CATIA V5
Driving Design Excellence with CATIA V5, a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) Software
Driving Design Excellence
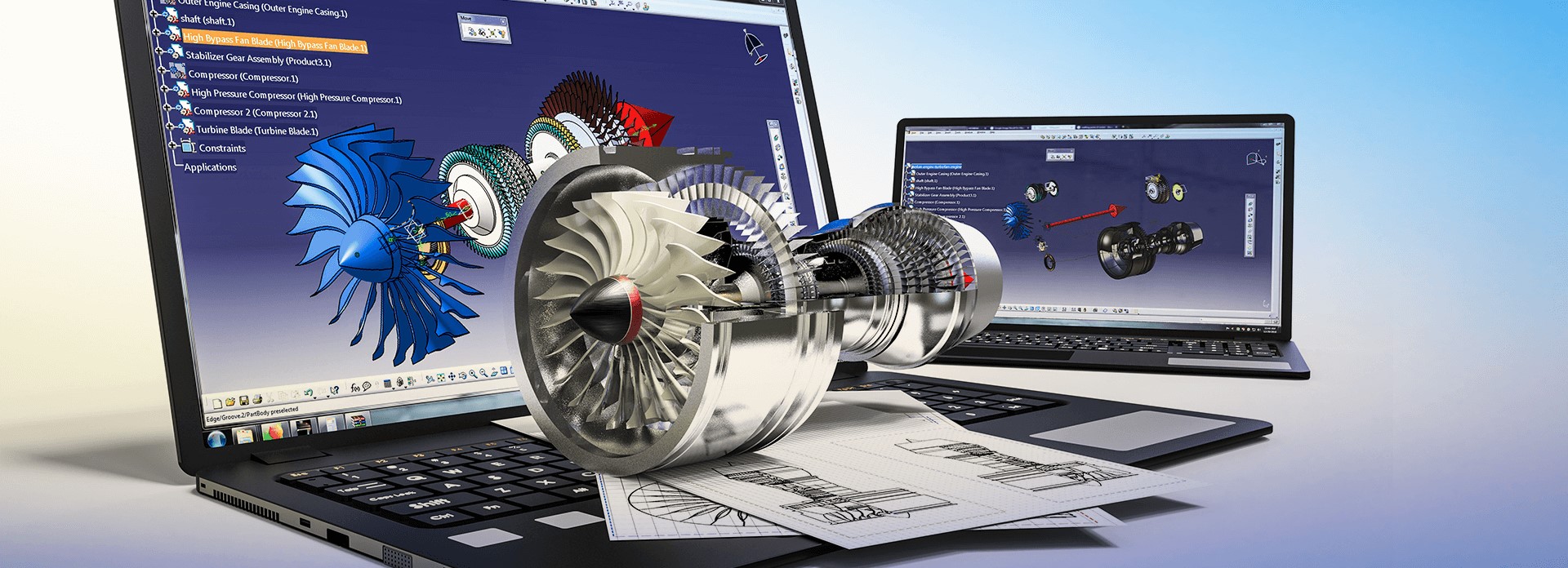
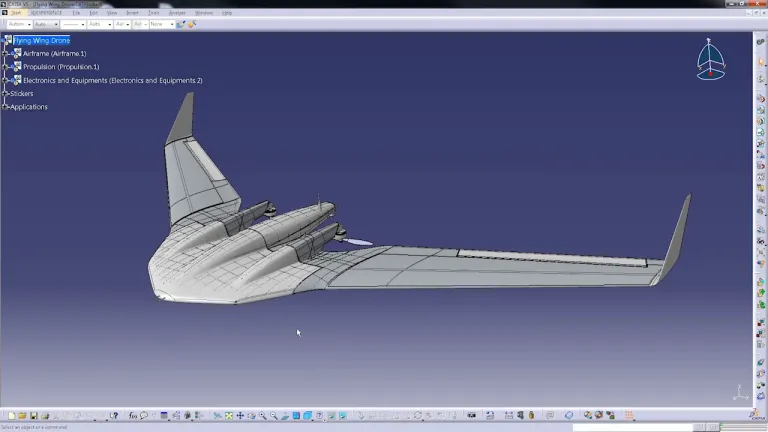
CATIA V5 - which stands for Computer-Aided Three-dimensional Interactive Application V5 - is a widely used software suite for computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and computer-aided engineering (CAE). It is an industry standard in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, and more. Many companies use CATIA V5 for product design and development.
Key Benefits
- Integrated with Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) solutions, CATIA V5 allows companies to manage the entire lifecycle of products, from concept to manufacturing.
- Consists of various modules, each tailored for specific design and engineering tasks. These modules include Part Design, Assembly Design, Drafting, Surfacing, and more.
- Offers a wide range of tools and features for creating complex and detailed designs.
- Is based on collaborative features that enhances concurrent engineering and enables multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously.
- Includes CAM Capabilities enabling the generation of toolpaths for CNC machining and manufacturing processes.
- Provides tools for simulation and analysis, allowing engineers to evaluate product performance, behavior, and structural integrity.
