Improving healthcare by collaborating, learning and practicing
By adopting virtual platforms to connect, link and share data, people working in the healthcare sector will be able to provide new therapies.
Of global GDP: healthcare expenditures in 2022
(Source: Deloitte, 2019)
Average annual growth in healthcare expenditures in low-income countries
(Source: WHO, 2018)
People who expect 3D-printed-to-order organs to have a direct impact on their health
(Source: Frost & Sullivan, 2014)
Although medical innovations have considerably improved people’s health overall, chronic diseases have never affected so many people. Epidemic crises are becoming more frequent and brutal. This is why people working in the healthcare sector need to adopt virtual platforms to connect, link and share data. By doing so, they will be able to provide new therapies that take into account the social and environmental factors that affect a person’s health.
Such platforms will make it possible to share information between patients, caregivers‘ practices, funding organizations and regulatory bodies to increase global knowledge in the life sciences field. They also will have a role to play in preventing disease and will make patients more independent by facilitating treatment at home. The quality, reliability and extent of a city’s healthcare infrastructure are central to that city’s appeal.
Smart cities are connecting the virtual and real worlds and developing sustainable urban solutions to protect the health of their growing, aging populations, while also offering a better experience to their citizens. Currently, a patient’s care pathway is fragmented between various specialists, resulting in a jumble of disconnected health services. Participants in the medical sector will increasingly need to pool their data to achieve genuine collaborative intelligence.
The experience economy, by putting patients at the center of value creation, offers a holistic care model that favors innovation. Since patients are central to their own care pathways, the right to access and control their personal data is becoming more vital than ever. The security and confidentiality of those data are a priority, and regulations relating to personal healthcare data will be gradually harmonized throughout the world. Data anonymization is essential.
The technology will result in new approaches for pre-symptomatic prevention and early diagnosis: recent progress in machine learning, combined with solid scientific knowledge, has resulted in prediction models that make use of imaging and genomics techniques. These new models can produce personalized recommendations for patients, taking into account their individual chances of developing specific diseases.
High-definition technologies are adding value in neurosurgery, where brain imaging is being combined with functional electrophysiology and perioperative assessments in the operating theater. In orthopedics, the patient’s virtual twin can be used to guide surgical planning by predicting the result of the operation. By 2030, 3D printing could be used to make prescription drugs or new tissue based on a 3D model of the patient’s organs.
Finally, home care can reduce the risk of complications arising from hospitalization, but requires complex infrastructure and a network that relies on new platforms capable of collecting patient data, producing diagnoses, connecting patients with healthcare professionals and checking the efficacy of treatments.
The Living Heart project is an excellent example of how virtual universes will radically improve the healthcare experience and the major contribution of virtual twins for monitoring, understanding, preventing, diagnosing and maintaining health.
Claire Biot, Vice President, Life Sciences Industry; Nicolas Pécuchet, Healthcare & Life Sciences Research Manager; Sébastien Massart, Head of Corporate Strategy; Patrick Johnson, Executive Vice President, Corporate Research & Sciences
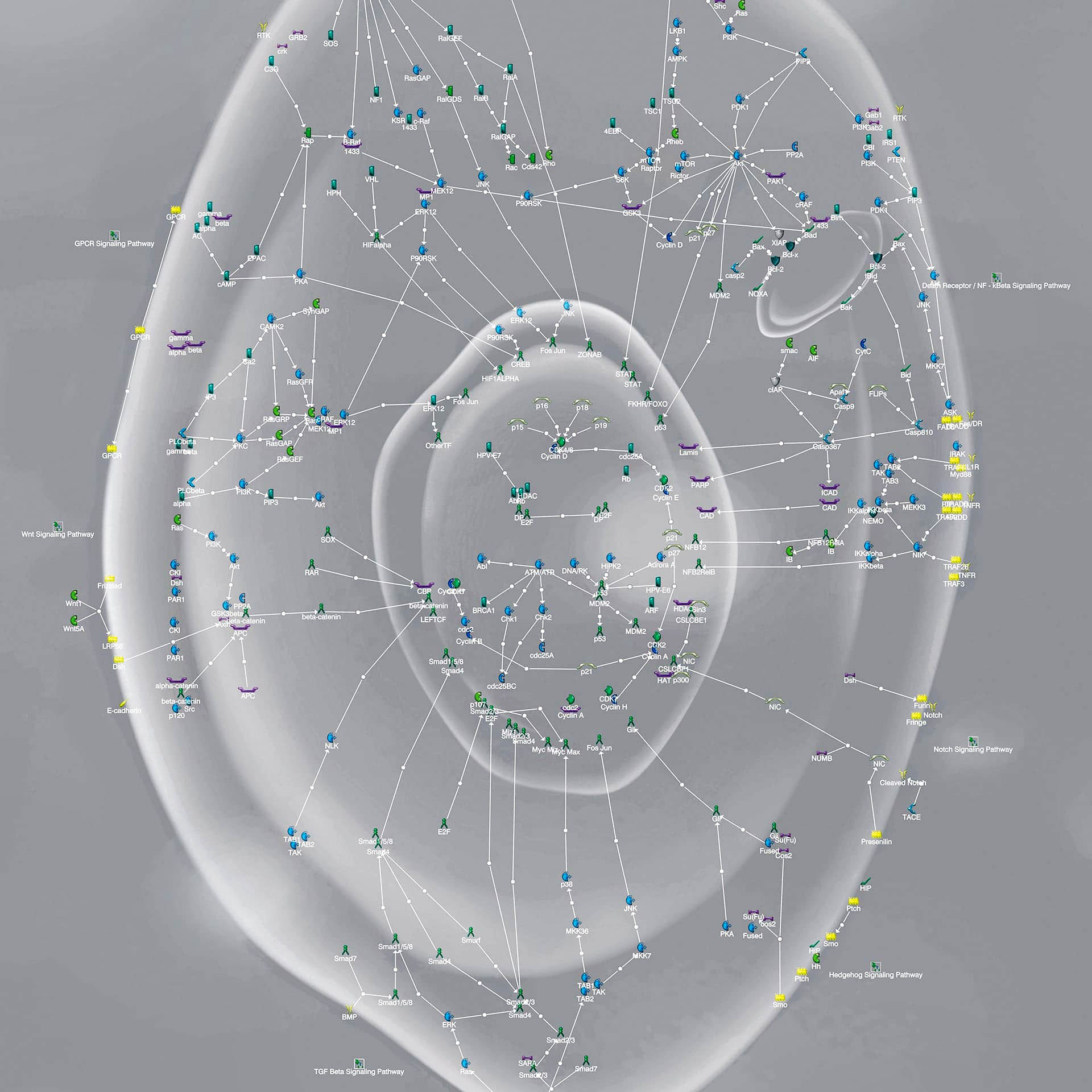
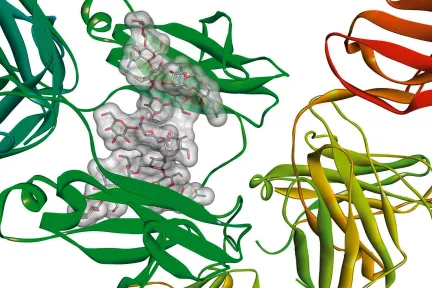
VIRTUAL MODEL OF A CANCER CELL
Systemic in silico modeling of a cancer cell, integrating the relationships between compounds and receptors (pathways).
INNOVATIVE PROCESSES WITHIN A STRICT REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
German company B. Braun is one of the world’s largest suppliers to the healthcare sector. It offers a comprehensive array of products and services in the fields of anesthesia, intensive care, cardiology, surgery and dialysis, serving healthcare establishments, pharmacies and home-care providers.
In 2019, B. Braun decided to invest in digital solutions to round out its product range, as well as improving efficiency, quality and collaboration in its supply chain, by adopting the License to Cure solution based on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
Dassault Systèmes is working in close collaboration with TECHNIA, one of the largest Life Sciences system integrators worldwide, to deliver business transformation to B. Braun. The solution is allowing the company to streamline its scientific and operational processes, from modeling and simulation to production, while meeting exacting quality and regulatory compliance standards. The result is to increase the benefits for patients and medics while also reducing costs.