clinical therapies and medical devices.
Every minute, a person dies from lung disease. Yet, pulmonary research lags. Thus far, researchers only have access to elementary simulations of the lungs, which limits our understanding of how the organ works and how the onset of dis-eases can alter pulmonary tissue integrity. Questions around the mechanics of healthy lungs and the level of stresses and strains they can handle continue to challenge medical professionals. Finding answers requires the ability to develop and study a functional model of a breathing lung that portrays accurate global and local behaviors of this critical organ.
La Fondation Dassault Systèmes is funding scientific research aimed at significantly advancing pulmonary knowledge and paving the way for new therapies. A research team led by Professor Mona Eskandari, Ph.D. at The University of California, Riverside is devising new techniques in experimental pulmonary biomechanics to investigate the lung's fundamental structural mechanics and to, in turn, construct 3D computational models and simulations to provide predictive insights into pulmonary physiology. Their research will provide the first 3D breathing model of the lung, accurately representing the cyclic deformations of a human breath. Ultimately, results will serve as a groundbreaking scientific platform for cough simulations, ventilation efficacy, lobectomies and disease states.
WE HAVE A UNIQUE, CROSS-DOMAIN FOOTPRINT IN LIFE SCIENCES & HEALTHCARE. WE SUPPORT:
Active clinical trials
Healthcare facilities
Of drugs & medical devices designed with our solutions
Of new clinical trials supported by our solutions