CATIA V5 domains
| Mechanical Design | Shape Design & Styling |
| Provides products for intuitive specification driven modeling for Solid, Hybrid and Sheetmetal Part design, Assembly design and integrated Drafting. | CATIA V5 offers highly intuitive tools to easily create, validate and modify any type of surfaces, from freeform surfaces to mechanical shapes. |
| Product Synthesis | Equipment & Systems Engineering |
| Knowledgeware solution set turns implicit design methods into explicit knowledge for obtaining the optimum design, while DMU solutions support complex DMU reviews and simulations for quick and efficient engineering and process decisions. | Integrates and exchanges electrical product, systems and structural design information during the product definition. |
| Analysis | Machining |
| Optimize product performance faster with integrated design analysis in CATIA. | Thanks to the entire complete product portfolio and due to the easy to use knowledge based V5 architecture, CATIA V5 Machining surpasses all the existing industry proven suites of NC Manufacturing applications. |
| Infrastructure | CAA-RADE |
| CATIA V5 provides a fully scalable platform for collaborative product creation and product data management. V5 breakthrough architecture delivers advanced design control for state-of-the-art engineering. | CAA-RADE product portfolio provides the most complete set of tools, guides and APIs that supports the development process, from the initial product definition to the final product packaging. |
| Web-based Learning Solutions | |
| CATIA Version 5 Web-based Learning Solutions (WLS) is an easy-to-use learning and support system. It provides all the required information and training in one source for maximum assured productivity of the user community. |
Option1: Take the Next Step
Would you like to expand your product development possibilities using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform?
Get your personalized 3DEXPERIENCE CATIA assessment. This easy-to-use online tool immediately calculates a prediction of savings and benefits based on your individual input.
Option 2: Work and Collaborate Better with CATIA V5
Do you want to be even more efficient with CATIA V5 while exploring the capabilities and benefits brought by the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform?
Get your personalized CATIA V5 assessment. This easy to use online tool immediately calculates a prediction of savings based on your individual input.
CATIA V5 Connected Engineering
When effective collaboration combines with world-class engineering, it is a winning combination that strengthens the existing CATIA user experience by extending the performance of CATIA V5 with the addition of new features.
CATIA V5 users can enjoy the benefits of the 3DEXPERIENCE platform on the cloud and will appreciate the mobility, collaboration and security it offers.
MODSIM for CATIA V5 Users
Innovation starts with great design. By unifying design and simulation tools, teams can left-shift the design process, supporting a performance-driven design approach that will result in market-leading products. In this context, you may complete the CATIA V5 tools you use for creating complex designs with simulation applications to analyze their performance and optimize it. A 2-option process is available to leverage this integrated MODeling & SIMulation approach, called “MODSIM”, at your own pace.
Join the conversation in the CATIA User Community!
FAQ About CAD & CAM
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software enables professionals to create precise 3D model of digital representations of objects or structures. This includes the ability to generate exact 2D drawings from detailed 3D models. It therefore offers drawing, modeling, rendering, and analysis tools for various industries like architecture, engineering, and manufacturing, enhancing design accuracy and efficiency.
CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design, involving computers to create, modify, and analyze designs. CAM, or Computer-Aided Manufacturing, employs computer software to operate machine tools for module manufacturing.
CAD technology is used for creating precise digital representations in 2D and 3D formats. It's utilized in various industries such as architecture, engineering, manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and product design for designing, modifying, analyzing, and documenting designs before production or construction.
CAD technology is utilized by a wide range of professionals across different industries, including:
- architects,
- engineers,
- drafters,
- product designers,
- automotive designers,
- interior designers,
- industrial designers,
- manufacturers,
- and construction professionals.
A CAD drawing is a digital representation of an object or structure created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. In the same way as the basic CAD, CAD drawing can be in 2D or 3D format and includes precise geometric information such as lines, curves, dimensions, and annotations.
Computer-Aided Drafting (CAD) primarily deals with creating detailed technical drawings in 2D format, emphasizing precision and detail. Conversely, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) extends beyond drafting to include:
- design development,
- modification,
- analysis,
- and optimization in both 2D and 3D formats.
CAD software offers tools for modeling, visualization, simulation, and documentation, enabling engineers to refine designs comprehensively. While CAD focuses specifically on drafting, CAD encompasses a broader spectrum of design-related tasks.
CAD Engineers, or Computer-Aided Design Engineers, specialize in using computer software to create, modify, analyze, or optimize designs. Their role is crucial in various industries such as manufacturing, construction, and engineering. Here are some key responsibilities and activities of CAD Engineers:
- Design and Drafting: They use CAD software to create detailed 2D or 3D designs. These designs can be for new products, structures, or systems. In 3D modeling, they also develop prototypes that can be used for testing and further development.
- Modification and Optimization: CAD Engineers often work on existing designs, modifying them for improved efficiency, cost-effectiveness, or to meet new specifications.
- Collaboration with Other Departments: They frequently collaborate with engineers, architects, and other professionals to understand the requirements and constraints of a design project.
- Analysis and Problem-Solving: Using CAD software, they can simulate and analyze the functionality of designs, identifying potential issues or areas for improvement.
- Documentation and Reporting: Creating detailed documentation of designs, including specifications, materials, and processes, is a vital part of their role. They may also need to create reports and presentations.
- Staying Updated with Software and Technologies: CAD Engineers must keep up-to-date with the latest CAD software and technologies, as these are constantly evolving.
- Compliance and Standards: They ensure that designs comply with industry standards, regulations, and quality requirements.
- Project Management: In some roles, they might be involved in project management, overseeing the progress of a design project from concept to completion.
- Customization and Automation: Advanced CAD Engineers might work on customizing CAD software or creating automated processes to improve efficiency in design tasks.
CAD Engineers are essential in sectors like automotive, aerospace, industrial design, civil engineering, and many others, where precision and efficiency in design are critical.
Choosing the right CAD software involves considering several factors:
- Industry and Use Case: Choose software tailored to your industry and intended use.
- Features and Functionality: Assess essential features like 2D drafting, 3D modeling, rendering, and collaboration.
- Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing software and file formats.
- Learning Curve: Consider the ease of learning for your team and training requirements.
- Technology costs and Licensing: Balance upfront costs and long-term value, including subscription fees.
- Support and Community: Evaluate vendor support, documentation, and user community activity.
Also Discover
Learn What CATIA Can Do for You
Speak with a CATIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right CATIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering